Teaching Methodology
Subtopic:
Teaching technology
EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY AND TEACHING AIDS
Educational Technology is a system in education in which machines, materials, media, men and methods are interrelated and work together for the fulfillment of specific educational objectives.
Examples of educational technology include:
Radios
Televisions
Computers
Projectors
Printers
Internet
Social Media
Software Packages
ADVANTAGES OF EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY
It makes education more productive: Educational technology enhances efficiency by streamlining administrative tasks, automating assessments, and providing tools for data analysis. This productivity boost allows educators to focus more on teaching and students to spend their time learning.
It can give instructions a more scientific base: Educational technology facilitates data-driven decision-making. Educators can collect and analyze data on student performance to tailor instructional methods, ensuring that teaching is evidence-based and targeted to specific needs.
It makes education more individualized: Technology enables personalized learning experiences. Students can access a wealth of resources and adaptive learning platforms that adapt to their unique learning styles and pace, making education more tailored to individual needs.
It makes access to education more equal: Technology breaks down geographical and socioeconomic barriers to education. Online courses and digital resources provide access to quality education regardless of a student’s location or financial resources.
It makes access to education more immediate: The internet and digital learning platforms offer on-demand access to educational content. Students can access lectures, materials, and resources instantly, reducing wait times and enhancing the immediacy of learning.
It fosters interactive and engaging learning: Educational technology includes multimedia elements, gamification, and interactive simulations that make learning more engaging and enjoyable for students. This interactive approach enhances comprehension and retention.
It encourages self-directed learning: Technology empowers students to take ownership of their education. They can explore topics of interest, conduct research, and set their learning goals, fostering a sense of responsibility and autonomy.
It facilitates collaboration and communication: Digital tools enable students and educators to collaborate, whether through online discussions, virtual group projects, or communication apps. This promotes teamwork and communication skills.
It supports lifelong learning: Educational technology encourages continuous learning beyond formal education. Online courses, webinars, and resources are readily available for individuals to upskill and stay current in their fields.
It prepares students for a digital world: By using technology in education, students gain valuable digital literacy and tech skills, which are essential for success in the modern workforce.

TEACHING AIDS
Teaching aids are materials used in teaching to help the learners grasp a given concept better or easily.
Teaching resources/materials are things that facilitate the teaching process, i.e., text books, classrooms, chalk, black board etc.
Types of Teaching Aids
Visual Aids: Visual aids refer to instructional tools that engage the sense of sight. Examples include actual objects, models, pictures, charts, maps, flashcards, flannel boards, bulletin boards, chalkboards, overhead projectors, and slides. Among these, chalkboards are among the most commonly used.
Audio Aids: Audio aids are teaching tools that involve the sense of hearing. Examples include radios, tape recorders, and gramophones.
Audio-Visual Aids: Audio-visual aids combine both visual and auditory elements to enhance the learning experience. Examples include computers, television and film projectors.
Factors Considered While Selecting Teaching Aids
When a teacher is considering the use of audiovisual aids, several factors should be taken into account:
Instructional Objectives: The teacher should assess whether the lesson’s objectives warrant the use of teaching aids and how the selected aid aligns with achieving those objectives.
Individual Needs and Learning Styles: Consideration should be given to materials that present information in various formats. Utilizing videos, images, and diverse media can make learning more engaging and cater to different learning styles.
Class Size: The size of the class affects the choice of teaching aid in terms of material size and visibility, ensuring that all students can adequately view and interact with it.
Cognitive Nature and Age of Learners: The age and cognitive development of the learners are crucial factors. Materials should be chosen that suit the learners’ attention spans, interests, and developmental stages.
Teacher’s Ability to Use the Material: The instructor should possess the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively use the teaching aid in the teaching and learning process.
Availability of the Aid: It’s essential to ensure that the chosen teaching aid is readily accessible to both the teacher and the students.
Amount of Advance Preparation Needed: Considering the time required for preparation is vital to prevent unnecessary delays and disruptions during lessons.
Characteristics of Good Teaching Aids
Effective teaching aids share several characteristics:
Alignment with Objectives: They should be directly related to the teaching objectives to support the intended learning outcomes.
Relevance to Learners: Teaching aids should be appropriate for the intellectual maturity and previous experiences of the learners.
Meaningful and Purposeful: They should serve a clear and meaningful purpose in the context of the lesson.
Motivating: Teaching aids should be interesting and relevant to students’ interests, thus motivating them to engage with the material.
Accessibility: Ideally, teaching aids should be improvised or made from locally available materials, ensuring easy access.
Simplicity: They should be simple and straightforward to avoid confusion or complexity.
Cost-Effective: Good teaching aids are cost-effective or affordable to ensure they can be used in a variety of educational settings.
Visibility: They should be large enough in size to be visible to the entire class, promoting engagement for all students.
Current and Up-to-Date: Teaching aids should reflect the most current subject matter, avoiding outdated or obsolete information.
Portability: They should be easily transported and set up, allowing for flexibility in their use across different teaching environments.
M-Maintenance(Time and Cost)
E- Expense
D- Distractions
I- Inadequate training.
A- Adaptation
S- Sensory
Advantages of Audiovisual Aids
Teaching aids play a very important role in the Teaching-Learning process. The importance of teaching aids is as follows:
Motivation: Teaching aids motivate the students so that they can learn better.
Clarification: Through teaching aids, the teacher clarifies the subject matter more easily.
Discouragement of Cramming: Teaching aids can facilitate the proper understanding of the students, discouraging the act of cramming.
Increase in Vocabulary: Teaching aids help to increase the vocabulary of the students more effectively.
Lively and Active Classroom: Teaching aids make the classroom lively and active, avoiding dullness.
Direct Experience: Teaching aids provide direct experience to the students.
Time and Energy Savings: They save time and energy for both teachers and students by simplifying complex issues within a short period of time.
Disadvantages of Audiovisual Aids (MEDIAS)
M-Maintenance: Audiovisual aids can require regular maintenance, which can be time-consuming. Projectors may need bulb replacements, and interactive whiteboards require software updates. Neglecting maintenance can lead to equipment malfunctions.
E- Expense: Audiovisual aids can be costly to acquire, limiting access for some schools or educators. High-quality projectors, sound systems, or interactive displays can come with a significant price tag, making them inaccessible to schools with limited budgets.
D-Distractions: Some audiovisual aids might be distracting if not used effectively, disrupting the learning process. Overusing animations or flashy graphics in presentations can divert students’ attention away from the content, causing distractions.
I- Inadequate Training: Teachers may need training to use audiovisual aids effectively, which can be challenging. Teachers may struggle to use such audiovisual equipments like computer or remote control.
A-Adaptation Issues: Audiovisual aids might not always be suitable for every topic or subject, requiring adjustments. While videos are great for demonstrating clinical teaching.
S- Sensory Limitations: Some audiovisual aids may not be usable by individuals with sensory limitations or impairments. Videos with or without audio descriptions may exclude students with hearing or visual impairments.

Chalkboard
The chalkboard is one of those aids that is usually present in the classroom. Some are portable and others are fixed. You can write on them during classroom sessions. It is possible to use different colors of chalk for writing a topic, new words, exercises, illustrations, brainstorming ideas, writing drafts, drawing pictures.
Guidelines for Using Chalkboards
Make sure everything needed for using the chalkboard should be kept ready before class begins.
Clean the board before starting class and leave it cleaned after the class. Blackboard should be kept clean so that writing on it could be easily read by the students from all parts of the room.
Divide the board into two or three parts by drawing vertical lines.
It should bear the date and the main topic of the day.
Diagrams and pictures can be sketched before the class on a flip chart.
Do not speak to the chalkboard. First talk to the class before writing on the board.
Do not crowd the chalkboard with too much matter.
Rub off the board periodically if you do not need the stuff.
Ensure that the handwriting is clear and readable.
Advantages of Chalkboard
No advanced preparation required.
The chalkboard is easy to use.
It is almost always available and is cheap.
It helps to focus the students on the lecture.
It is useful in building up maps, graphs, and diagrams.
It improves on writing skills of the person.
Information on the board is very useful for recapitulation (summarizing and restating main points).
Technology is not dependent on electricity.
Disadvantages of Chalkboard
It needs some skill to be able to use the chalkboard effectively.
Occasionally, the teacher has to turn his/her back to the students.
Time-consuming if you have a lot to write.
Handwriting may be difficult to read (legibility, size, glare, etc.).
Can’t go back to something you’ve erased.
Chalkboard – Advantages & Disadvantages (MEDIAS Framework)
M – Maintenance: Chalkboards are low-maintenance teaching aids, requiring minimal upkeep.
Advantage: Chalkboards are easy to clean, and chalk is readily available and inexpensive.
Disadvantage: Chalk dust can accumulate and cause allergies or respiratory issues for some individuals.
E – Expense: Chalkboards are cost-effective, making them accessible for many educational institutions.
Advantage: Chalk and chalkboards are affordable and have a long lifespan, reducing overall costs.
Disadvantage: Chalkboards lack the dynamic features of more modern aids, limiting their usability for interactive or multimedia lessons.
D – Distractions: Chalkboards are simple and less distracting, keeping the focus on the content.
Advantage: Chalkboards can help maintain a clear and focused learning environment without multimedia distractions.
Disadvantage: Chalkboards offer limited opportunities for engaging visuals, which may not suit all learning styles.
I – Inadequate Training: Teachers usually require minimal training to use chalkboards effectively.
Advantage: Chalkboards are user-friendly, and most educators are already familiar with using them.
Disadvantage: Lack of training may lead to issues like inconsistent handwriting or insufficient use of space.
A – Adaptation Issues: Chalkboards are versatile and suitable for various subjects.
Advantage: Chalkboards can adapt to different subjects, from math equations to language lessons.
Disadvantage: Complex diagrams, detailed illustrations, or color-coded content can be challenging to create effectively on chalkboards.
S – Sensory Limitations: Chalkboards primarily rely on visual and auditory senses.
Advantage: Chalkboards are accessible to most students with standard sensory abilities.
Disadvantage: Students with visual impairments or hearing impairments may face challenges with chalkboard content.
Flip Chart
The flip chart is made of paper of different quality which you can write on using marker pens of different colors, just like the chalkboard.
Advantages of Flip Chart
The flip chart is inexpensive.
It is easy to carry and the information does not have to be removed from the classroom; it can be referred to later.
It can be used to capture ideas during brainstorming, a lecture, or during revision.
It can have diagrams and whatever else the teacher needs to show.
The teacher can decide and prepare it in advance.
Disadvantages of Flip Chart
It needs skill to use effectively.
Most educators tend to use it as a scribbling surface (write on it carelessly) and fail to demonstrate its effective use.
M – Maintenance: Flip charts are relatively low-maintenance, offering convenience in the classroom.
Advantage: Flip charts require minimal upkeep and can be easily prepared for each lesson.
Disadvantage: The cost of flip chart paper or markers might add up over time.
E – Expense: Flip charts are cost-effective and readily available. They are budget-friendly teaching aids.
Advantage: Flip chart paper and markers are affordable, making them accessible to most educators.
Disadvantage: The cost of markers and paper can accumulate if used frequently.
D – Distractions: Flip charts are simple, with limited distractions, promoting a clear focus on content.
Advantage: Flip charts can help maintain a straightforward learning environment without multimedia interruptions.
Disadvantage: They may lack the versatility to engage visually for more complex topics.
I – Inadequate Training: Teachers typically require minimal training to effectively use flip charts.
Advantage: Flip charts are easy to use, and many educators are already familiar with them.
Disadvantage: The quality of presentations may vary based on the teacher’s drawing and writing abilities.
A – Adaptation Issues: Flip charts can be versatile and adapted to various subjects and teaching styles.
Advantage: Flip charts are suitable for a wide range of subjects and can be customized as needed.
Disadvantage: Creating complex diagrams or illustrations can be time-consuming and may not be as effective as multimedia tools.
S – Sensory Limitations: Flip charts primarily rely on visual and auditory senses.
Advantage: Flip charts are accessible to most students with standard sensory abilities.
Disadvantage: Students with visual or hearing impairments may face challenges with flip chart content.
Charts and Models
These are already made visual aids usually used to display factual data in different forms.
Charts and Models – Advantages & Disadvantages (MEDIAS Framework)
M – Maintenance: Charts and models are relatively low-maintenance, offering convenience in the classroom.
Advantage: Charts and models require minimal upkeep and can be easily reused for multiple lessons.
Disadvantage: The need for occasional revision to keep information up to date.
E – Expense: Charts and models are cost-effective and visually engaging. They offer a budget-friendly way to convey information.
Advantage: These teaching aids are affordable, and their visual appeal can enhance understanding.
Disadvantage: Initial creation or purchase costs may be involved.
D – Distractions: Charts and models simplify complex data and help students focus on essential information.
Advantage: They reduce cognitive load by presenting data in an organized, easy-to-understand format.
Disadvantage: Overly intricate charts or models may overwhelm students.
I – Inadequate Training: Teachers usually require minimal training to effectively use charts and models.
Advantage: They are user-friendly and suitable for educators with varying levels of expertise.
Disadvantage: The quality of presentation may depend on the teacher’s ability to explain the data.
A – Adaptation Issues: Charts and models are versatile and can be adapted to various subjects and teaching styles.
Advantage: They are suitable for a wide range of subjects and can be customized as needed.
Disadvantage: Creating complex charts or models might be time-consuming and may not effectively convey certain concepts.
S – Sensory Limitations: Charts and models primarily rely on visual and sometimes tactile senses.
Advantage: They are accessible to most students with standard sensory abilities.
Disadvantage: Students with visual or tactile impairments may face challenges with charts and models.

Handouts
Handouts are well-planned documents prepared by the teacher for his/her students in order to promote their participation in the teaching-learning process. They ensure every student has access to the same information and can review that information whenever necessary.
Advantages of Using Handouts
Keeps you and students focused.
Useful as study aids.
Good for absent students.
Can cover previous material.
Can include review or supplementary/look-ahead material.
Ensures consistency.
Reusable.
Disadvantages
Might be considered a study-aid crutch where the teacher puts emphasis on reading the content instead of explaining.
Some handouts are not up-to-date or may have brief contents.

Projector
A projector is an electrical device that enlarges words or diagrams on a screen or clear wall. It’s a very popular and versatile visual aid that has been made available to the modern-day lecturer.
Advantages
The machine is portable.
Little technical attention is required if it is looked after well.
It can be used without darkening the room.
It allows for a lot of creativity because the teacher can create overlays and other varieties of presentations.
The transparency paper is easy to prepare.
During use, the teacher does not turn his/her back to the learners.
The teacher can prepare in advance.
There is no need to rely on printed textbooks.
Using a projector can save time used to write on a blackboard.
Disadvantages
The transparency paper can be expensive.
It can only be used where there is electricity.
You need to pay attention to the focus so that the learners see clearly. Position it so that all students can see.
Use a pointer rather than fingers (This point is more of a guideline or tip within the disadvantages section in the source, but I will include it as requested by extracting the provided text).

Computers
Computers are being used in teaching because they have the advantages of speed, accuracy in transmitting information; they are convenient and store large amounts of information. Once prepared, the teacher does not need to be there. Students can learn at their own pace.
Advantages of Using Computers:
Accurate Information: Computers provide accurate information.
Convenience and Storage: They are convenient and store lots of data.
Self-Paced Learning: Students can learn at their own pace once prepared.
Peer Learning: Encourages peer learning through study groups.
Visual Learning: Visual illustrations on computers make lessons easier to understand.
Personalized Learning: Each student having a computer personalizes their learning.
Less Textbooks: Reduces the need for carrying many textbooks.
Disadvantages of Using Computers:
Lack of Guidance for Psychomotor Skills: Computers don’t adequately guide psychomotor skills.
Distraction: Computers can be distracting when used for personal reasons during class.
Writing Skills: They can’t teach students how to write essays or sentences correctly.
Costly: Computers are expensive, limiting access for some schools and students.
Power Consumption: They consume power.
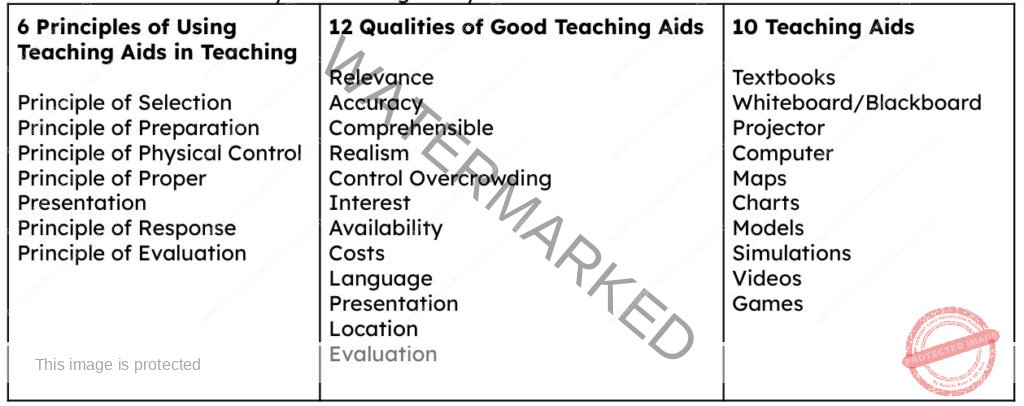
A. Outlineany6principlesofusingteachingaidsinteaching
B. Outlineany12qualitiesofgoodteachingaids
C. Outlineany10teachingaidsyouknow.
Principles in the use of teaching aids
Teaching aids prove effective only when they suit the teaching objectives and unique characteristics of the special group learners. Following points may be kept in view in this regard:
Principle of selection:
They should suit the age-level, grade-level and other characteristics of the learners.
They should have specific educational value besides being interesting and motivating.
They should be the true representative of the real things.
They should help in the realization of desired learning objectives.
Principle of preparation: This principle requires that following points should be attended to:
As far as possible, locally available material should be used in the preparation of an aid.
The teachers should receive training in the preparation of aids.
The teachers themselves should prepare some of the aids.
Principle of physical control: This principle relates to the arrangement of keeping aids safely and also to facilitate their lending to the teachers for use.
Principle of proper presentation: This principle implies the following points: Teachers should carefully visualize the use of teaching aids before their actual presentation.
They should fully acquaint themselves with the use and manipulation of the aids to be shown in the classroom.
Adequate care should be taken to handle an aid in such a way as no damage is done to it.
The aid should be displayed properly so that all the students are able to see it, observe it and derive maximum benefit out of it.
As far as possible, distraction of all kinds should be eliminated so that full attention may be paid to the aid.
Principle of response: This principle demands that the teachers guide the students to respond actively to the audio-visual aids stimuli so that they derive the maximum benefit in learning.
Principle of evaluation: This principle stipulates that there should be continuous evaluation of both the audio-visual material and accompanying techniques in the light of the realization of the desired objectives.
Qualities of good teaching aids
Relevance: The aid should be relevant and directly related to the subject matter.
Accuracy: The representation of the aid should be accurately related to the content and the aid should never give incorrect concepts. They should be up-to-date.
Comprehensible: The concepts produced in the aid should be according to the mental level of the students. When it is too simple or difficult it loses interest among students.
Realism: The virtue of the aid increases as it becomes more realistic. A different concept and difficult ones can be well explained with the aid which is more realistic.
Control overcrowding: Too many aids may confuse the students.
Interest: The arousal of interest makes learning charming and absence of interest, repulsive and detestable. It is the most elusive factor in learning.
Availability: Aids should be available when required; therefore it has to be easily portable.
Costs: Aids should be less expensive.
Language: Language of aids should be simple, clear and easy to follow.
Presentation: Teachers should be well prepared to present the aids and use them as well.
Location: Aids should be placed in manner it is visible to all students.
Evaluation: Aids should be evaluated at regular intervals in order to know their effects.
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co

