Specialized Nursing Care Procedure
Subtopic:
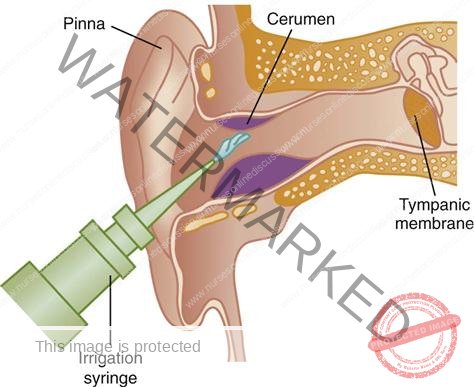
Ear irrigation
Learning Objectives
Define ear irrigation and distinguish it from related procedures like syringing and lavage.
Identify the purposes and indications for ear irrigation, including wax and foreign body removal.
Recognize contraindications to ear irrigation to avoid harm or complications.
List the equipment required and describe its proper use in a clinical setting.
Demonstrate step-by-step ear irrigation procedure using correct technique and patient positioning.
Document post-procedure observations and reassess the patient for any adverse effects.
Definition
- Ear irrigation is a procedure that involves gently flushing the external ear canal with a stream of warm, sterile water or saline solution. The purpose is to remove accumulated earwax (cerumen), foreign objects, or debris.
- Ear syringing or ear lavage are terms sometimes used for similar procedures, but they may involve a larger volume of water or a more forceful stream delivered with a syringe.
Aims/Purposes of Ear Irrigation
Remove Earwax: The most common reason for ear irrigation is to remove impacted or excessive earwax that may be causing hearing loss, discomfort, or other symptoms.
Remove Foreign Objects: To dislodge and remove small foreign objects from the ear canal.
Cleanse the Ear Canal: To remove dirt, debris, or other substances from the ear canal.
Indications for Ear Irrigation
Impacted Earwax: To soften and remove hardened earwax.
Foreign Body Removal: To dislodge certain foreign bodies (excluding objects that swell with water, such as organic matter, or tightly wedged objects).
Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear): To cleanse the ear canal and remove debris associated with this outer ear infection.
Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion (Glue Ear): To cleanse the ear canal in cases of purulent discharge.
Pre-Surgical Preparation: To clean the ear canal before certain ear surgeries.
Hearing Test Preparation: To remove debris that could interfere with hearing test accuracy.
Ear Mold Impression Removal: To help remove a mold impression after it’s been taken.
Ear Pressure Relief: To relieve pressure related to altitude changes.
Localized Inflammation and Discomfort: To soothe inflammation and discomfort in the ear canal.
Antiseptic Application: To deliver antiseptic solutions to the ear canal.
Therapeutic Heat or Cold: To apply warm or cold water for therapeutic purposes.
Vestibular Function Testing: To aid in assessing the inner ear’s balance system (e.g., during a bi-thermal caloric test).
Contraindications for Ear Irrigation
Perforated Eardrum: A hole in the eardrum is a strict contraindication, as fluid could enter the middle ear and cause infection or further damage.
Active Ear Infection: Irrigation may worsen pain, inflammation, and potentially spread the infection in cases of acute or severe ear infections.
Recent Ear Surgery: Irrigation could disrupt the healing process after ear surgery.
History of Ear Surgery: Certain ear surgeries, like the placement of ventilation tubes, may make irrigation unsafe.
Severe Pain or Discomfort: If the procedure causes significant pain, it should be stopped immediately.
Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, weakened immune systems, or certain skin conditions may increase the risk of complications.
Presence of Grommets: Irrigation is contraindicated if the patient has grommets in place.
Unable to follow instructions Irrigation should not be done if the patient is uncooperative or unable to follow instructions.
Prescribed Solutions
Boric acid 2-4% solution
Sodium bicarbonate solution 1%
Normal saline
Hydrogen peroxide 2%
Sterile water
Warmed to body temperature.
Equipment
Tray: To hold the necessary supplies.
Ear Syringe in a Receiver: (Or another appropriate irrigation device).
Auroscope: To examine the ear canal.
Basin and Vomitus Bowl: For collecting the irrigation fluid.
Receiver: For collecting used supplies.
Clean Gloves
Waterproof Cape: To protect the patient’s clothing.
Patient’s Towel
Cotton Swabs
Prescribed Solution (as listed above)
Bowl of Warm Water: To warm the solution to body temperature.
Adjustable Light and Screen: For adequate visualization and patient privacy.
Plastic Apron
Handwashing Equipment
Procedure for Ear Irrigation
Step | Action | Rationale |
| 1. | Adhere to standard nursing procedure guidelines. | |
| 2. | Use an otoscope with adequate illumination to examine the ear canal. | |
| 3. | Position the patient sitting upright, head tilted gently towards the affected side. Drape a mackintosh and towel across the shoulder and upper arm beneath the affected ear. Position the curved component of the receiver beneath the tilted ear. | |
| 4. | Instruct the patient to hold the receiver in place under their ear. | |
| 5. | Using solution-dampened cotton swabs, cleanse the auricle and the auditory meatus. | |
| 6. | Load the bulb syringe with the irrigation fluid. If utilizing an irrigation container, ensure air is expelled from the tubing. | Air forced into the ear canal is noisy and therefore unpleasant for the patient. |
| 7. | Correctly position the ear canal by pulling the auricle downwards and posteriorly for children, and upwards and posteriorly for adults. | To ensure the ear canal is straightened, facilitating the irrigating solution to reach the full length of the canal. |
| 8. | Carefully introduce the syringe tip and direct a slow, consistent stream of solution towards the superior aspect of the ear canal, applying enough pressure to dislodge secretions. | Gentle technique minimizes risk of tympanic membrane damage. Continuous inflow and outflow of the irrigating solution prevents pressure build-up. |
| 9. | Continuously monitor the patient during the irrigation process. | To promptly identify and address any potential complications. |
| 10. | Upon completion of irrigation, loosely insert a cotton ball into the ear canal opening and instruct the patient to lie on their affected side on a towel or absorbent pad. | The cotton ball absorbs excess fluid, and gravity facilitates drainage of residual fluid from the ear canal. |
| 11. | Pat dry the patient’s auricle and remove the towel and mackintosh. | |
| 12. | Perform hand hygiene. | |
| 13. | Record the procedure details, the characteristics of any discharge, and the patient’s reaction. | |
| 14. | Tidy up the procedure area. | |
| 15. | Properly decontaminate all instruments and materials used during the procedure. | |
| 16. | Re-assess the patient in 10-15 minutes, remove the cotton ball, and evaluate their condition. | To check for pain, which could suggest tympanic membrane injury. |
Join Our WhatsApp Groups!
Are you a nursing or midwifery student looking for a space to connect, ask questions, share notes, and learn from peers?
Join our WhatsApp discussion groups today!
Join NowRelated Topics
- Apply Nursing process to the management of patients
- Administer prescribed medicine appropriately
- Instilling medication (general)
- Blood transfusion
- Perform Shortening and removal of drains
- Perform Colostomy Care
- Prepare Abdominis Paracentesis (Abdominal Tapping)
- Prepare Lumbar Puncture
- Perform Gastrostomy Feeding
- Carry out gastric Lavage
- Perform Tracheostomy Care
- Ophthalmological Care
- Care of the patient`s ears
- Pre-Operative Eye Care
- Ear Care
- Peri-Operative Care:
- Orthopedic Nursing Care
- Prepare for Neurological Assessment
We are a supportive platform dedicated to empowering student nurses and midwives through quality educational resources, career guidance, and a vibrant community. Join us to connect, learn, and grow in your healthcare journey
Quick Links
Our Courses
Legal / Policies
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved | Design & Developed by Opensigma

