Microbiology
Subtopic:
Classification and Types of Microorganisms
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms that cannot be seen by the naked eyes. Microorganisms /microscopic organisms are living organisms which can only be seen with an aid of a microscope.
The microorganisms of medical importance are four that is to say:
Bacteria
Viruses
Fungi
Protozoa
Branches of Microbiology
Bacteriology – the study of bacteria and diseases they cause
Parasitology- the study of parasites and the diseases they cause.
Mycology- the study of fungi and the diseases they cause
Virology – the study of viruses and the diseases they cause.
Entomology – study of vectors/insects which transmit diseases
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
PROKARYOTES are single celled organisms that luck membrane bound nucleus, mitochondria and any other membrane bound organelles’. They reproduce by binary fission e.g. bacteria.
EUKARYOTES are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other organelles enclosed with in membranes. They reproduce by mitosis. Eg protozoa, gung helminthes etc.
Differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
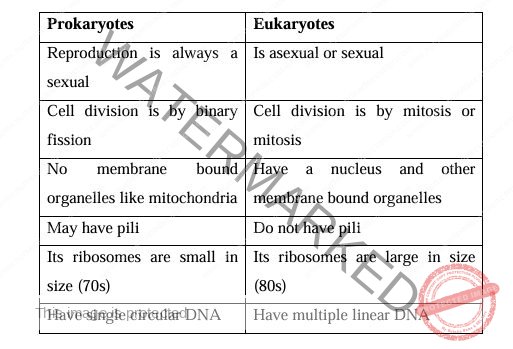
Parasitology
Parasitology is the study that deals with medically important parasites.
Definitions of terms used:
Parasite is an organism that lives on or inside of another orgnaism to detrimente of the hosts organism.
Host. Is an organism which support the parasite.
Parasitism. Is a form of symbiosis in which one organism benefits from the expenses of another organism usually of a different species.
Ecto parasite. Are parasites that live on the surface of the host such as lice and mice.
Endo parasite. Are parasites that live inside the host such as Giardia-lamblia, Ascaris lumbricoides.
Facultative parasite. Is an organism that exhibit both parasitic and non-parasitic mode of living in that it does not absolutely depend on the parasite mode of life. E.g Naegleria flowleria.
Trophezoite. Is the active feeding stage of a protozoa parasite
Cyst/Oocyst. Is the inactive feeding or infective form of a parasite.
Reservoir. Is host that makes the parasite available for transmission to another host and is usually not affected by the infections.
Obligate parasite. Is parasite that must always live in contact with its host.
Definitive host. The host in which sexual reproduction takes place.
Intermediate host. Host where/that harbours the larval stages of the parasite or where a sexual stage cycle of development occurs from.
Classification of Parasites: Parasites of medical importance are classified into two: Protozoa and Helminthes.
Mycology
Mycology is the study of fungi. Fungi are non-motile eukaryotic organisms which exist as saprophyte (derives its nourishments from decaying organic matter) or as parasite.
Virology
Virology is the study of viruses.
We are a supportive platform dedicated to empowering student nurses and midwives through quality educational resources, career guidance, and a vibrant community. Join us to connect, learn, and grow in your healthcare journey
Quick Links
Our Courses
Legal / Policies
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved | Design & Developed by Opensigma

