Obstetric Anatomy and Physiology
Pelvic Floor Muscles
Table of Contents
PELVIC FLOOR (PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES)
DEFINITION: The pelvic floor is a muscular structure which forms the soft tissue which fills the outlet of the bony pelvis.
SITUATION: Found in the outlet of the bony pelvis supporting the pelvic and abdominal organs.
SHAPE: Gutter-shaped structure. It has 3 canals each with an orifice run through, the urethra, the vagina and rectum. The gutter shaped structure influences the relation of the fetal head. It’s higher anteriorly than posterior.
GROSS STRUCTURE They are 6 layers of tissues:
- An outer covering of the skin
- Subcutaneous fat
- Superficial muscle enclosed in fascia. These are important because they can be damaged (infused) during labor.
- Pelvic fascia thickened to form pelvic ligaments.
- Peritoneum
LAYERS OF THE PELVIC FLOOR
Superficial pelvic floor muscles
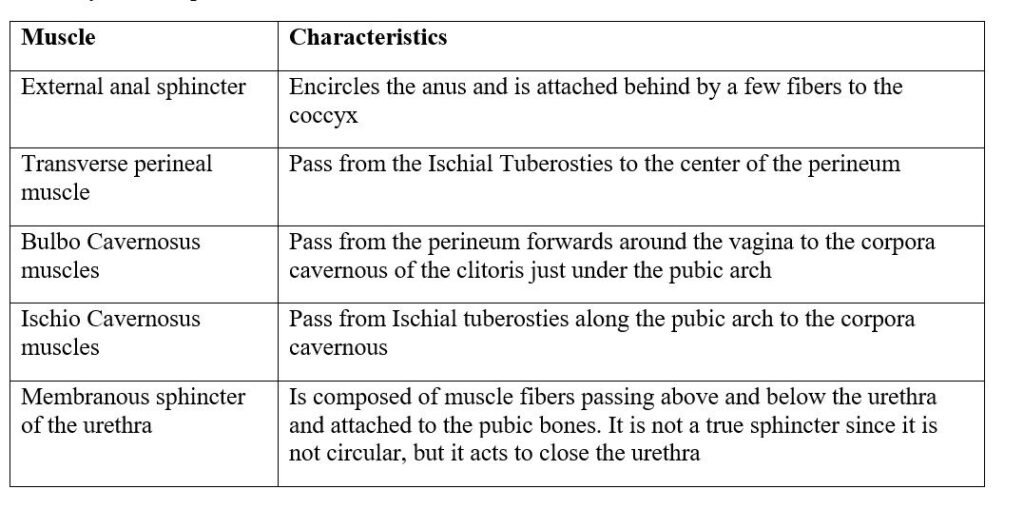
- Transverse perineal muscle: One muscle arises from each ischial tuberosity and they meet in the center of the perineal body.
- Bulbocavernosus: Two muscles arise in the center of the perineum, they pass one on each side of the urethra and vaginal encircling the orifices then inserted into the pubic bone.
FUNCTIONS
- Causes venous congestion
- Causes vaginal excitement and decrease the lumen of the vagina.
(3) Ischiocavernosus: One muscle runs from each ischial tuberosity to the pubic bone. This still leaves 4 areas at the outlet not filled with tissue. The posterior areas are filled with fats; the anterior areas are filled with triangular ligaments.
(4) The membranous sphincter of the urethra: This is formed by two bands of muscle that pass front and behind the urethral orifice and controls the passage of urine.
(5) The rectal sphincter: This is a ring of muscle encircling the anus and controls the passage of stool and flatus.
SUPERFICIAL MUSCLES OF THE PELVIC FLOOR (PICTORIAL)
MUSCLE LAYERS OF THE PELVIC FLOOR
The superficial layer
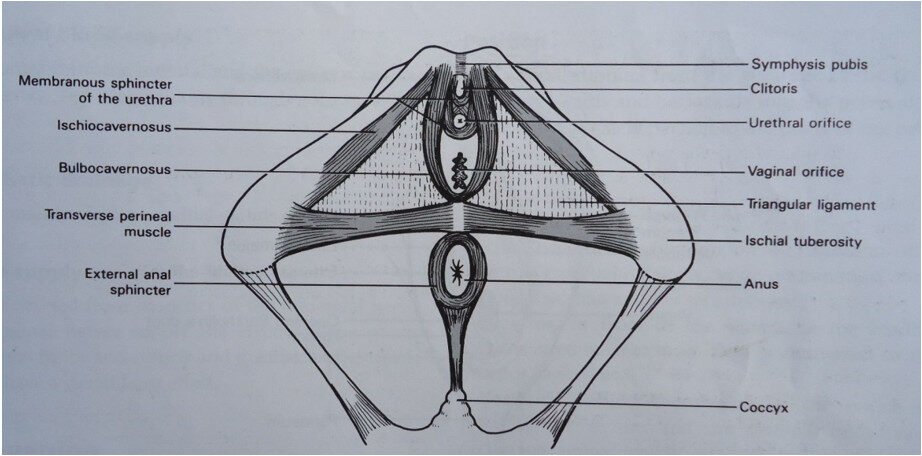
This layer is composed of five (5) muscles.
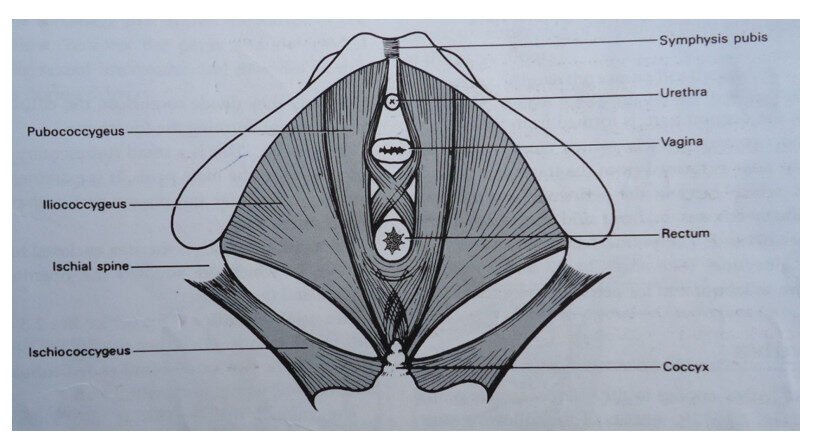
LEVATORES ANI MUSCLES (DEEP MUSCLES OF THE PELVIC FLOOR)
There are 3 pairs of muscles which all have the insertion around the coccyx and because of this they are sometimes called coccygeus muscles. They are about 5 mm thick and their anatomical name is the levatores ani muscle.
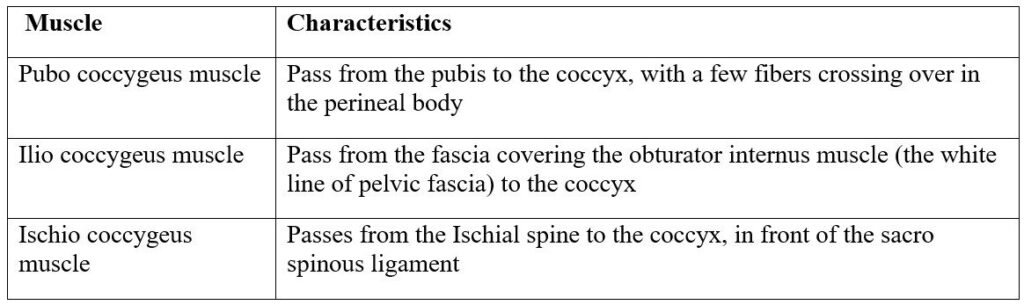
(1) Iliococcygeus: It rises from a point on the ilium known as the white line of fascia, and it passes backwards to the coccyx.
(2) Ischiococcygeus: This arises from each ischial spine and passes to the coccyx and lower border of the sacrum.
(3) Pubococcygeus: Each muscle arises from the pubic bone and passes backwards surrounding the urethra, vagina and rectum before inserting into the coccyx.
DEEP MUSCLES OF THE PELVIC FLOOR (LEVATORES ANI MUSCLE)
BLOOD SUPPLY
By pudendal arteries branches of the internal iliac arteries.
VENOUS DRAINAGE: Corresponding veins of pudendal veins and branches of the internal iliac veins.
NERVE SUPPLY: From the perineal branch of the pudendal nerve.
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE: This is into the inguinal and external iliac glands.
FUNCTIONS
- Support the pelvic and abdominal organs
- Assist in the process of defecating and child birth
- Assist in sneezing, coughing and laughing
- Forms a diaphragm which fills the outlet
INJURIES TO THE PELVIC FLOOR
The pelvic floor may be injured in 2 ways:
- Tearing or laceration
- Over stretching
During the last weeks of pregnancy this pelvic floor softens in preparation for laboring, during the 1st stage the woman bears down the tissues and cervical ligaments will become strained. The uterus may move downwards and after delivery becomes inverted or prolapsed.
2nd stage of labor If there is prolonged 2nd stage the muscles around the vagina and bladder becomes over stretched. This will cause cystocele or rectocele.
PERINEAL TEARS TEARS: The perineal muscles may become badly torn and this may also include levatores ani muscles. There are 3 types of tears known as:
- 1st Degree tear: Involved the fourchette and skin this may need to 2 stitches.
- 2nd Degree tear: This is where the tear is deep and large and has torn the skin and the muscles.
- 3rd Degree tear: Is when the whole length of the perineum is torn through the skin and muscles and sphincter, the patient will be, therefore with incontinence of faeces through anus. This must always be repaired by the doctor and by the midwife.
PREVENTION OF INJURIES TO PELVIC FLOOR DURING ANC
- Encourage all pregnant mothers to attend ANC.
- Good ANC where good selection of mothers is carried out.
- Correct malpresentation early.
- Advice about balanced diet so as to get a health skin which cannot be torn easily.
- Health Education, mothers what to do during antenatal period.
- Advice about exercise.
- Anemia should be corrected if not corrected mother will have body weakness with weak muscle which can tear easily during labor.
- Discourage native medicine.
DURING LABOUR
- Recognize any malpresentation and get doctor to see her.
- Ensure an empty bladder throughout labor.
- Gain the mother’s confidence by instructing what to do during first stage.
- Give analgesic if accessing or severe pain.
- Midwife rubs the mothers back and relieves pain.
- Prevent anemia.
DURING SECOND STAGE
- Deliveries to be conducted by skilled midwife who can prevent tears occurring.
- Give a timely episiotomy after infiltrating it with local anesthesia 5 mls into the perineum.
- Mother is advised to push where there is a contraction. To pant when it passes off. After crowning of the head the mother is advised not to push but to pant.
- Proper guarding of the perineum. Fetal head to allow a small diameter to distend the perineum.
Join Our WhatsApp Groups!
Are you a nursing or midwifery student looking for a space to connect, ask questions, share notes, and learn from peers?
Join our WhatsApp discussion groups today!
Join Now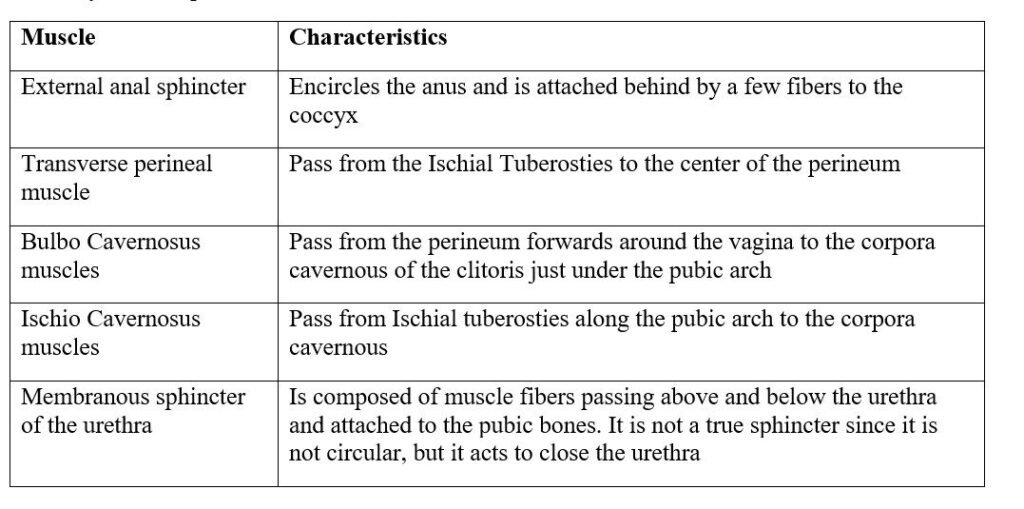
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co

