Medical Nursing
Subtopic:
Terms used in Medical Nursing
Introduction to Medical Terminologies
Most medical terms contain at least one root, and they may also contain one or more prefixes or suffixes.
Word Parts
If all three word parts are present in medical terminology, they will be in the following order:
Prefix → Root Word → Suffix
For example:
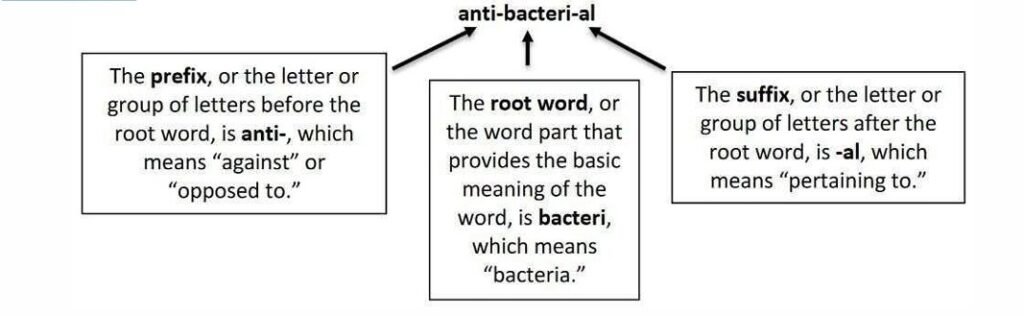
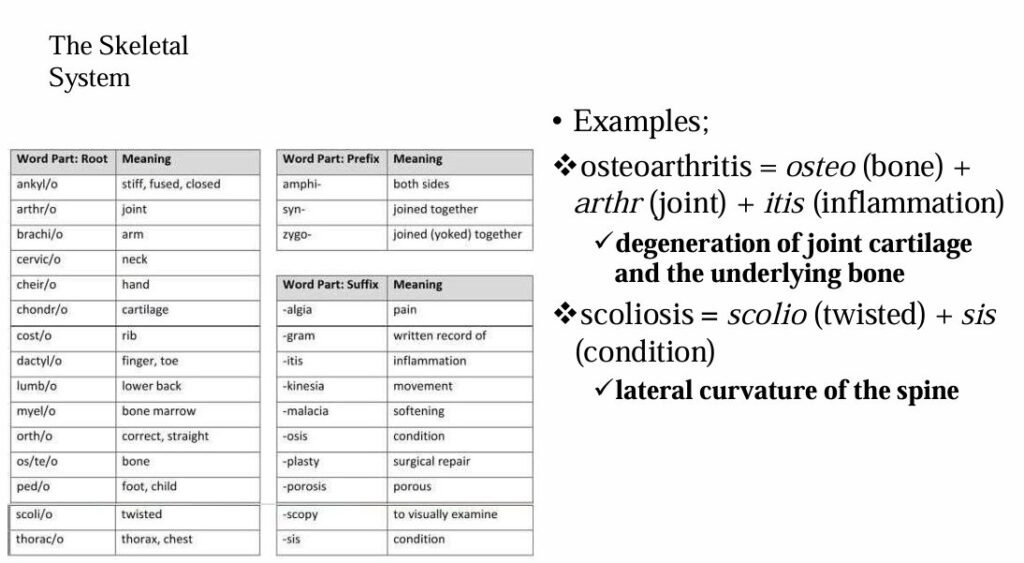
While many medical terms contain all three word parts, others will contain varying combinations such as root/suffix, prefix/root, prefix/suffix, etc. Some words will even contain two roots, such as osteoarthritis (osteo = bone, arthr = joint).
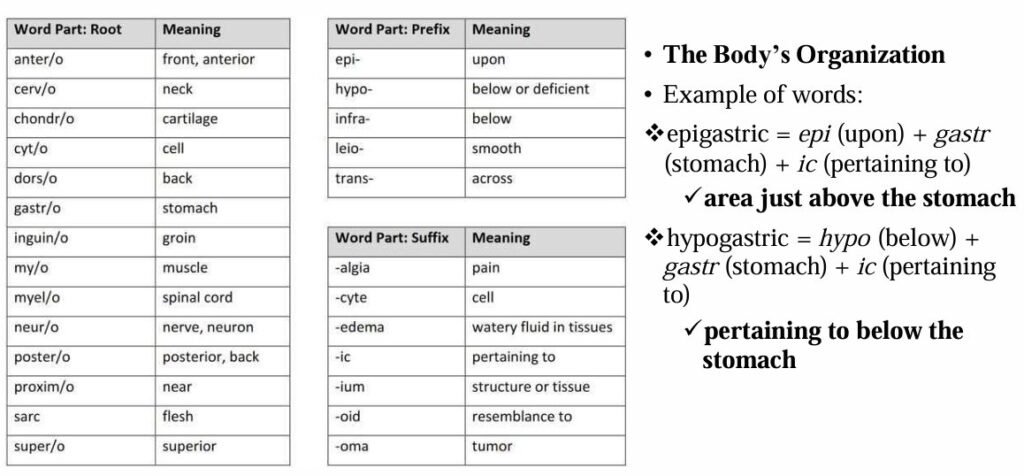
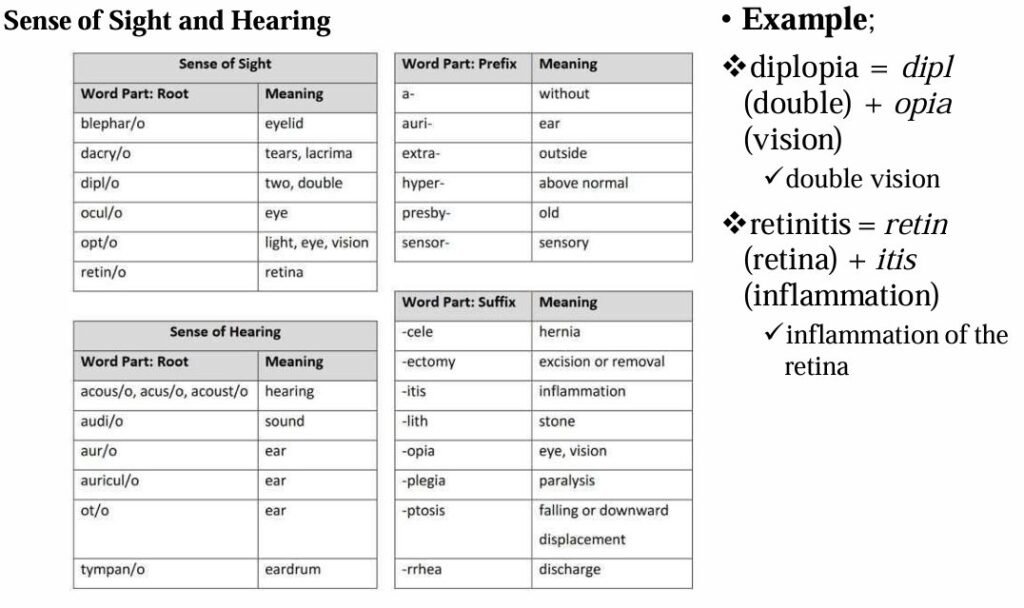
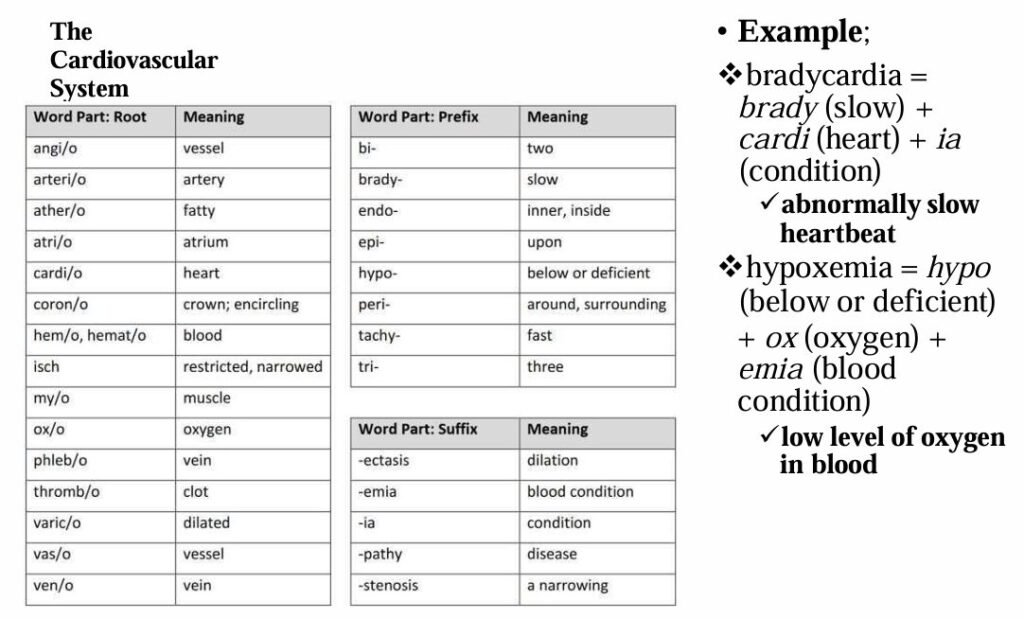
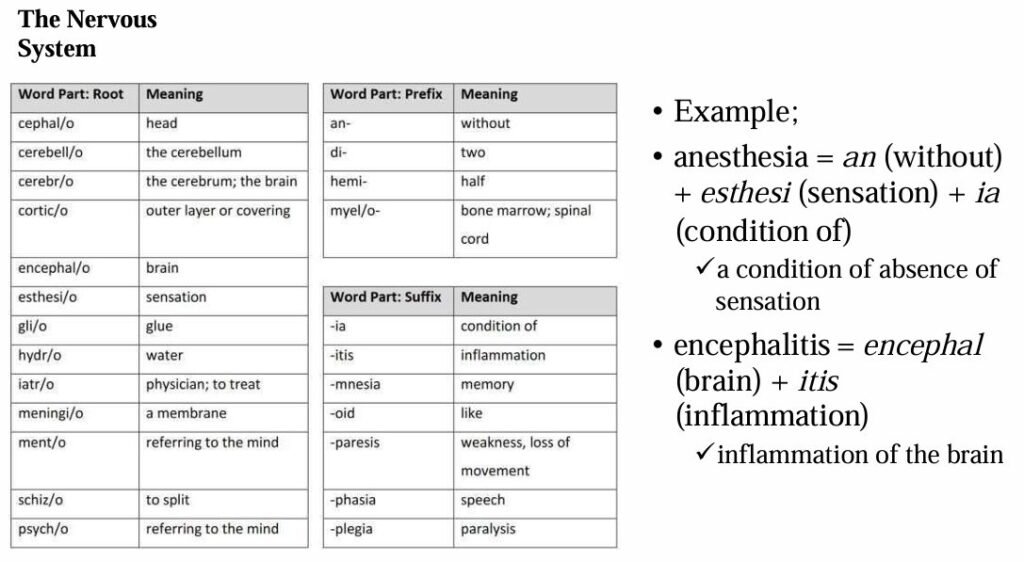
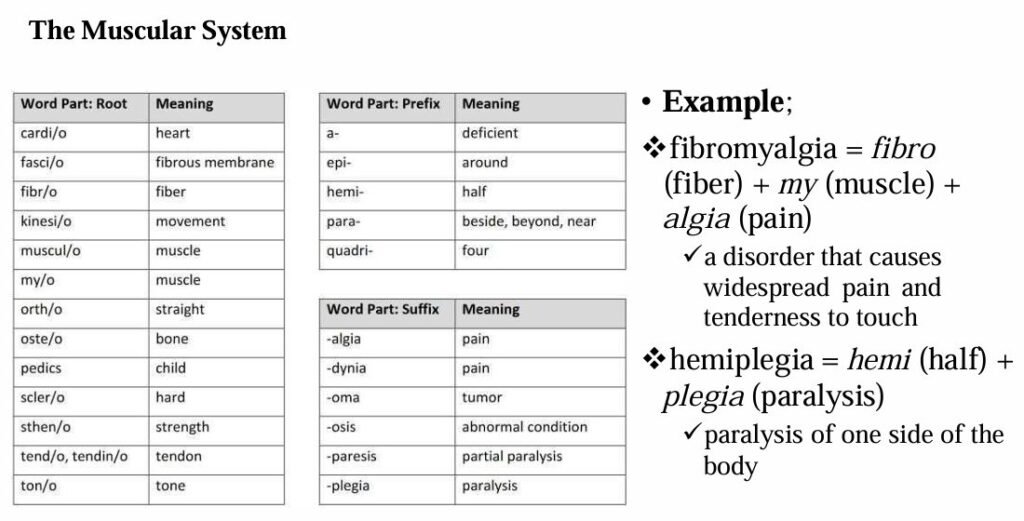
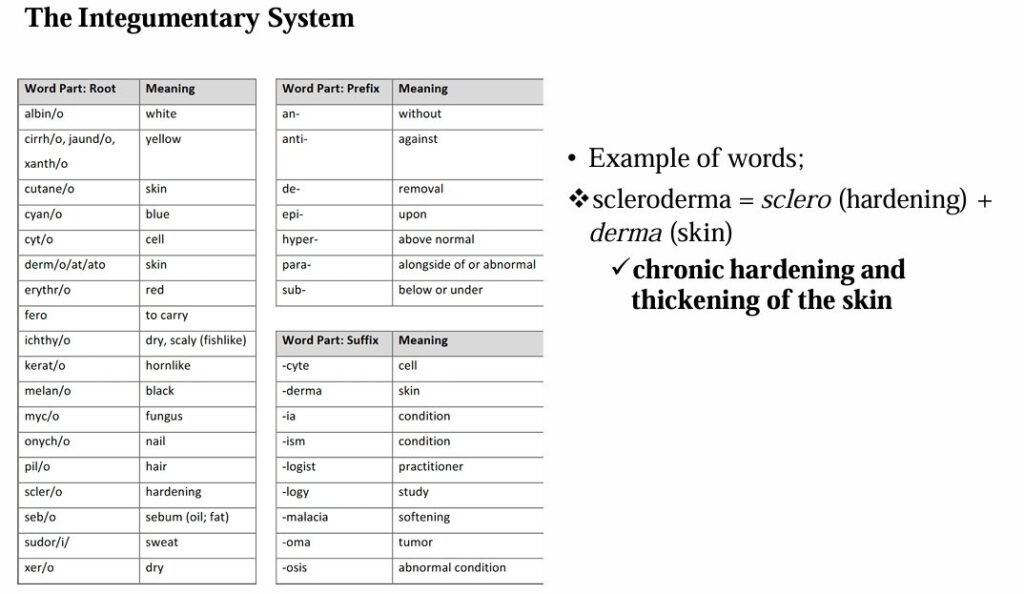
The most common roots, prefixes, and suffixes used in the different body systems are displayed in the table below.
Examples:
Epigastric = epi (upon) + gastr (stomach) + ic (pertaining to)
➤ Area just above the stomachHypogastric = hypo (below) + gastr (stomach) + ic (pertaining to)
➤ Pertaining to below the stomach
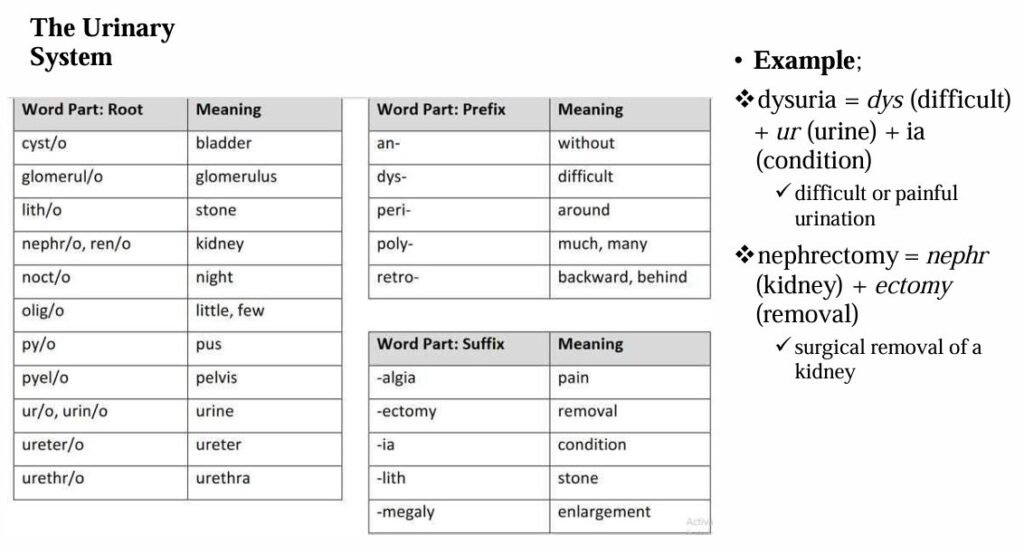
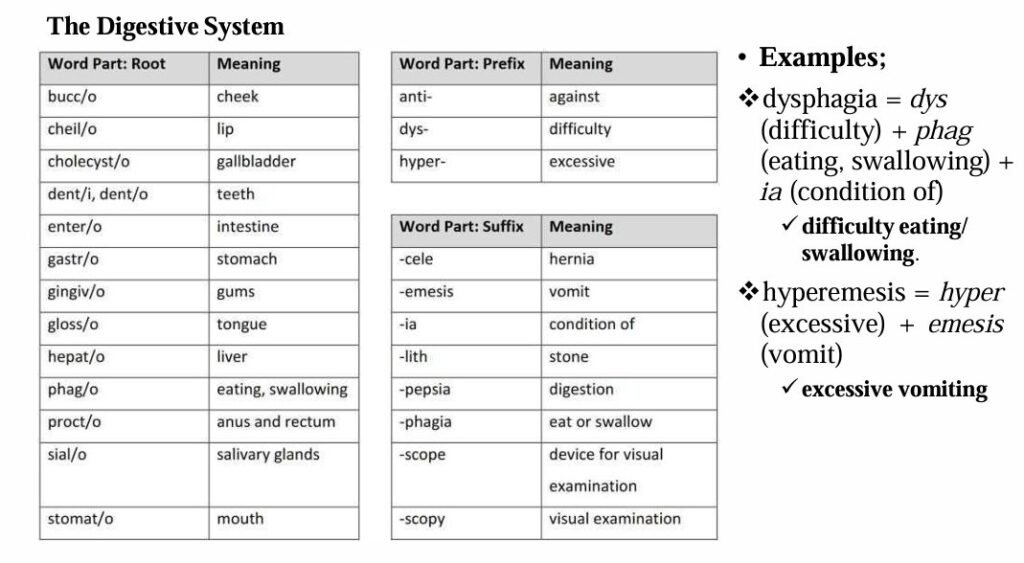
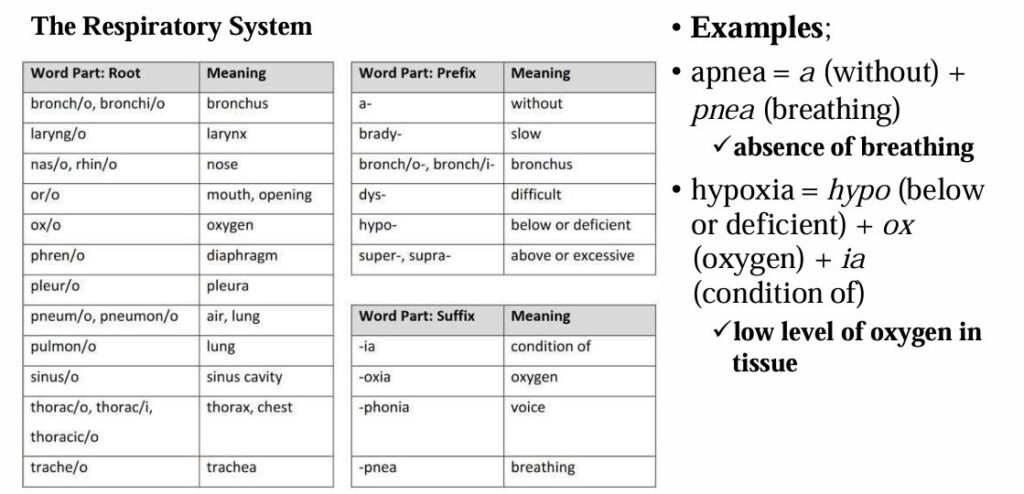
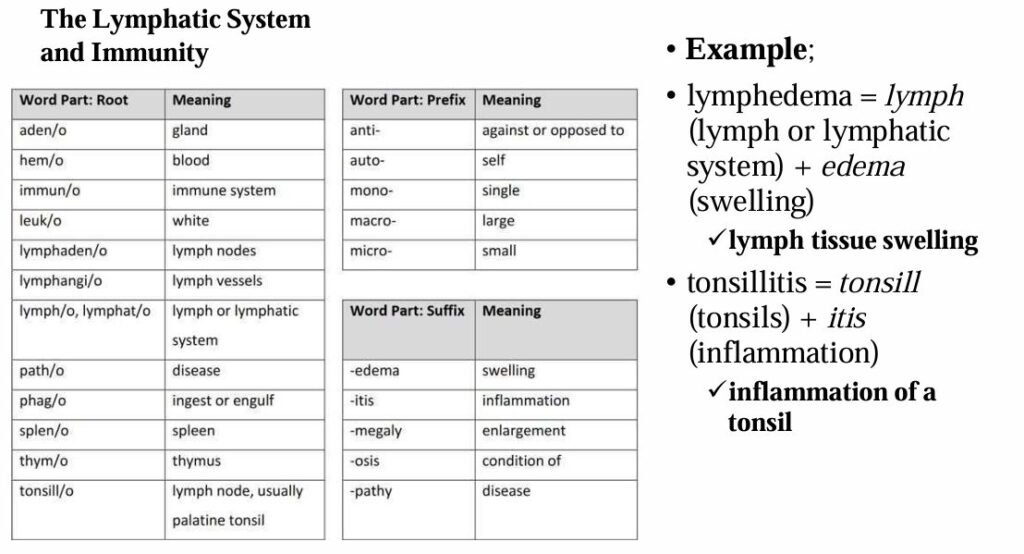
Definition of Terms Used in Medical Nursing
Acute: Used to refer to conditions with sudden onset, usually severe (life-threatening), but short-lived, lasting less than or equal to three weeks.
Chronic: Used to refer to conditions with gradual/progressive onset, usually less severe (non-life-threatening), and long-lasting (recurrent or persistent) for more than three months/six weeks.
Sub-acute: Used to refer to conditions that fall between acute and chronic characteristics, especially when closer to acute.
Acute-on-chronic: Means an exacerbation or a flare-up of a medical disease that is chronic in nature.
Disease: An abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and is not initially/primarily due to any external injury. Diseases are associated with specific signs and symptoms.
Illness: A condition in which the body or mind is harmed because an organ or part is unable to work as it usually does. It can be a disease or sickness.
Sickness: Impairment of normal physiological function affecting part or all of an organism.
Critical: Refers to when the patient’s vital signs are out of the normal range, and the patient may be unconscious.
Inpatient: Status of a patient who requires hospital admission or one who is admitted in the hospital. Such a patient sleeps in the hospital, mainly for close monitoring and overnight care.
Outpatient: Status of a patient who is not admitted to hospital for overnight care. Common for patients on oral drug therapy or those with a mild form of diseases.
Common Medical Terms
Abrasion: A scrape in the skin or mucous membranes that can be treated from home.
Abscess: A tender, pus-filled pocket, usually due to infection.
Aneurysm: A bulge in the wall of an artery that weakens the artery and can lead to rupture.
Aortic dissection: A tear in the inner layer of the aorta.
Bradycardia: Refers to a reduced/slowing heart rate – typically less than 60 beats per minute for adults.
Tachycardia: Refers to a rapid/fast heart rate – typically higher than 100 beats per minute for adults.
Bradypnoea (bradypnea): Refers to reduced/slow respiration rate – typically less than 15 breaths per minute for adults.
Tachypnoea (tachypnea): Refers to rapid/fast respiration rate – typically more than 20 breaths per minute.
Temperature-Related Terms
Pyrexia: A body temperature above the upper limit – typically above 37.5°C.
Hyperpyrexia: Very high fever – typically above 40°C.
Hyperthermia: Elevated body temperature – above 37.5°C.
Hypothermia: Body temperature below the lower limit – typically below 35.5°C.
Types of Fever
Intermittent fever: Body temperature alternates at regular intervals between periods of fever and periods of normal or subnormal temperature.
Remittent fever: A wide range of temperature fluctuations (more than 2°C) occurs over the 24-hour period, all of which are above normal.
Relapsing fever: Short febrile periods of a few days are interspersed with periods of 1 or 2 days of normal temperature.
Constant fever: Body temperature fluctuates minimally but always remains above normal.
Additional Medical Terms
Benign: Usually refers to a tumor or an abnormal growth of tissue/cells that is not cancerous/malignant.
Biopsy: A small sample of tissue that’s taken for testing to discover the cause or extent of disease, by microscopically examining the nature of cells.
Cyanosis: A condition characterized by bluish skin and mucous membranes due to prolonged lack of oxygen in the blood.
Diagnosis: Identification of a condition, disease, or disorder by evaluation of symptoms, tests, and other factors.
Thrombus: A blood clot within blood vessels that affects normal blood flow.
Edema: Tissue swelling caused by fluid accumulation in the interstitial space.
Embolus: A blood clot, air bubble, or any other foreign small particle dislodging in blood vessels.
Hypertension: Abnormally high blood pressure.
Hypotension: Abnormally low blood pressure.
Ischaemia: Refers to lack of blood flow to an organ or part of the body, e.g., cardiac ischaemia refers to reduced/lack of blood flow to the heart.
Palpitation: Abnormally strong heartbeat/contraction.
Malignant: Usually refers to tumors or abnormal tissue growths that are cancerous.
Tumor: A swelling or mass of tissue, often due to uncontrolled/dysregulated growth.
Cancer: A mass of related cells due to dysregulation in their multiplication, in which some spread into other parts of the body, interfering with normal body function.
Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA): Commonly called stroke; occurs when the brain is deprived of blood and oxygen either by blockage or rupture of a blood vessel.
Sepsis: A serious condition caused by the body’s response to severe infection in the blood and can lead to organ damage/failure.
Fibrillation: An uncoordinated, quivering movement of the heart muscle, resulting in irregular pulses and poor blood flow, e.g., atrial fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation.
Bacteraemia: Presence of bacteria in blood circulation.
Parasitemia: Presence of parasites in blood circulation.
Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes due to poor bile excretion, resulting in abnormally high levels of bilirubin in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia).
Lymphadenopathy: Refers to swelling, pain, or tenderness of the lymph nodes.
We are a supportive platform dedicated to empowering student nurses and midwives through quality educational resources, career guidance, and a vibrant community. Join us to connect, learn, and grow in your healthcare journey
Quick Links
Our Courses
Legal / Policies
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved | Design & Developed by Opensigma

