Communicable Diseases
Subtopic:
Trypanosomiasis (Sleeping Sickness)

TRYPANOSOMIASIS (SLEEPING SICKNESS)
It’s a protozoan infection transmitted to humans, cattle and wild animals by the Glossina fly (tsetse fly). It’s characterized by fever, general weakness and cerebral involvement.
Mode of transmission
It’s transmitted by a vector called Glossina (tsetse fly) between animals and from animals to human beings following bites
- Glossina palpalis-along rivers and responsible for Trypanosoma brucei gambiense transmission
- Glossina morsitans-responsible for Trypanosoma Rhodesiense transmission
Life cycle
The tsetse fly (genus Glossina) is a large, brown, biting fly that serves as both a host and vector for the trypanosome parasites.
While taking blood from a mammalian host, an infected tsetse fly injects metacyclic trypomastigotes into skin tissue. From the bite, parasites first enter the lymphatic system and then pass into the bloodstream. Inside the mammalian host, they transform into bloodstream trypomastigotes, and are carried to other sites throughout the body, reach other body fluids (e.g., lymph, spinal fluid), and continue to replicate by binary fission.
A tsetse fly becomes infected with bloodstream trypomastigotes when taking a blood meal on an infected mammalian host. In the fly’s midgut, the parasites transform into procyclic trypomastigotes, multiply by binary fission, leave the midgut, and transform into epimastigotes. The epimastigotes reach the fly’s salivary glands and continue multiplication by binary fission.
The entire life cycle of the fly takes about three weeks.
Horse-flies (Tabanidae) and stable flies (Muscidae) possibly play a role in transmission of nagana (the animal form of sleeping sickness) and the human disease form.
Mechanism
Tryptophol is a chemical compound that induces sleep in humans. It is produced by the trypanosomal parasite in sleeping sickness.
Clinical picture
It occurs in three phases for both species
a) Primary chancre stage
It’s more commonly seen in Trypanosoma brucei Rhodesiense. It’s characterized by;
- Appearance of a painful indurated nodule at site of fly bite lasting for 1-2 weeks then resolves
- Fever
- Headache
- Joint pains
- itching
- Localized swelling of lymphnodes
- Scar formation
b) Systemic/blood stage
It occurs following dissemination of Trypanosomes to blood and lymph nodes. It’s characterized by;
- Fever for a few weeks
- Lymphadenopathy
- General malaise
- Anemia
- Severe headache
- Myalgia
- arthralgia
Other signs and symptoms
- pruritic rash for 6-8 weeks
- hepatosplenomegaly
- impotence and menstrual irregularities
- cardiac failure for Trypanosoma brucei Rhodesiense
- abortion and still births in pregnancy
c) cerebral stage
It occurs due to invasion of the brain by the Trypanosomes. It’s characterized by;
- progressive mental deterioration tremors
- over sleeping during day (sleeping sickness)
- restlessness at night
- hemiplegia
- facial palsy
- coma
- death if un treated
Investigations
- Microscopic examination of fluid from a chancre
- Wet blood smear
- Thick blood smear
- CSF analysis
- Serological tests to look for antibodies against Trypanosomes
- FBC to assess for anemia and thrombocytopenia
Differential Diagnosis
- Malaria
- Meningitis
- Typhoid fever
- Tuberculosis
Management
- For the chancre and blood stages, drugs of choice are;
- Pentamidine IM 200mg OD x 2/7
- Suramine 250mg-1g IM OD x 5/7
- For the cerebral stage, add Melarsoprol because it’s the only drug that can penetrate the blood brain barrier to act on the Trypanosomes in the brain
- Manage other symptoms appropriately g. steroids for carditis, Analgesics for headache and other pains
Prevention and control
- Reduce exposure to tsetse flies by using insect repellants, use of insecticides, clearing the bushes where tsetse flies stay
- Early detection and treatment of cases especially in endemic areas
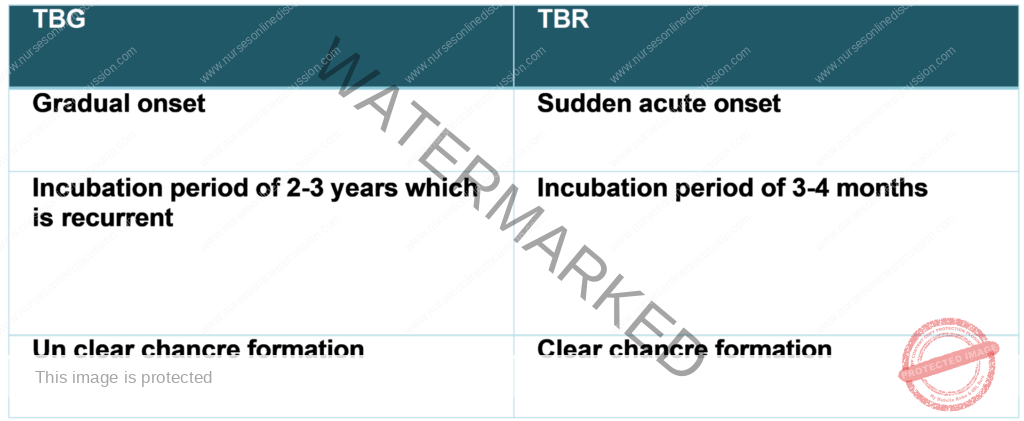
Differences between Trypanosoma brucei gambiense & Trypanosoma brucei Rhodesiense
We are a supportive platform dedicated to empowering student nurses and midwives through quality educational resources, career guidance, and a vibrant community. Join us to connect, learn, and grow in your healthcare journey
Quick Links
Our Courses
Legal / Policies
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2026 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved

