Communicable Diseases
CHICKEN POX(VARICELLA)
Table of Contents

Learning Objectives
- Understand the cause and transmission of chickenpox, including the role of the varicella-zoster virus and how it spreads.
- Identify the signs, symptoms, and key characteristics of chickenpox, such as its prevalence, incubation period, and potential long-term effects like shingles.
- Recognize diseases that present similarly to chickenpox for differential diagnosis, such as impetigo and scabies.
- Learn patient care and home management strategies, including isolation, hygiene, and hydration.
- Identify appropriate and inappropriate foods and nutritional supplements to manage symptoms and boost immunity during a chickenpox infection.
- Describe the various treatment options for symptomatic relief, including analgesics, antihistamines, soothing lotions, and when antiviral drugs might be recommended.
CHICKEN POX(VARICELLA)
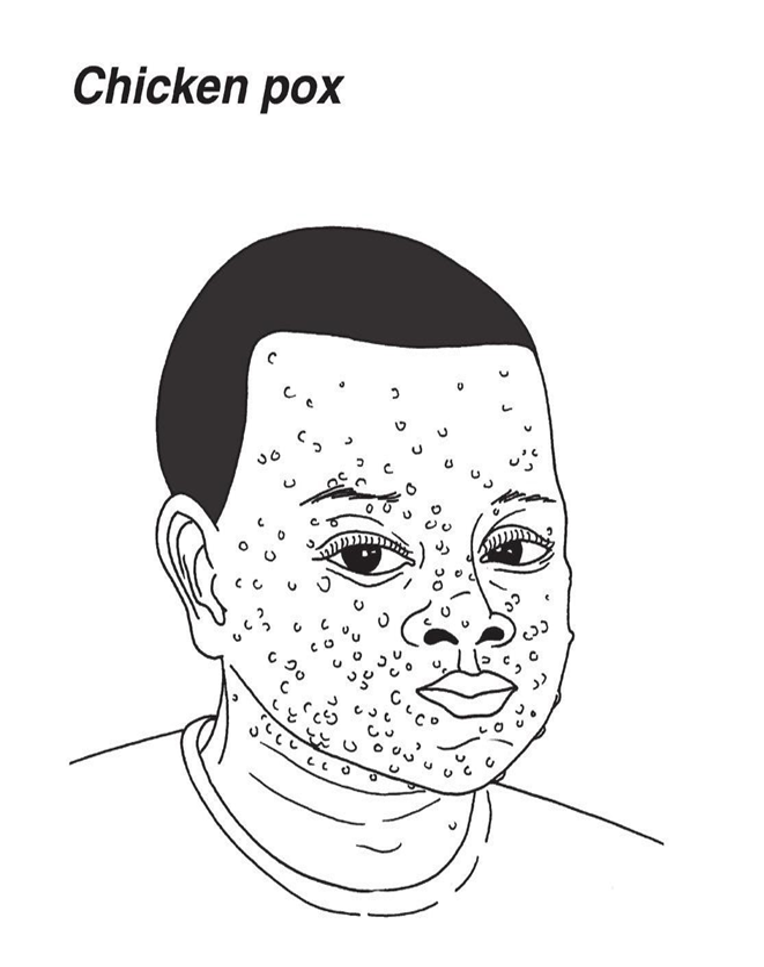
- Chicken pox is a highly contagious viral disease characterized by itchy skin rash and fever.
- It spreads easily from person to person and affects many house hold children within a short time.
- The first case of chicken pox was identified in 1875 by Rudolf Steinem and the varicella vaccine was introduced in 1995.
Prevalence of chicken pox
- Chicken pox affects both children and adults.
- It presents with mild symptoms among children but it is more severe in adults.
- Immunocompromised.
- persons have a high risk of developing severe symptoms of chicken pox with complications.
Causes of chicken pox
- Chicken pox is a primary infection caused by varicella-zoster virus, a DNA virus which is a member of the herpesvirus.
- Primary infection results in chicken pox.
- After primary infection, varicella –zoster virus remain dormant in the CNS for life.
- Reactivation of the dormant infection results in herpes zoster (shingles).
Incubation period of chicken pox
- The incubation period for chicken pox ranges from 14-16 days after exposure to an infected person.
- The infected person is infectious from 1-2 days before the onset of skin rash until all the blisters have healed.
Transmission of chicken pox
- Transmission occur through contact with infectious secretion from the nose of a person with chicken pox or herpes zoster.
- It can also be transmitted through contact with vesicle fluids.
Signs and symptoms
- Red skin blisters.
- Itching of the skin.
- Fever.
- Headache.
- Sore throat.
- Body weakness.
- Loss of appetite.
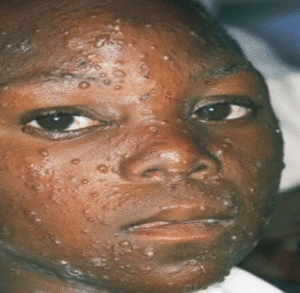
Differential diagnosis of chicken pox
- Diseases that may present with skin rash like chicken pox include:.
- Impetigo.
- Drug-induced eruption.
- Scabies.
- Insect bites.
Long term story of chicken pox
- Most people who suffer from chickenpox will be immune to the disease for the rest of their lives.
- However, the virus remains dormant in nerve tissue and may be reactivated resulting in herpes zoster (shingles) later in life.
- Reactivation occur as result of immunosuppression due to HIV/AIDS and cancer.
Management of chicken pox
- Chicken pox has no cure.
- Treatment focus on relieving symptoms.
Patient advise
- Chickenpox is contagious there fore keep the child or adult at home until the skin lesions have healed.
- Cut the finger nails short to avoid bruising the skin during scratching.
- Recommend bathing with antiseptic soap such as Dettol soap.
- Advise the patient to drink a lot of water.
Best food for patients with chicken pox
- A diet for patient with chickenpox should contain soft and non-acidic foods such as:.
- Mashed potatoes.
- Sweet potatoes.
- Avocado.
- scrambled eggs.
- beans.
- boiled chicken and fish.
Foods to avoid incase of chicken pox
- The food that worsen symptoms of chicken pox include.
- Fried foods like chips.
- Garlic.
- Pop cons.
- Pineapples.
- Tomatoes.
Nutritional supplements
- Vitamin supplements containing vitamin A,C, D and E boost the bodies immunity.
- Minerals like zinc and selenium also help to boost the immune system.
- Vitamin B 12 helps to keep the myelin sheath healthy since the virus affects the nerves.
- Lysine is an essential amino acids that help to strengthen immune system against the herpes family of viruses.
Antiviral herbs
- Elderberry and echinacea are antiviral herbs.
- They reduce viral replication to aid in faster resolution of symptoms.

Analgesics and antipyretics
- Antipyretics such as paracetamol or ibuprofen can be recommended for at least 3 days.
- They reduce fever and pain.
- Do not use aspirin or aspirin containing products to relieve fever from chickenpox.
Oral antihistamines
- Recommend sedative antihistamines to control skin itching.
- Hydroxyzine.
- Chlorpheniramine.
- Promethazine.
- Others cetirizine.
Antihistamines
- Recommend sedative antihistamines to.
- control skin itching.
- Hydroxyzine.
- Chlorpheniramine.
- Promethazine.
- Others such as cetirizine may be recommended.
Soothing lotions (calamine lotion)
- Skin itching can be relieved by use of calamine lotion.
- Apply to the affected area every 12hours.

Antiviral drugs
Oral antiviral such as acyclovir may be recommended in case of :
- Immune suppression.
- Unvaccinated children above 12 years.
- Severe eczema.
- Chronic pulmonary disease.
Join Our WhatsApp Groups!
Are you a nursing or midwifery student looking for a space to connect, ask questions, share notes, and learn from peers?
Join our WhatsApp discussion groups today!
Join NowGet in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co

