Antimicrobial Agents
Subtopic:
Quinolones
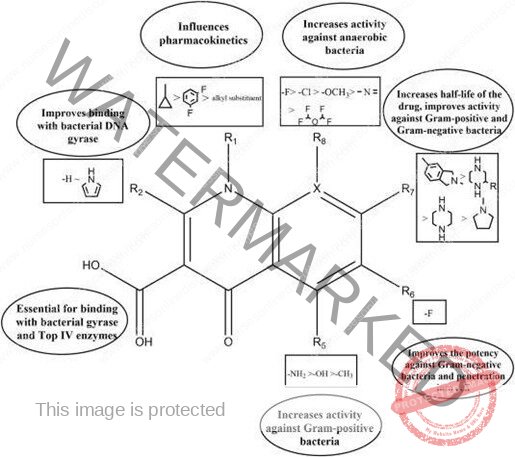
- Bactericidal broad spectrum It belongs to the DNA synthesis inhibitors.
- Increasingly used because of their relative safety, their availability both orally and parenterally and their favorable pharamacokinetics
- There is increasing concern about the emergence of resistance to these agents.
- Quinolones are They inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis in several ways causing rapid cell death.
- Quinolones bind the DNA-DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) complex blocking further DNA
- Quinolones block topoisomerase IV interfering with separation of interlocked (concatenated), replicated DNA molecules.
- There appear to be additional sites of quinolone action that are as yet not well
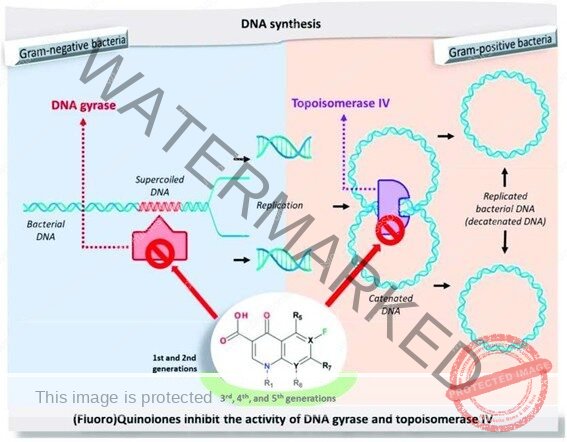
Mechanism of action of Quinolones
- Quinolones are They inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis in several ways causing rapid cell death
- Quinolones bind the DNA-DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) complex blocking further DNA replication.
- Quinolones block topoisomerase IV interfering with separation of interlocked (concatenated), replicated DNA molecules
- There appear to be additional sites of quinolone action that are as yet not well
Generations of quinolones
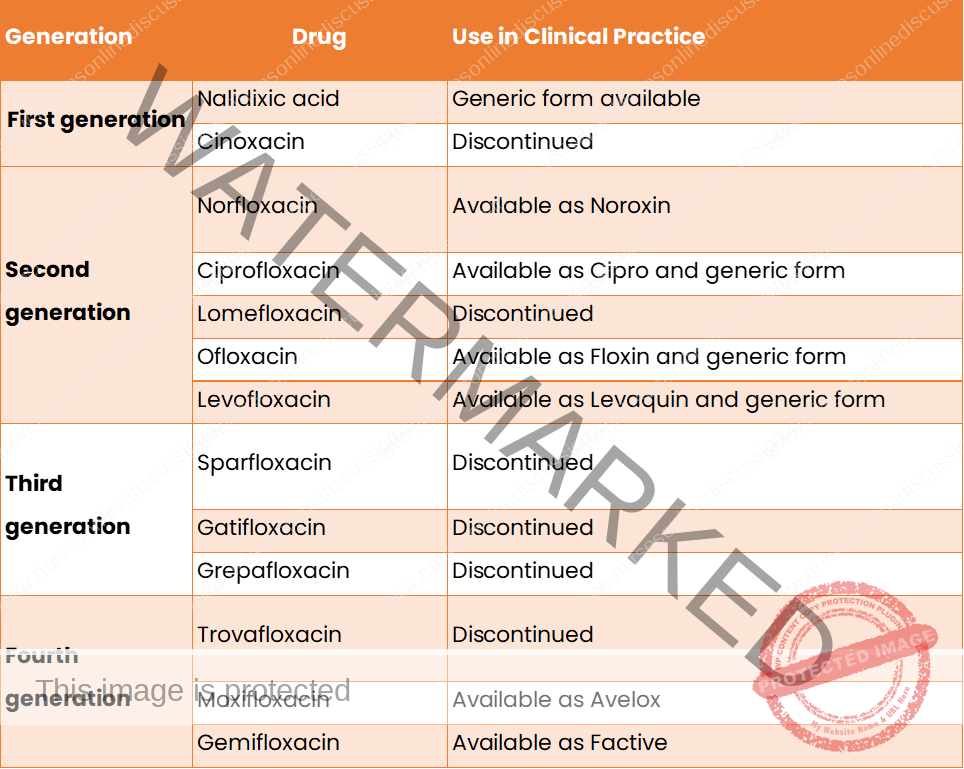
Generations of quinolones and spectrum anti-bacterial effect
1st generation (quinolones like nalidixic acid):
- limited to Gram negative enteric bacteria (UTIs)
2nd generation (fluoroquinolones like norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin):
- Improved Gram negative coverage with activity against S. aureus (systemic infections) , pseudomonas and also against B. anthracis
- Addition of fluorine and piperazine derivative
3rd generation (fluoroquinolones – levofloxacin):
-Improved activity against Gram positives e.g. staphylococci and pneumococci, also has activity against mycoplasma and legionella (systemic infections)
- Longer half life
- Increased structural complexity, greater antimicrobial spectrum but also increase in some toxicity
- Gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin are two newer agents with extended half-lives and enhanced Gram positive activity
Pharmacokinetics of quinolones
- Well absorbed orally – bioavailability of ≥ 50%
- Some fluoroquinolones are available parenterally
- Excellent tissue distribution -Conc’ns in kidney, prostate, lung and bile usually > serum.Conc’ns in bone, CSF < serum.
- Quinolones also achieve high intracellular conc’ns (e.g. PMNs)
- Elimination- Most are eliminated by the kidneys, although some are eliminated by the liver.
- Drug interactions- decreased oral absorption following co- administration of metal cations
NALIDIXIC ACID
- First generation quinolone
- Dosage forms and strength
- Tablet: 500 mg
- Suspension: 300mg/5ml
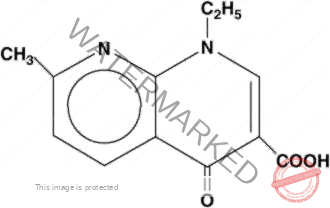

Nalidixic acid
Uses/indication;
- Urinary tract infections
Contra-indications;
- Hypersensitivity to quinolones
Side effects;
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhoea
- Headache, dizziness, vertigo, weakness
- Rash, pruritus
- Stevens- Johnson syndrome
- Toxic psychosis

Interactions;
- Warfarin (enhanced anticoagulant effect)
- Artemether/ Lumefantrine (increased risk of arrhythmias)
- Ciclosporin (increased risk of nephrotoxicity)
- NSAIDs (increased risk ofconvulsions).
Patient instructions
- Take your medication at least one hour before a meal or 2 hours after a meal
Caution
Use with caution in liver and renal disease. Avoid if eGFR is less than 20 ml/minute/1.73 m2
Drug is safe for use in pregnancy and breastfeeding.
CIPROFLOXACIN
- Broad spectrum 2nd generation fluoroquinolone antibacterial.
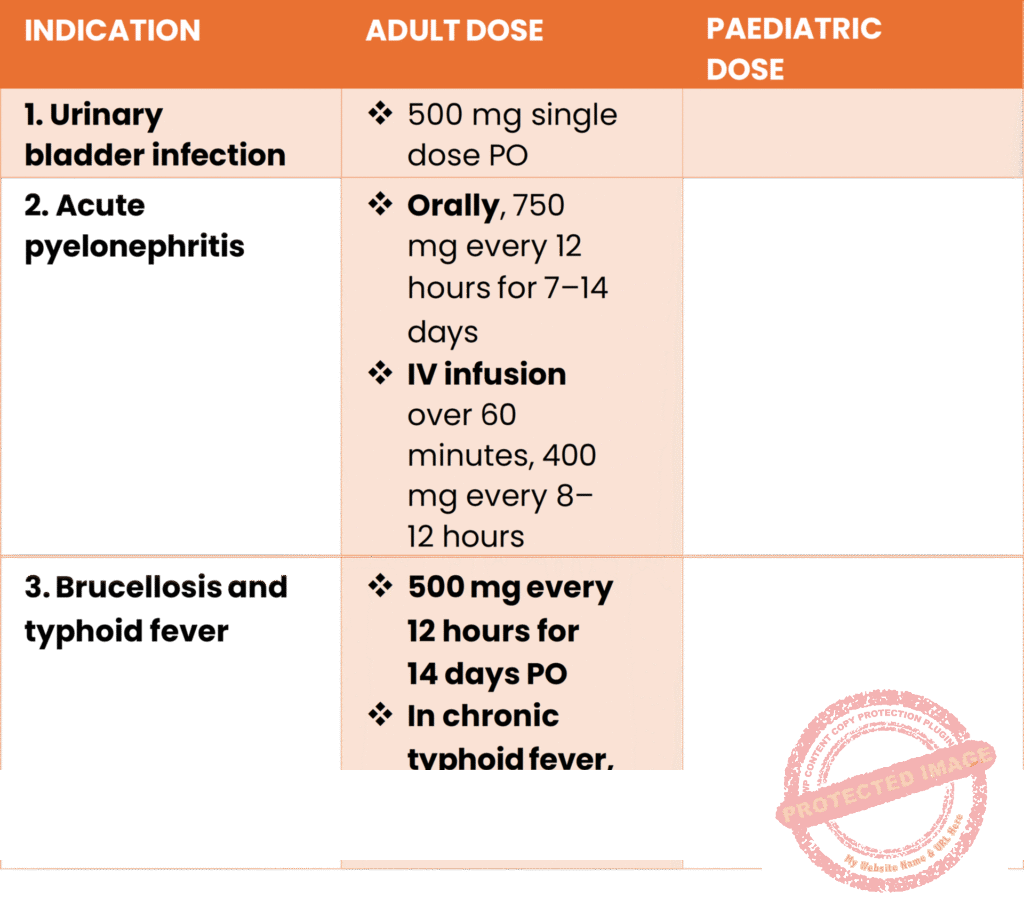
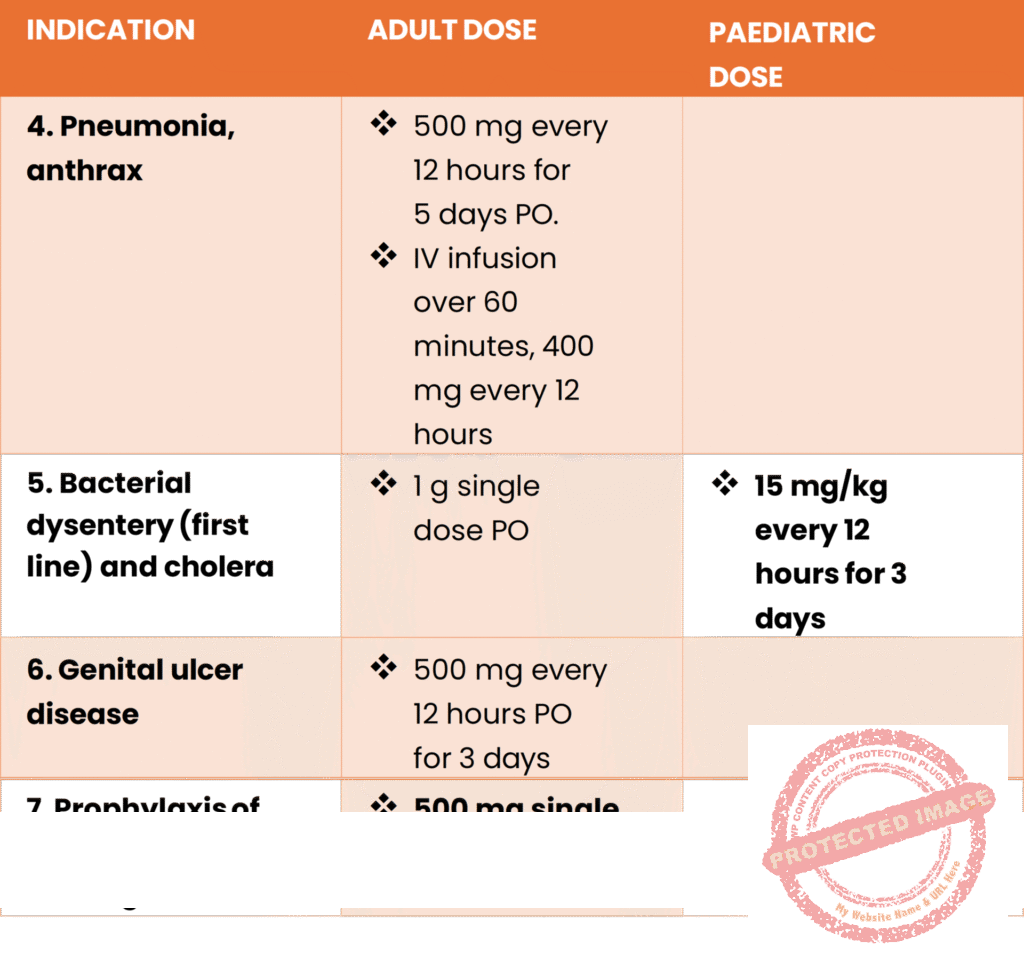
- Uses/indications;
- Urinary bladder infection
- Acute pyelonephritis
- Brucellosis
- Anthrax
- Typhoid fever
- Pneumonia
- Bacterial dysentery
- Cholera
- Genital ulcer disease (without blisters)
- Prophylaxis of meningococcal meningitis
- Corneal ulcers
- Superficial ocular infection

- Tablets: 500 mg
- Solution for IV infusion: 2 mg/ml
- Eye drops: 3%
Dose and duration of Cipro
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co
×

