Introduction to Midwifery
Normal Pregnancy
Table of Contents

Learning Objectives
Define the criteria and timeline for a normal pregnancy, including gestational age classifications.
Identify and differentiate the three categories of pregnancy signs: presumptive, probable, and positive.
Describe physiological and anatomical changes associated with early pregnancy symptoms.
Recognize diagnostic signs used in clinical confirmation of pregnancy, including Hegar’s, Jacquemier’s, and Osiander’s signs.
Interpret definitive indicators of pregnancy such as fetal heart sounds, ultrasound findings, and actual delivery.
Distinguish pregnancy from similar conditions through differential diagnosis of abdominal enlargement.
Normal Pregnancy
refers to the growth and development of a fertilized ovum, beginning from fertilization until the fetus is expelled from the uterus. Normally, the fetus is expelled at term, which is around 9 months, 40 weeks, or 280 days.
If the fetus is expelled before 28 weeks, it is called an abortion.
If the fetus is expelled after 28 weeks but before 37 weeks, it is called premature labor.
If the fetus is born after 42 weeks, it is termed post-mature.
Criteria for a Normal Pregnancy:
The fertilized ovum is growing in the uterine cavity.
One fetus is forming, with one placenta and two membranes.
There is approximately 1000-1500ml of amniotic fluid.
The fetus has a vertex presentation (head-down).
There is no bleeding until the “show” in the first stage of labor.
The mother remains healthy with no serious pregnancy disorders.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF PREGNANCY
When a woman misses one or two menstrual periods, she may suspect she is pregnant. This is often accurate, especially if she has been experiencing regular menstruation.
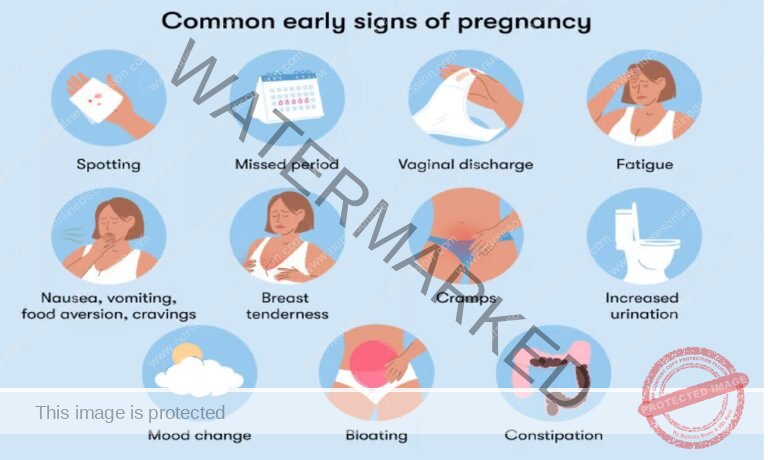
The signs of pregnancy are classified into three groups:
Presumptive
Probable
Positive
Presumptive Signs:
These are signs that suggest pregnancy but are not definitive.
Amenorrhea: Absence of menstruation. While a strong indicator, it can also be caused by factors like contraception, environmental changes, illness, or emotional disturbances.
Breast Changes: Many women experience tingling, prickling, enlargement, and tenderness of the breasts.
Morning Sickness (Nausea and Vomiting): Occurs in 30-50% of pregnant women, typically between weeks 4 and 14. Often subsides by the end of the first trimester.
Increased Frequency of Urination: The growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder, especially before 12 weeks. This symptom tends to decrease once the uterus rises out of the pelvis.
Skin Changes:
Striae Gravidarum: Stretch marks appearing around the 16th week on the abdomen, thighs, and breasts.
Chloasma (Mask of Pregnancy): Darkened patches of skin on the face.
Linea Nigra: A darkened line appearing above and below the umbilicus.
Darkening of Areolas: Primary areolas darken, and secondary areolas may form. These changes are caused by melanin hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland.
Quickening: The first fetal movements felt by the mother, usually around 18-20 weeks for first-time pregnancies (primigravida) and 16-18 weeks for women who have been pregnant before (multigravida).
Fatigue: Common due to increased blood production, lower blood sugar, decreased blood pressure (influenced by progesterone), sleep disturbances, and nausea.
Mood Changes: Physical stress, metabolic changes, fatigue, and hormonal fluctuations (progesterone and estrogen) can lead to mood swings.
Probable Signs:
These signs are more indicative of pregnancy but still not conclusive.
Hegar’s Sign: Detectable between weeks 6 and 12. A softening of the isthmus (lower uterine segment) is felt during a bimanual examination (one hand on the abdomen, two fingers in the vagina).
Jacquemier’s Sign: Bluish discoloration of the vaginal walls, noticeable from the 8th week onwards, due to pelvic congestion.
Osiander’s Sign: Increased pulsation felt on the lateral vaginal fornices from the 8th week onwards, due to increased vascularity.
Softening of the Cervix (Goodell’s Sign): The cervix softens from the 8th week onwards, feeling like the lower lip compared to the tip of the nose in a non-pregnant state.
Uterine Soufflé: A soft blowing sound heard on abdominal auscultation from the 16th week, due to increased uterine vascularity.
Abdominal Enlargement: Rapid and progressive uterine enlargement from the 16th week, distinguishable from other causes like gas, a full bladder, fibroids, or ascites.
Braxton Hicks Contractions: Painless contractions beginning from the 16th week, felt during abdominal palpation, occurring approximately every 15 minutes.
Internal Ballottement: A sharp tap on the uterus above the cervix causes the fetus to float upward and then sink back down, felt by fingers in the vagina between weeks 16 and 28.
Presence of hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): Detectable in blood as early as 9 days after conception and in urine around 14 days after conception. Also present in conditions like hydatidiform mole.
Positive Signs:
These signs definitively confirm pregnancy.
Fetal Heart Sounds: The fetal heart begins beating around the 24th week after conception. It can be heard with a Doppler device as early as 10 weeks and with a fetoscope by 24 weeks. The normal fetal heart rate is 120-160 beats per minute.
Ultrasound Scanning of the Fetus: The gestation sac can be visualized as early as the 4th week, an embryo by the 4th week, and fetal body parts by the 10th week.
Palpation of the Entire Fetus: A trained examiner can feel the head, back, and upper and lower body parts.
Palpation of Fetal Movement: Skilled healthcare providers can feel fetal movements after the 24th week.
X-ray: Identifies the complete fetal skeleton as early as the 12th week, but not recommended due to radiation risks to the fetus.
Actual Delivery of the Baby: The conclusive evidence of pregnancy.
Differential Diagnosis
Abdominal enlargement can be caused by conditions other than pregnancy. These include:
Ovarian Cysts: Cause swelling distinguishable from the uterus, and pregnancy tests will be negative.
Fibroids: Noncancerous uterine growths that can cause a hard mass, but pregnancy tests will be negative.
Distended Urinary Bladder: Due to urine retention, relieved by catheterization, with no other pregnancy signs.
Pseudocyesis (False Pregnancy): Mimics pregnancy symptoms, including amenorrhea, but pregnancy signs are absent, and tests are negative. Often occurs in women with a strong desire to conceive or high anxiety related to pregnancy.
Multiple Choice Questions:
Which of the following is a presumptive sign of pregnancy?
a) Fetal heart sounds
b) Softening of the cervix
c) Palpation of fetal movement
d) Morning sickness
Hagar’s sign is detected by:
a) Auscultation of fetal heart sounds
b) Palpation of fetal movement
c) Vaginal examination
d) Ultrasound scanning
Which sign is a probable sign of pregnancy?
a) Fetal heart sounds
b) Ovarian cysts
c) Presence of HCG
d) Pseudocyesis
What is the normal fetal heart rate?
a) 60-80 beats per minute
b) 90-120 beats per minute
c) 120-160 beats per minute
d) 180-200 beats per minute
Which sign can help in determining the gestational age if the mother is unsure of her dates?
a) Quickening
b) Internal ballottement
c) Jacquemier’s sign
d) Amenorrhea
Which diagnostic tool can visualize the gestation sac and fetal parts?
a) X-ray
b) Ultrasound scanning
c) Fetal palpation
d) HCG test
What is the most accurate method to confirm pregnancy?
a) Palpation of fetal movement
b) X-ray
c) Actual delivery of the baby
d) Ultrasonography
Which condition can cause abdominal enlargement and yield negative pregnancy test results?
b) Ovarian cysts
a) Fibroids
c) Pseudocyesis
d) Morning sickness
Osiander’s sign is characterized by:
a) Softening of the cervix
b) Increased pulsation in the vaginal fornices
c) Bluish discoloration of the vaginal walls
d) Enlargement of the breasts
Which sign can be detected by both Doppler and fetoscope?
a) Fetal heart sounds
b) Uterine soufflé
c) Internal ballottement
d) Quickening
What differentiates fibroids from pregnancy?
a) Positive pregnancy test results
b) Palpable fetal movements
c) Presence of uterine soufflé
d) Hard mass felt on palpation (and negative pregnancy test)
What is the purpose of X-ray in pregnancy?
a) To visualize the fetal heart rate
b) To determine the gestational age
c) To confirm pregnancy definitively
d) It is not recommended due to radiation risks
What differentiates pseudocyesis from a true pregnancy?
a) Amenorrhea
b) Fetal heart sounds
c) Palpation of fetal movement
d) Negative pregnancy test results (and absence of positive signs)
What is the primary cause of morning sickness during pregnancy?
a) Increased blood production
b) Hormonal changes
c) Bladder pressure
d) Emotional upsets
Which sign is considered a positive sign of pregnancy?
a) Morning sickness
b) Softening of the cervix
c) Distended urinary bladder
d) Palpation of fetal movement (by a skilled examiner)
fill the blanks
- ____________ is the absence of menstruation and a presumptive sign of pregnancy.
- _____________ can be detected by performing a vaginal examination and palpating the isthmus.
- Increased pulsation in the lateral vaginal fornices is known as ______________.
- __________ is a condition in which a woman experiences symptoms resembling pregnancy, but pregnancy tests are negative.
- Fetal heart sounds can be detected by a _____________ or a fetoscope.
- The normal fetal heart rate ranges between _______ beats per minute.
- Ultrasound scanning can visualize the ____________ and identify the fetal parts.
- Palpation of ______________ is necessary to assess the position and size of the fetus.
- X-ray is not recommended for pregnancy confirmation due to potential ____________risks.
- The delivery of a live newborn is the _______ _____evidence of pregnancy.
_____________________________________________________
the answers
Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation and a presumptive sign of pregnancy.
Hegar’s sign can be detected by performing a vaginal examination and palpating the isthmus.
Increased pulsation in the lateral vaginal fornices is known as Osiander’s sign.
Pseudocyesis is a condition in which a woman experiences symptoms resembling pregnancy, but pregnancy tests are negative.
Fetal heart sounds can be detected by a Doppler or a fetoscope.
The normal fetal heart rate ranges between 120-160 beats per minute.
Ultrasound scanning can visualize the gestation sac and identify the fetal parts.
Palpation of the entire fetus is necessary to assess the position and size of the fetus.
X-ray is not recommended for pregnancy confirmation due to potential radiation risks.
The delivery of a live newborn is the conclusive evidence of pregnancy.
Join Our WhatsApp Groups!
Are you a nursing or midwifery student looking for a space to connect, ask questions, share notes, and learn from peers?
Join our WhatsApp discussion groups today!
Join NowGet in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co

