Microbiology
Subtopic:
Normal floras
Normal floras are organisms that inhibit the body of health person without causing diseases under normal circumstances. Majority of them are bacteria or yeasts. Viruses, protozoa and worms are not considered to be among the normal floras.
Types of Normal Floras
Resident flora: are microorganisms commonly found in a particular area of the body at a given age
Transient flora: are microorganisms that are present at a given time and disappear or die off within hours, days, weeks or months
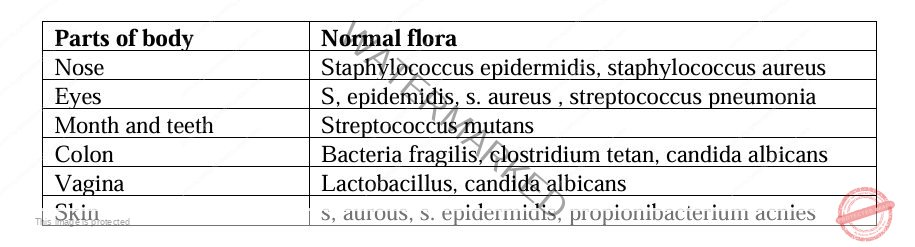
Distribution of Normal Flora
Importance of Normal Flora
Prevent colonization by pathogens as they occupy space which would have been occupied by pathogens and also compete for nutrients.
They stimulate antibody mediated immune response that may cross react with future pathogens thus preventing diseases.
Lactobacilli a normal flora in the vagina produce acid which maintains acidic ph thus preventing growth of micro organisms like over growth of Candida albicans.
Normal floras in gut secrets vit k and B12 enteric bacteria and other vit b by lactic acid bacteria by e into food which help in food supplementation and others produce antimicrobial substances which kill or inhibit pathogen growth eg intestinal bacterias produce avariety of substances ranging from relatively non specific fatty acids and peroxides to highly specific bacteriocins which inhibit or kill other bacteria.
Disadvantages of Normal Floras
In case of immune suppression can act as opportunistic pathogens
May be a source of infection to other persons
They may share nutrients with pathogens leaving the host with nothing hence leading to infections
Mechanisms that can Disrupt Normal Floras
Suppression of the normal flora by antibiotics allowing overgrowth of resistant species
Changes in the general health of the person such as immunity suppression
Local trauma such as skin breakage due to accident or surgery
Introduction to a new site e.g. migration of E. coli from anus to vagina leads to urinary tract infections
Hormonal changes especially during pregnancy and menstruation
Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiosis: is a close interaction between two organisms of different species that is to say host and symbiot living together. Host is usually the larger organism and symbiot is the small one in the relationship. Symbiotic relationships may be classified as below:
Mutualism: an association in which both organisms benefit from the relationship eg E.coli in the colon produces vit k for the host while the host provides nutrients and shelter to it
Commensalism: association in which one organism benefits and the other is left an affected eg most of the normal floras
Parasitism: an association in which one organism benefits and the other is harmed eg the worms in our bodies
Related Topics
- Concepts of Microbiology
- Classification and Types of Microorganisms
- Pathogenic Microorganisms
- Normal Flora
- Characteristics and Mode of Spread of Disease-Causing Microorganisms
- Pathological Effects of Microorganisms
- Simple Laboratory Tests
- Infection Prevention and Control
- Introduction to Immunity
- Antibodies
- Principles of Immunization
We are a supportive platform dedicated to empowering student nurses and midwives through quality educational resources, career guidance, and a vibrant community. Join us to connect, learn, and grow in your healthcare journey
Quick Links
Our Courses
Legal / Policies
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved | Design & Developed by Opensigma

