Health Service Management
Delegation
Table of Contents

Delegating authority and responsibility
- To delegate is to give another person some of one’s authority or in other words, to give another person the power to make decisions. Authorities and responsibility may go together but are not the same people use authority to get work done for which they are responsible.
- Delegation is the use of personnel to accomplish a desired objective through allocation of authority and responsibility.
- Delegation is not merely distributing care. It is a path to and a significant success factor for professional practice.
- Delegation is a link that joins organizational concepts with the management process; it is that which allows a manager to manage. In the past, effective delegation has not been an activity emphasized in nursing. As a result many nurses do not value this skill. Educational programme has emphasized primary nursing as the dominant method of delivering nursing care which focuses on the skill of individual nurse.
- As a nurse manager it is essential to know about the principles, purpose, steps, and concepts of delegation. It is also necessary to know about the barriers of delegation and the effective measures to overcome those barriers.
Definition
- Delegation: Delegation is transferring to a competent individual the authority to perform a selected nursing task in a selected situation. (The National Council of State Boards in Nursing, 1995)
- Delegator: The delegator possesses the authority to delegate by virtue of both positions in the agency
- Delegate: The delegate receives direction for what to do from the
The concept of delegation
The supervisor passes down to the subordinates a share of his/her own responsibility together with the necessary authority to discharge the tasks delegated.
- But the supervisor retains the ultimate The subordinate has immediate responsibility
- Hence the superior has the right to retract or withdraw the authority delegated
- Because of the ultimate responsibility concept, the superior has the duty to supervise the performance of the delegated authority.
- Hence delegation does not mean abdication
Purposes of delegation
- When work is spread over a large area, as in rural health work, the health workers on the spot must be able to make decisions according to circumstances
- Delegation of responsibility saves delays that occur when awaiting decisions from a central office or other distant authority.
- Health workers who are allowed to make decisions enjoy their work more and become more knowledgeable and skillful
- To achieve organizational goal
- Time and cost savings
- Professional growth of employees and it mears imparting training to
- Professional growth of the manager and decrease the burden of tasks
- Helps the chief executive to devote more time in decision making, policy formulation and planning
- Makes the organization to act efficiently and economically and bring flexibility in it
- Helps in creation of managerial class and develops a sense of responsibility in subordinate
- Delegation avoid delay and helps in succession
- To save time for other duties
- To train the subordinate
- Motivate staff
- Prepare future managers
- Allow yourself as a manager to learn from the subordinates
- Allow a person on the sport to make decisions
- Avoid resistance to change
Benefits of delegation
- Delegation can improve quality of work by allowing the employees who have direct knowledge of products and services to make decisions and complete tasks.
- Employees/delegates have more time to do their own jobs when they assign tasks to
- Saves time for the accomplishment of a task since the sub tasks have been delegated to other employees hence work is done in shortest time possible.
- Development; when you delegate you will teach your team members new skills and give them the opportunity to develop themselves and achieve their goals.
- Raises employees’ self-esteem whereby when you give a teammate a task, it shows that you have trust and confidence in them. Having interesting and challenging work feels good, and being trusted to complete the job raises self-esteem.
- Builds teamwork: Delegating new tasks to team members allows them to build contacts with others whom they do not normally work. This can lead to greater teamwork and communication networking.
- Provides continuity of work: When a manager is on leave the work is taken by subordinates and provides continuity in functions.
Disadvantages
- If wrong decisions are made, the work may not be done or it may be done less
- A leader may delegate all the work, leaving very little to do
- A leader may delegate decisions to people with insufficient
- Burden on Employees: Giving an employee too many tasks to complete. If you place too much of a burden on your employee’s shoulders, that employee may stop viewing himself as a trusted employee and start viewing himself as an abused employee.
- Poor quality of the work done: If work is delegated to wrong/unskilled personnel may yield poor results.
- Failures result in destroying worker
Principles of effective delegation
The dos and don’ts of delegation
- Clarify what you delegate
- Select the person you trust and have confidence in
- Inform all other stake holders of your delegate
- Do not interfere unnecessarily
- Be prepared for mistakes
- Give the needed authority, resources and support
- You can only delegate those tasks which according to the law you can delegate
- A president cannot delegate his role as a commander-in-chief
- A delegate cannot also delegate
Rules of delegating authority and responsibility
- Be clear about what is delegated
- Select the person who you are sure can do the work
- Explain to others that you have delegated work and to
- Do not interfere unless asked to and be prepared for
- Give support as needed and follow-up the progress of
Three foundations for delegation
Delegation depends on a balance of responsibility, accountability and authority
- Authority: is the power and right of a person to use and allocate the resources efficiently, to take decisions and to give orders so as to achieve the organizational objectives.
- Responsibility: is the duty of the person to complete the task assigned to A person who is given the responsibility should ensure that he accomplishes the tasks assigned to him.
- Accountability: means giving explanations for any variance in the actual performance from the expectations set. Accountability cannot be delegated.
Differences between Authority and Responsibility

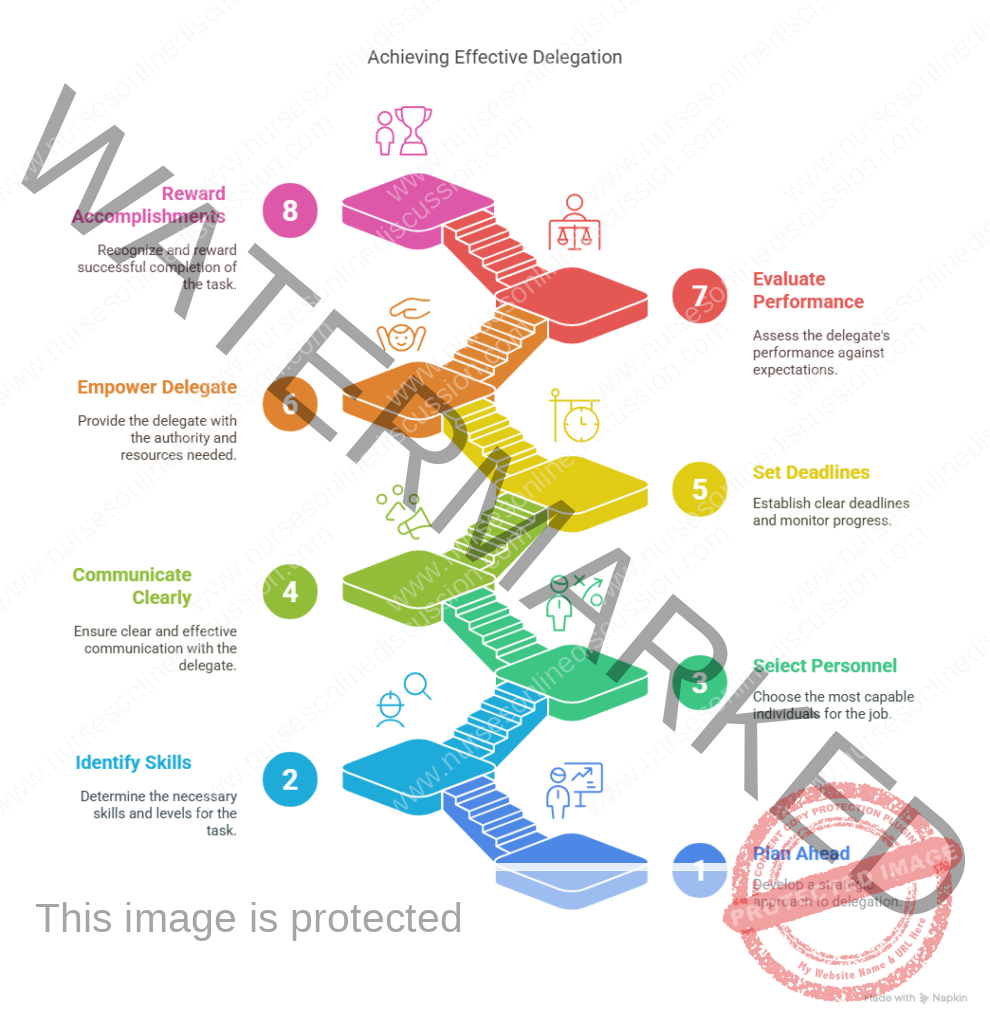
Steps in delegation
- Plan ahead
- Identify needed skills and levels
- Select most capable personnel
- Communicate clearly
- Set deadlines and monitor the progress
- Empower the delegate
- Evaluate the job performance
- Reward accomplishments
Determine what you will delegate. Effective delegation begins with defining your responsibilities. Write down all of your activities and responsibilities. Review your master list and categorize all of the items into two secondary lists: things you alone must do and things that others could do or help you complete. Anything that falls into the second list presents an opportunity for delegation.
Choose the right/capable person to delegate the task to. Andrew Carnegie said, “The secret to success lies not in doing your own work, but in recognizing the right person to do it.” The key to finding the right person to delegate an assignment to is matching skills and attitude to the task at hand.
Clarify the desired results. When the results are clear, it allows the employee to use his or her own creativity and resources to accomplish the task. An added benefit of effective delegation is the individual may find a better and more effective way to accomplish the task or achieve the desired results.
Clearly define the employee’s responsibility and authority as it relates to the delegated task. Clearly communicate the expectation, responsibilities, and timeline (and set deadlines). Be sure to ask the employee to share his or her understanding.
Establish a follow up meeting or touch points. The follow up meetings should be focused on two things-monitoring progress and determining the need for assistance. The number of follow up meetings will vary based on the scope of the task or project and whether the employee is new or a long term member of the department.
Reward accomplishments: appreciation of successful accomplishments.
Kinds of delegations
- Full delegation
- Partial delegation
- Conditional delegation
- Formal delegation
- Informal delegation
Errors in delegation
- Under delegation: The manager may become over worked and overwhelmed. This frequently comes from his/her assumption that delegation may be interpreted as the lack of ability on his/her part to do a correct or complete job. Another frequent cause for under delegating is the manager desire to ‘do the whole job by myself’ because of the belief that he/she needs experience or the belief that he/she can do it better and faster than anyone
- Over delegation: Some managers over delegate as they are poor monitors of time and spend most of their time just trying to get organized. Others over delegate because they feel insecure in their ability to perform a task
- Improper delegation: It includes delegating at the wrong time, wrong person for a wrong reason. It may include assigning the task and responsibility that are beyond the capability of the person
- Upward delegation: When the manager delegated a task to a subordinate, the subordinate makes use of the manager to complete the task
CONSTRAINTS TO EFFECTIVE DELEGATION
- Lack of confidence in the
- Reluctance of the supervisor to delegate since he/she feels can accomplish the
- Feeling of insecurity that is the subordinate may subsequently take over her
- Lack of communication skills to make the delegate understand her/his role/responsibilities.
- The delegate may lack technical skills required to accomplish the
- Lack of willingness by the staff/subordinate to take up the
- Prestige and power consciousness by the manager
- Confidential nature of task
- Legal impediments associated with the way the task is done/accomplished.
Factors that affect delegation
- Size of organization: usually small organizations have limited role/activities to accomplish therefore delegation is minimal yet in bigger organizations delegations is very necessary.
- Importance of the duty or decision: important sensitive organizational decisions need the involvement and control by the top manager while less sensitive/important tasks can
- Task complexity: some tasks are better performed by the managers because of their expertise and thus cannot be delegated since the subordinates may lack enough expertise to accomplish them. Whereas others may be performed by any employee of the organization.
- Organizational culture: these are the norms, expectations and values of the organization whereby some organizations always prefer the manager to be the final decision maker in all organizational activities hence do not opt/support delegation which is opposite in other
- Qualities of subordinates: before delegating roles to subordinates consideration of their abilities, strengths and weaknesses should always be put at the back of the mind.
Obstacles in delegation
- Fear of being disliked
- Inability to give up any control of the situation
- Inability to prioritize using Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
- Lack of confidence to move beyond their level
- Tendency to isolate oneself and choosing to complete all tasks alone
- Lack of confidence to delegate to staff who were previously one’s peers
- Ineffective to communicate effectively and develop working relationships with other team
- Thinking of oneself as the only one who can complete the task
- Lack of knowledge about staff’s capability
Barriers of delegation in different level
Organizational level
- Lack of established methods and procedures
- Lack of means of coordination and communication
- Unstable and changing nature of work
- Size and location of an organization Managerial level
- Superiors are afraid that others will not make proper decisions or carry them in a desired manner
- Fear that disloyal centers will develop among strong subordinate
- In public administration political consideration often make delegation difficult
- At time who desire to delegate do not know how to do it
- “I can do it better myself” fallacy
- Lack of ability to direct
- Lack of confident in staff
- Absence of control that warn of impending difficulties
- Aversion of taking risk Subordinate level
- Easier to ask the boss
- Fear of criticism
- Lack of necessary information and resources
- Lack of self confident
- May have more work than the employee can do
- Positive incentive may be inadequate
- More work than once capacity to work
- Lack of resources and information to do a good job
Symptoms of poor delegation
- Long queue before boss room
- Boss is always busy
- Boss taking suitcase to home at evening
- Subordinate unhappy
- Disorganized resource
- Always delay in work
Five rights for delegation
- Right person
- Right task
- Right circumstances
- Right communication
- Right supervision
Development of delegation process in patient care
- Know the patient
- Know the staff member
- Know the task delegated
- Explain the task and expected outcome
- Expect responsible action from the delegates
- Assess and supervise job performance
- Evaluate and follow
Delegation skills
- Create an environment of trust and co operation
- Create environment of teaching and learning
- Promote client satisfaction
- Communicate effectively
- Provide feedback and follow-up evaluation
Guidelines to effective delegation
- Defining the task clearly
- Outlining the scope of the task
- Assigning a deadline for follow up and task
- Clear unity of command; each person in an organization should report to one
- Trust the delegate in terms of honest and confidence
- The duration of the delegated task should be specified to the delegatee
- Explain to others that you have already delegated the work and to whom
- Do not interfere unless asked to and be prepared for some mistakes
- Members of the organization should know the proper flow of authority and chain of command
Join Our WhatsApp Groups!
Are you a nursing or midwifery student looking for a space to connect, ask questions, share notes, and learn from peers?
Join our WhatsApp discussion groups today!
Join NowGet in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co

