Antimicrobial Agents
Subtopic:
Anti-Helminths
Anti-helminths
Helminth means worms.
- Helminthiasis is an infections caused by parasitic
- Anti-helminthics are drugs used to treat parasitic infections due to
- Anthelmintics act through two mechanism
- Vermicide (kill); used to kill parasitic intestinal
- Vermifuge (expel); used to destroy or expel worms in the intestine
Helminths are 3 types
- Nematodes (round worms); ascarids (Ascaris), filarias, hookworms,pinworms (Enterobius), and whipworms (Trichuris trichiura)
- Cestodes (tape worms); multiple species of flat worms, Taenia saginatum, Taenia solium(cysticercosis, hydatid(echinococcus),
- Trematodes (flukes); liver flukes, lung flukes, schistosoma
Classification of Anti Helminthics based on chemical Structure
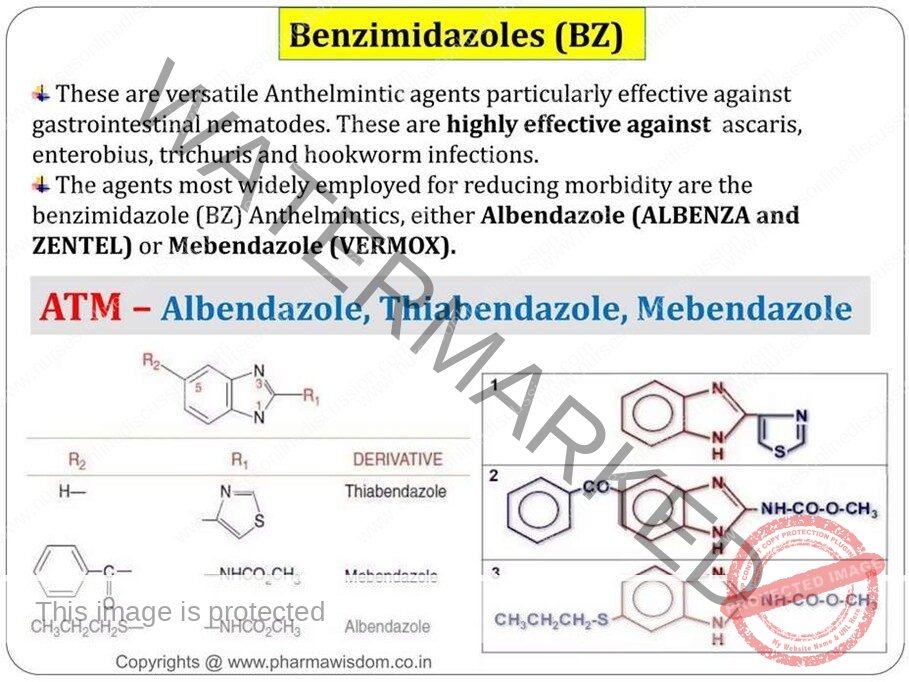
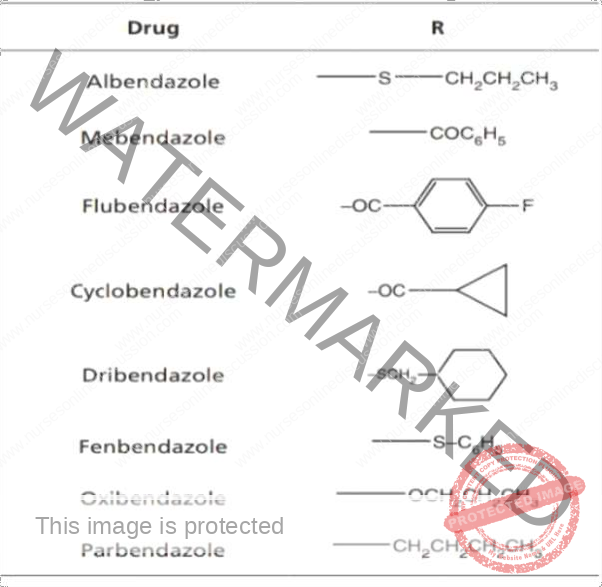
- Benzimidazoles : Albendazole , Mebendazole ,Flubendazole, Cyclobendazole,Thiabendazole, Fenbendazole, Oxibendazole, Parbendazole
- Quinolines and isoquinolines [Heterocyclics]: Oxamniquine, Praziquantel
- Piperazine derivatives: Piperazine citrate, Diethyl carbamazine
- Vinyl pyrimidines: Pyrantel pamoate, Oxantel
- Amides : Niclosamide
- Natural products: Ivermectin
- Organo phosphorus: Metrifonate
- Imidazothiazoles: Levamisole
- Nitro derivatives: Niridazo

Classification based on clinical use

Benzimidazole
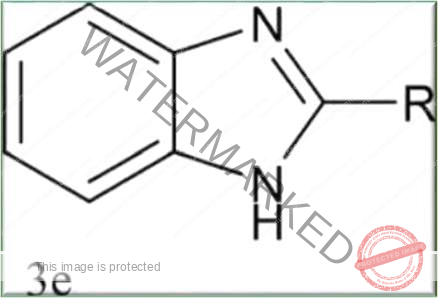
- Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound consists of the fusion of benzene and
- Many anti-helminthic drugs(albendazole, mebendazole, ) belong to the benzimidazole class of compounds.
Examples of benzimidazoles
benzimidazoles
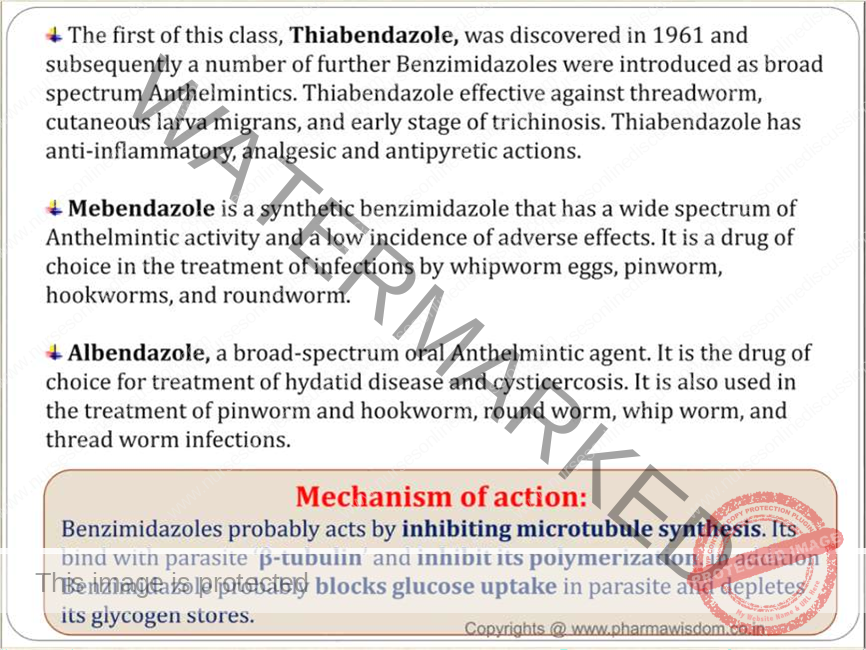
ALBENDAZOLE
- Broad spectrum anti-helminthic with activity against almost all types of intestinal worms.
- Dosage forms
- Tablet:400 mg
- Tablet: 200mg
- Uses
- Intestinal worms (round worm, thread worm, hookworm, strongyloidiasis,tapeworm, whipworm).

Albendazole: Dose and duration
All worms (except strongyloidiasis)
Adult and child >2 years: 400 mg single dose
Child 1–2 years: 200 mg single dose
In severe infections: a 3-day course may be given to clear worm infestation. Repeat doses every 6 months.
Strongyloidiasis
Adult and child >10 kg: 400 mg 1–2 times daily for 3 days
- Contra-indications
- Children <1 year
- Side effects
- Stomach upset
- Patient instructions
- Chew tablet or swallow whole with water
- Pregnancy
- Do not use
- Breast-feeding
- Can be used
MEBENDAZOLE
- Intestinal anti-helminthic (dewormer).
- Dosage forms
- Tablets: 100 mg, 500 mg
- Uses
- Intestinal worms (roundworm, threadworm, hookworm, strongyloidiasis, tapeworm, whipworm)
- Echinococcosis (hydatid disease.
Mebendazole: dose and duration
Intestinal worms
- Adult and child >2 years: 500 mg single dose
- Child <2 years: 250 mg
- A 3-day course may be required for severe
Echinococcosis (in combination with surgery)
- 5 g every 8 hours for 6 months
Contra-indications
- Children <6 months
Side effects
- Stomach upset
- Headache, dizziness
- Allergic reactions
- Patient instructions
- Chew the tablet or crush and mix with drinking water
- Take between meals
- Pregnancy
- Do not use
- Breast-feeding
- Can be used
- Caution
- Preferably use albendazole as it is active against more types of worms
- Treat all family members
- Repeat dose 2–4 weeks later as re-infection occurs easily
- All children should repeat the dose every 6 months
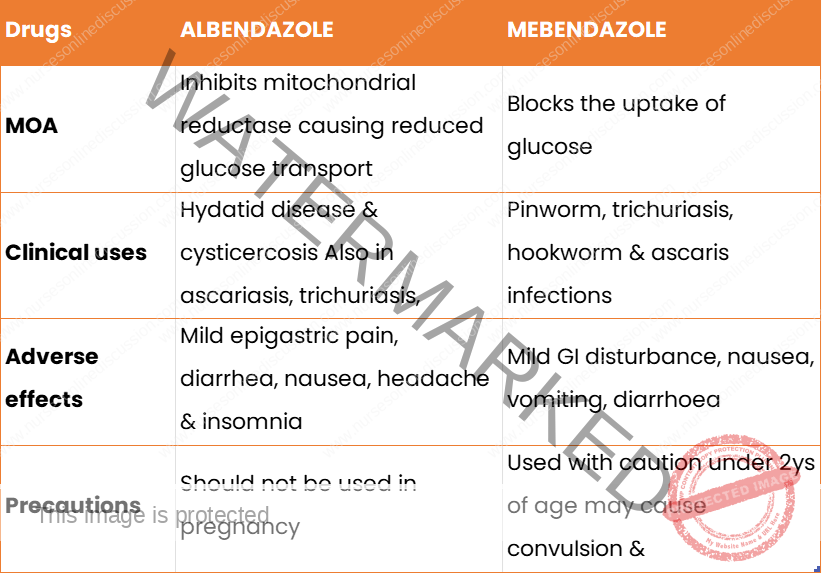
Comparison between albendazole and mebendazole
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co
×

