Respiratory System Conditions
Subtopic:
Acute pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis
- Acute pharyngitis is an inflammatory syndrome of the pharynx and/ortonsils caused by several different groups of
- Most common throat disorder
- Usua ly subsides in 3 to 10 daysunless complications
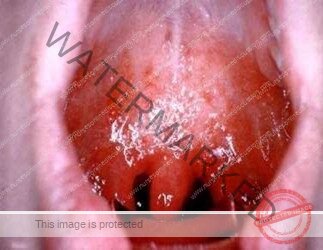
Etiology of Acute pharyngitis
- Viral or bacterialinfection
- Beta-hemolytic streptococcus (15%to 20% of acute pharyngitis cases).
- Mononucleosis
- Streptococcus bacterial infections(in children)
- Candida infection is common as a source of sore throat in immunocompromised individuals, including those undergoing chemotherapy or oropharyngeal irradiation for
.
Pathophysiology
- Acute pharyngitis results from infection and inflammation of the pharynx, the details of which are both pathogen- and host-
- Most commonly the disease is localized to the pharynx alone, but rarely it may be part of a systemic infection (e.g., infectious mononucleosis, tularemia, or HIV).
Incidence of Acute pharyngitis
- Widespread among adults who:
- Live or work in dusty or
- Uses their voice excessively
- Use tobacco or alcohol habitually
- Suffer from chronic sinusitis, persistent coughs, or a l
Clinical manifestations of Acute pharyngitis
History
- Sore throat
- Slight difficulty swallowing
- Sensation of lump in thethroat
- Content aggravating urge to swallow
- Headache
- Muscles and joint pain
Test Results
- Lab (throat culture, rapid strep test & WBC)
- Imaging (CTallocate theabscess)
Risk Factors of Acute pharyngitis
- nasal colonization with group AStreptococcus (GAS)
- GAS-infected contact
- sexual activity or abuse
- ingestion of nondomestic meats
- immunocompromised host
- use of inhaled corticosteroids
- lack of immunization or vaccinefailure
- chemotherapy or oropharyngeal irradiation for cancer
Risk Factors of Acute pharyngitis
- nasal colonization with group AStreptococcus (GAS)
- GAS-infected contact
- sexual activity or abuse
- ingestion of nondomestic meats
- immunocompromised host
- use of inhaled corticosteroids
- lack of immunization or vaccinefailure
- chemotherapy or oropharyngeal irradiation for cancer
Risk Factors of Acute pharyngitis
- nasal colonization with group AStreptococcus (GAS)
- GAS-infected contact
- sexual activity or abuse
- ingestion of nondomestic meats
- immunocompromised host
- use of inhaled corticosteroids
- lack of immunization or vaccinefailure
- chemotherapy or oropharyngeal irradiation for cancer
Complications
- Otitis media
- Sinusitis
- Mastoiditis
- Rheumatic fever
- Nephritis
Treatment of acutepharyngitis
- General (warm saline gargles, hospitalization for dehydration, elimination of the underlying cause & adequatehumidification)
- Diet (adequate diet, avoidance of citrus juices, easy toswallow food)
- Activity (bed rest while febrile)
- Medications( anesthetic throat lozenges, analgesics as needed, antibiotics, antifungal agents, antipyretics and equine antitoxins)
- Surgical (abscess drainage)
Nursing consideration
- Nursing diagnosis (acute pain, fatigue, imbalance nutrition; less than body requirements, impaired oral mucous membrane or risk for deficient fluid volume)
- Outcomes (the pt will express feeling of increase comfort decreased pain, verbalizes importance of adequate daily calorie intake , maintain intact mucous membranes or maintain normal fluid volume)
- Nursing interventions (administer medication as orders, throat culture as orders, instruct pt to use a warm saline gargles, encourage adequate oral fluid intake and perform meticulous moth care and maintain as restful environment
Patient teaching
- Be sure to cover :
- Disorder, diagnostic test and treatment
- Importance of completing prescribed antibiotic therapy
- Adverse reactions to medications
- Avoidance of excessive exposure toair conditioning
- Smoking cessation
- Ways to minimize environmental sources of throat irritation
- Importance of throat cultures
We are a supportive platform dedicated to empowering student nurses and midwives through quality educational resources, career guidance, and a vibrant community. Join us to connect, learn, and grow in your healthcare journey
Quick Links
Our Courses
Legal / Policies
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2026 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved
×

