Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship Skills
Table of Contents

The Concept of Creativity
- Creativity is the ability to bring something new into existence. It is the ability to come up with innovative solutions to needs and to market them.
- It is the ability to produce work that is both unique and appropriate. In business an entrepreneur’s creativity is often the different between success and failure hence creativity is allowing you to make mistakes.
Characteristics of creative individuals
Creative people usually possess the following characteristic as listed below.
- They usually have originality. Creative people are capable of doing something that no one else has done. They think of an idea, redesign it and make something new out of it.
- They are independent thinkers. Creative people always think for themselves. They are observers and analysts who gather all the information they can and then analyse it to come up with their own analysis.
- They promote growth and change. Creative people search for change constantly. They do not restrict themselves to using the same old way of doing things. They learn to change for the better, so that they can grow and prosper.
- They are flexible. Creative people are flexible and always learn the current inventions.
People are challenged daily to be flexible in work, relationships, life and learning new things in general.
- They are innovative. They have the courage to try new things and build something out of the ordinary. Innovation and having courage are necessary for creativity.
- They normally ask questions. They always ask questions and ask people to explain what they mean and the things they don’t understand. They don’t accept things as they are.
- They are Sensitive; people who are creative are sensitive to the world and their environment so as to raise their creativity
- Search for better ways to do tasks, they focus on what they do and find new possibilities and new ways of doing things
Creativity Process
- Preparation/immersion (knowledge accumulation). This involves gathering data, opinions and speculation to obtain an inner depth grasp of the problem at hand.
- It is kind of brainstorming exercise eg if you are a writer, this means looking at old pieces of work and trying to decide where to go from there.
- Investigation, involves developing a solid understanding of the problem, situation or decision at hand.
- Transformation, involves viewing the similarities and differences in the information collected
- Incubation/gestation. It involves allowing the mind to continue thinking over the problem and possible solutions. It involves making the necessary connections that are made in order to lay the idea.
- Illumination / insight. It involves building inspiration. This may come abruptly by revelation. E.g. this is the moment for a writer when an idea just hits them and they need to grab a piece of paper in order to remember it.
- Verification and application. This involves testing the ideas, alternative solutions, possibility for their applicability before picking the most suitable solution.
- Implementation, this involves transforming the idea into reality
obstacles to creativity in business
- Negativity/negative thinking. This involves the tendency to focus on the negative aspects of problems and expand energy on worry.
- Thinking that you are not creative This results from the lack of self confidence
- Fear of failure. Fear of looking foolish or being laughed at hinders creativity. Failure is a necessary condition of and stepping stone to success.
- Limited or lack of quality thinking time. The over-stressed person finds it difficult to think objectively at all. Unwanted stress reduces the quality of all mental processes.
- Over-conformance with rules and regulations. A tendency to confirm to accepted patterns of belief or thought i.e. the rules and regulations hampers creative thinking. Some rules are necessary, but others encourage mental laziness.
- Wrong assumptions. This hinders creativity such as assuming that the failure of a business is due witch craft, inherited bad lack from parents etc
- Application of too much logic to a problem or situation slows down or hinders creativity.
- Dehumanizing mass media. This involves spending a lot of time immersed in popular culture i.e. televisions or listening to pop music
- Unfavourable or poor working conditions or limiting the freedom of workers in the business also limits their creativity.
- Competition in the present environment hampers motives for creative output. Concerns with job advancement or opportunities as opposed to job stability or security affect motives to be creative at work.
- High conflicting goals and objectives. These also hinder creativity.
- Noisy environment, which do not provide quite enough time for reflection and introspection.
- In the present environment hampers motives for creative output, concerns with job advancement or opportunities as opposed to job stability or security affect motives to be creative at work.
- Demands for quick production of results
- Belief, having a strong belief in something limits response options and the way things are perceived from outside world
Techniques for developing a creative ability
- Thinking beyond the invisible frame works that surround problems/situations
- Recognizing when assumptions are being made and challenge them
- Developing/adapting ideas from more than one source
- Transferring technology from one field to another
- Being open and prepared to use chance on unpredictable things/events to advantage
- Drawing on the experiences of other individuals business to widen the field of vision
- Practicing for tune i.e. having a wide attention span and range of interests
- Note down thoughts/ideas that apparently drop into the mind unsolicited so that they are not forgotten
- Using analogy i.e. improve imaginative thinking to find models or solutions in nature, in existing products/services or in other organisations
- Trying as appropriate to sometimes make the strange familiar and the familiar strange to spark new ideas
- Knowing when to leave a problem i.e. remain aware but detailed
- Tolerating ambiguity and occasionally live with doubt and uncertainty
- Stimulating own curiosity in everything and the skills of observation, listening, reading and recording Characteristics of non-creative person
- Not able to think positively about a problem
- Too busy or stresses to think objectively
- Very self-critical
- Timid in putting forward a new idea
- Prone to apply logic as a first and last resort
- Unable to think laterally
- Always goes with what others say
importance of creativity
- It increases awareness by paying attention to insights and sounds that are ordinary ignored
- It leads to development of new and original ideas and using the existing ideas as an initial point
- It is used to update products and services
- It enables an entrepreneur to make proper use of limited resources
- It is used to promote products and services of a business
- It solves everyday problems in business
Innovation in Business
Innovation is the way of transforming resources of an enterprise through the creativity of people into new resources and wealth.
The goal of innovation is positive change to make someone or something better.
Innovation and the introduction of it that leads to productivity is a fundamental source of increasing wealth in an economy.
Types of Innovation
- Business model innovation. This involves changing the way the business is being done in terms of capturing value e.g Nile Breweries Vs. Uganda Breweries.
- Marketing innovation. This is the development of new marketing methods with improvement in product, design, packaging, product promotion or pricing e.g soft drinks firms to change to plastic packing of their products.
- Organisational innovation. This involves creation of new business structures, practices and models and may include process, marketing and business model innovation.
- Process innovation. This involves implementation of a new or significantly improved production or delivery method.
- Product innovation. This involves a good or service that is new or improved substantially. This might include improvements in functional characteristics, technical abilities, ease of use etc. today firms that manufacture mobile phones are continuously coming up with phones that are not only serving oral communication but also phones with other functional characteristics like those with radios, television, those that can work as computers, those with cameras etc.
- Financial innovation. This involves the development of new financial attributed i.e. risk sharing liquidity and credit in innovative ways as well as exploiting the weakness of the tax law.
- Supply chain innovation. This is an improvement in a way of getting inputs (raw materials) from suppliers and delivery of output of products to the customers
- Service innovation. This is an improvement in a way services are provided e.g use of ATM machines to withdraw and deposit money, yaka system of UMEME, mobile money services, internet banking
Sources of Innovation
Internal sources (innovations within the society)
- Unexpected occurrences. Unexpected success; unexpected failure of unexpected outside event can be as symptom of a unique opportunity. It is often through such unexpected occurrences that new ideas are born from new information brought to light.
- A discrepancy/difference between reality and what companies or the industry assumes it to be or between what is and what ought to be can be an innovative opportunities.
- Process needs. Here, innovators are inspired by missing links in the production process that need to be created to support some other product or process.
- Industry and market changes. These are mainly shifts in the industry and market conditions for example changes in demand, technology etc that result into changes in products or services delivery.
External sources (societal environment sources)
- Demographic changes. Changes in population size, age structure, sex composition, employment, level of education and income can generate innovative in the level of education in Uganda has resulted in qualified workers going for somehow good paying jobs.
- Changes on perception mood and meaning. Innovative opportunities can develop when a society’s general assumptions attitudes and beliefs change. For instance despite the fact that health care in Uganda has continually become better and more accessible, people have become increasingly concerned about their health and the need for better and more accessible care.
- New knowledge. Advances in scientific and non-scientific knowledge can create new products and new skills and markets.
characteristics/features of innovation (innovators)
- They have a compelling vision. Innovative people believe that they are part of something better to come and that their willingness to contribute to the vision will make it happen.
- They are opportunity oriented. Innovators are constantly thinking about new ways of doing things and they are not afraid of doing something new.
- They are self-disciplined. Innovators are able to prioritize their time so that they are doing the important work first. They have the ability to do the hard work to make them happen.
- They are inner-directed. Innovators are inner directed and goal oriented and do not need any one else to motivate them because of the self-discipline and ability to focus.
- They are extra ordinary persistent. Innovators are committed to achieving their goals. They keep going and do not let obstacles get in their way.
- They are passionate about belief. Innovative people are truly passionate about what they believe; they give in everything they have. They are passionate about a thing and they go after that with all their hearts and souls.
- They are trend spotters. Innovators are trend spotters they are able to identify something new and its social responsibility
- They associate with positive people. Innovative people usually surround themselves with people with positive attitudes towards creating something new.
Principles of innovation
Below are five principles that can help you take advantage of new innovation that you may have discovered
- Begin with an analysis of the opportunity
- Analyze the opportunity to see people will be interested in using the innovation
- To be effective, the innovation must be simple and clearly focused on a specific need
- Effective innovators start small. By appealing to a small, limited market, a product or service requires little money and few people to produce and sell it.
- Aim at market leadership. Leadership here means dominating a small market niche. If an innovation does not aim at leadership in the beginning, it is unlikely to be innovative enough to successfully establish itself
ways to foster / promote innovation in a small business or ways of encouraging innovaton in small businesses
- Expecting change at all times: This helps the entrepreneur to always be ready to come up with new things that ensures that businesses cope up with change.
- Developing innovative strategies: e.g. trying out new technology through research.
- Implementing new rules: i.e. an entrepreneur needs to learn to go beyond the existing indicators of competition in the business environment by looking for new ways of doing things.
- Thinking globally: this enables an entrepreneur to look for new market for its products abroad, look for new technology abroad among others.
- Avoiding barriers that limit innovators: i.e. entrepreneurs need to put in place measures that ensure good internal co-operation among departments to promote good relations with each other and other outside parties so as to create a good environment for innovations.
- Acting fast to take advantage of any new business opportunity: i.e. by coming up with new things that utilize the identified opportunity.
- Being always a learner: through listening to other people.
- Measuring performance indicator: the entrepreneur needs to concentrate on key strategic and profitable indicators by focusing energies on new things that drive the future success of the business.
- Doing things well for others: for example for customers, suppliers etc. this help small business to stay ahead of competitors.
- Always thinking like entrepreneur: this helps one to always have ideas and even go ahead to improve on them in case of failure to start Advantages of innovation
- It helps in locating new technologies and become a foundation of a new set of customers. This improves product design and quality
- It assists a company in packaging and repositioning its products for global distribution
- It helps in developing new distribution channels and added value to make the organization’s products /services stand out
- It helps in reviewing the company’s objectives and comparing them with customers’ needs to find out what to offer to customers. This creates greater responsiveness to customer’s demands
- Innovation alternative approaches create alliances with venture partners. This enables a company to position its opportunity to match the interest of investors which improves the focus and objectives of the organisations
- It lowers organizational research and development and operating costs
- It streamlines relationships with suppliers and customers
- It leads to production of variety of products which expends the product range
Innovations in small businesses
A good business innovation involves developing new products of improving existing techniques, processes, designs and marketing to solve problems and reach new customers
Small businesses have the following qualities that make them more likely than larger businesses to use innovation successfully
- Personal connection with customers, small businesses understand customers’ needs and identify new opportunities quickly and efficiently
- Personally invested and passionate. Most small business owners are willing to try new approaches to make their business more successful
- Alertness and adaptation, small businesses can quickly adapt to changing market conditions and implement new business practices
- Experimentation/improvisation, many small business owners experiment and improvise by accepting failure in order to succeed
- Resource limitations, small businesses prefer to use less resources and do something much. The limited resources enable them to be innovative
- Information sharing and collaboration, small businesses traditionally rely on strong local social networks to share information needed for innovation thinking
Coping with change
Change is to give a completely different from or appearance to an object. Change in an organization is inevitable. It involves transforming an object into a completely different one.
Types of Change
Developmental Change. This occurs when a company makes an improvement on their current business. If a company decides to improve their processes, methods, performance standards, this is referred to as developmental
change. Companies are continually processing developmental change in order to stay competitive
Characteristics of developmental change
- The Company improves on its processes, methods or performance standards.
- Development appears gradually with little stress.
- Employees acquire new skills in order to manage the developments.
- It does not mean necessary the company changing its goals but to improve on the processes so as to achieve them.
Transitional Change. This type of change involves replacing existing processes or procedures with something that is completely new to the company. It involves dismantling of the old processes and includes corporate reorganisation, merger, and acquisition, creating new products or services and implementing new technology. Transitional period this is a period when the old process is being dismantled and the new process is being implemented.
Characteristics of Transitional change
- The old processes are completely replaced with new ones.
- There is a significant shift in the behavior of the employees.
- The company develops new products and services. Ø The company destiny or future is unknown.
- Employee’s level of engagement in the new procedures is increased
Transformational Change. This type of change occurs after transitional change. It involves making drastic transformation in the business rather than methodologically implementing new process. Transformational change may involve both developmental and transitional change where the businesses recognize that they need to over haul (the act of drawing something) the way they do business.
Characteristics of transformational change
- Top management is prepared to involve employees in transition.
- There is complete change in the methods of production.
- There is a complete change in the vision, mission and objectives of the company.
- Companies are faced with an expectant competition arising from existing companies.
- Employees look for an ideal situation for placing themselves in a new change i.e. undertaking training.
Other types of change include;
- Social change, refers to modification of established relationships in the business by influencing workers to achieve set goals of the business eg empowering workers , introducing team work etc
- Planned change, refers to change that occurs when leaders/management of the business deliberately plan to bring changes and take action to bring the desired changes
- Radical change, refers to the process by which a business regains its competitive advantage after it has lost it
- Strategic change, refers to change that involves long term planning for the business while adopting a strong external orientation
- Remedial change, refers to that change made by a business to address or correct a particular undesirable situation which needs immediate attention
Factors that bring about change in the business
- Efficiency: This is the ability of the business to achieve its objectives within the shortest time possible without losing quality and wasting any other raw materials.
- Environmental change: With increasing pollution resulting from industrialization and excessive exploitation of natural resources, managers and academicians are now showing great interest in the area of change.
- Social changes: These are behavioral changes that can be brought about by growth in population which results into change of needs of the community and various development aspects; hence an entrepreneur must make changes that satisfy the growing needs of the society.
- Competition: This includes those businesses that sell similar products or give similar services as well and they compete for the same customers, therefore companies must be considered as competitors because the products produced and put on market are similar and target the same customers.
- Change of technology: Technology is constantly changing the demand of consumers hence businesses need new technological developments to produce new products and services.
- Change of Desires: Entrepreneurs use their altitudes to control conditions hence opposite mental altitude helps to focus on desired activities and events that result into better use of available resources.
- Government directives: Sometime governments issue policy statements which cause entrepreneurs to develop enterprises that meet the identified needs of the economy e.g. government of Uganda directing schools and students take all sciences compulsory.
Critical factors to be considered in planning for change in small businesses
- Capital: Capital becoming very expensive to obtain overtime by many small businesses.
- Raw materials: This is becoming increasingly expensive and difficult to obtain due to difficulties in transport and misuse of the available raw materials among others; therefore, small firms resort to holding large quantities of raw materials.
- Labour: Labour is abundant to small firms but skills in business management are lacking; hence many firms opting to use capital then labour.
- Technology: every firm is a having a future in technology, however, it is becoming expensive; this is due to changes in taste of customers.
- Markets: markets are based on products which customers demand. Hence there is need to change enterprise`s markets as competition grows stiff.
- Government regulations of business activity: Due to the increasing demand for economic development and self-sustenance, officials are struggling to keep the country in the economic process.
- Behavior of entrepreneurs, with the changing demand for goods and services entrepreneurs are struggling to offer quality goods and services with emphasize of professionalism.
- Life styles, consumers` life style is changing towards quality at less cost as many copy the western way of living, forcing entrepreneurs to go western than local.
- Nature of Management. Entrepreneurs will have to exhibit greater professionalism and foresight if they are to guide the small sector through the period of economic scarcity which is now in the underway.
Importance of Change
- It helps the enterprise to adopt new technology; this increases the ability of the enterprise to increase productivity and growth.
- It helps the organization to respond to customer’s needs, as satisfied customers are able to bring in more income and at the same time it contributes to the growth of an enterprise.
- It helps employees to get new skills and knowledge i.e. for change to occur employees must adopt it by learning new skills and exploiting new opportunities to exercise creativity in the new way.
- It determines the direction of the organization. That is to say with increasing demand for products and services; it mean that a company must consider expansion that might involve addition of new staff and new facilities.
- It is used to change the status quo i.e. change is used to develop new ideas and innovations that directly impact and benefit the enterprise.
- Change helps the organization to achieve production of new goods and services e.g. the transformational change which leads to complete dismantle of the old processes which are inefficient and replaced with efficient modern method of production.
- Change is used as a tool to out compete other business e.g. change in the product line, change in the marketing strategies, change in customer care etc.
Disadvantages of change in a business
- It may sometimes result into unemployment of some workers when they are replaced by few machines adopted by the business.
- It may result into over reliance on computers, information technology and information support systems which sometimes break down. This may cause disruption of business activities.
- It may cause inconveniences to both workers and the business due to relocation of industries and workers.This may cause resentments from both workers and the community around.
- It leads to increased complexity of the methods of production. This may become expensive to the business due to increased costs of buying the technology, maintaining it and training the workers to use it.
- It may reduce the market share of the business when the change is caused by entry of a new competitor into the market area of the business or movement of the target population to other areas, which in turn reduces the profits of the business.
- It may result into pollution of the environment due to industrialization and the exploitation of resources like trees minerals etc
- It may result into wastage of resources. For example, change in technology may force business to purchase new technology that they may not really be needed.
Reasons why people resist change
- It is not common to find that change is totally accepted by everyone. This is partly due to the following
- Change benefits some people while it hurts others. That is why people resist it especially when change is seen as damaging in some way.
- Change sometimes is very expensive i.e. many changes require financial investment in the short run or it may be in the best interest of the few.
- Not being consulted. If people are not allowed to be part of the change there is less resistance.
- Some people resist change because they feel they are not capable of handling it, this may be the result of the general lack of self-confidence.
- Some people resist change because they feel they are not secure, e.g. when a small business seems to be running smoothly, any change may represent a threat of insecurity.
- Some people take pride of being stubborn and independent; hence they resist change no matter how convincing evidence is in favor of it.
- Some individuals resist change because they were not consulted before; hence they look at it as being undermining their efforts.
- It is because some people may lose their status in an organization, e.g. a change that involves merging department may be resisted because some people lose their status as being heads of departments.
- Some people resist change because they fear taking on new responsibilities, therefore they resist it to satisfy their personal interest
Indicators of resistance to change in an organization
- Low workforce efficiency
- Grievances about pay
- Aggression against management
- Restriction of output
- Increased absenteeism
- Expression of feelings of failure
- Low level of aspiration
- Expression of feeling of frustration
some strategies for reducing resistance to changes in business
- Adopting effective communication system so that any change to be made by the business is properly communicated to the workers. It should be made clear that changes are not going to affect their interests.
- Involving the majority of workers in deciding to make the changes. The business should invite the opinions of and suggestions of the workers before the changes are finally made so as to make them feel that they part of the changes.
- Carrying out changes that are necessary for the business. The business owner needs to carry out changes that are inevitable. This will reduce the possibility of resistance from workers.
- Planning how to make the changes. The entrepreneur should make pre-determined plan with clear objectives for making changes. This move will reduce resistance from workers.
- Conducting research on the most appropriate way of introducing new changes. This helps the owner to discover early ways of minimizing resistance from workers.
- Building support networks.
- Using managerial authority and status
- Offering assistance to those involved
- Offering extra incentives
- Encouraging and supporting those involved.
Techniques for coping with change
By knowing the reasons for resisting change, we can better understand what attitudes can counteract this resistance and help entrepreneurs cope with change more effectively and in a positive manner or way.
Techniques / ways to foster change in business
Below are some of the tips for managing the complex and difficult change process in business.
- Rewarding success. Simple acknowledgement or thanks for what someone has done well may make a lot of difference in the attitude of employees regarding change.
- Giving explanation. There should be formal or informal meetings in which leaders can explain why the change is taking place, the potential impacts of the change and the goals related to the change. Such explanations, when done in an open forum, give the impression that all members of the group are valued equally, which creates a sense of unity. This sense of unity may help the group turn toward the change of a common purpose.
- Providing adequate training lets individuals meet the challenges the change requires and eliminates the excuse that the change cannot be implemented for lack of knowledge or preparedness.
- Encouraging feedback on progress. People may be more likely to accept change if they have a chance to tell leaders their thoughts and concerns. Feedback also gives administrators a chance to monitor progress and determine whether action plans related to the change are working properly.
- Managing resistance. This involves preparing yourself for anything anyone might do in order to stop the change. For example, you might set up a policies and procedures manual that clearly states what the consequences of not following the changes are. Another resistance management option is to place strong leaders who are accepting of changes as project managers.
- Assessing readiness. These measure how prepared employees and administrators are to handle modifications. These assessments may include evaluations of inventory or other resources, but they may also include interviews with employees and administrators in analyze what is needed to accommodate the change.
Sample questions
1 a) explain the benefits of change to an enterprise
- Explain reasons why people in an enterprise may resist change
- Suggest ways of promoting change in a business 2 a) Why is there need for change in a business b) What are effects of change in a business?
- a) Explain the critical factors considered for planning for change is small enterprise b) What importance of change in business
- a) Explain the causes of fear of change
- b) Suggest ways of encouraging change in a business
The concept of entrepreneurial motivation
This is a strong desire, impulses, dedication and drive of individuals to accomplish a specific business goal. It results from the desire to accomplish some psychological needs of recognition, responsibility, esteem and participation. It is a dynamic force and as such, it changes with time and space.
Motivation
This is an inner state that activates or moves the intervening variables which are not directly observable and in turn influence individual’s behaviors. The variables include internal variables and psychological processes Motivation consists of all those inner striving conditions described as wishes, desires, drives, needs and impulses. It is concerned with how behavior get started energized sustained, directed stocked and what type of subjective reaction is present in the organisation while all this is going on
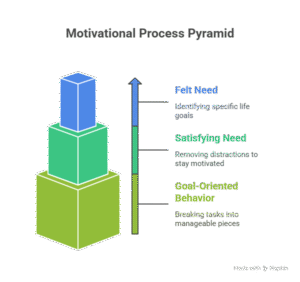
The motivational process
- Felt need. This involves determining what you want to be motivated to do or accomplish. This is a specific goal in a very specific area of your life.
- Satisfying the need by removing one’s distractions so that he stays motivated.
- Developing goal – oriented behavior. These are the things one needs to do, like read his goals each morning. This part helps to break up the task up into manageable and convenient sized pieces.
Classical concepts of entrepreneurial motivation
This refers to the altitude which strongly influenced by and they cannot be really accounted.
Power motives. Is the ability to acquire others to behave in a way that suits others e.g. an infant a great deal of power.
Competence motive. This is the interest in getting to know what the world is like to be able to make things happen to create even rather than merely waiting for the possible e.g. in adults the competence motive is a desire for job mostly and professional endurance for affiliation motives.
Affiliation motives. This is a desire to be with other people regardless of whether nothing that the country has against people seeks to gain some kind of interpersonal reward which others met out such as money favour. Entrepreneur is action oriented highly motivated individuals who take risks to achieve goals that are referred to as being achievements motivate. They assume responsibilities for work; therefore the government motivates them in achievement motivated. They assume responsibility for work therefore government motivate them in achieving their goals through;
- Providing good infrastructures.
- A providing conducive environment that facilitate entrepreneurial activities.
- Reliable utility supply such as water.
- Recognition of the utility.
- Providing investable
- Putting of laws that protect them.
Achievement Motivation This is the intensive urge to excel and do something unique. The people with strong need to achieve have an intensive desire for success.
They want to be challenged so they set moderately difficult but not impossible goals for themselves take realistic risks and prefer to assume personal responsibility to get the job done.
Characteristics of achievement motivation
- Formulating of a concert goal to be achieved. Goals that are formulated is in such a way that stretches one’s ability and efforts.
- Goals set are not impossible or too difficult but are not too easy to be achieved.
- Develop a strong internal commitment or involvement with a goal.
- Taking personal responsibility for the outcome.
- Analyzing the environment to create opportunities for achievement rather than passively waiting for chances to come one way. That is one is able to see possibilities and opportunities in addition to the problem.
- Experimenting with novels activity to reach the goal. This is through anticipating possibilities of success rather than failure and doing something about obstacles which can cause failure.
- Seeking help from experts rather than from friends i.e. overcome both external blocks and internal or personal limitation.
- Delivering maximum satisfaction from achievement i.e. self and less from other factors like recognition and money.
- Experiencing positive feelings of joy and satisfaction in achieving moderately challenging goals and disappointment but not self-condemnation in failure.
- Learning from feedback through analyzing whether the right methods were employed orchanges should be carried out.
Benefits of Motivation (advantages of achievement motivation)
An entrepreneur who has a high level of achievement motivation has a greater chance of success it has the following advantages:
- Increasing self-confidence of a person, who has achieved success, hence is able to set more challenging goals.
- Producing high performance or results i.e. person who has obtained success use the same experience to deal with any future challenge.
- It enables the entrepreneur to use of environment profitably, and plan how to attain more success.
- Motivates entrepreneurs to take carefully calculate risks; this reduces wastage and produce high chances of success.
- It creates much interest into the person to develop concrete measures of how he/she is performing.
- It leads to better utilization of the available resources in order to achieve greater success.
Challenges of Motivation
Achievement motivation is an urge to excel, to compete and does something unique that it must be associated with constant pressure and stress which may lead to high anxiety regarding performance resulting in fear or failure hence the challenges include:
- Setting goals that are too low to ensure success.
- It is associated with constant pressure and stress; this is because achievement motivation argues a person to do something unique.
- It leads to high level of fear for failure which in most cases makes one not even to do anything.
- Setting goals that are too high which might fail i.e. some entrepreneurs have the urge to excel or to set goals that are not easily achievable.
- Thinking of weakness and problems in the environment only i.e. one does not think of the available strength and opportunity.
- The challenges of obtaining the right input to work with to ensure success
Factors which hinder entrepreneurial motivation
Entrepreneurial motivation can be hindered by certain social, political, economic and cultural factors
- Inadequate education orientation, limited entrepreneurial experience and market opportunities. Individuals do not have enough knowledge and skills to handle or deal with some entrepreneurial activities, this may demotivate them from going ahead with entrepreneurship
- Unfriendly economic environment in terms of high interest rates of loans, absence of lending/funding organisation, this demotivates individuals to access money from financial institutions to carry out investments.
- Inadequate provision of physical economic infrastructures like reliable roads,water, electricity and machinery in a given geographical setting.
- Some social-cultural beliefs in that society acts as a barrier to entrepreneurial development, for instance a belief that certain roles are for particular social, gender or ethical category, like in the past we would lose female entrepreneurs as they were always taken to be week sex that cannot get involved in business.
- Political systems which discourage individuals’ freedom, free market economy and private enterprises may also hinder entrepreneurial motivation. Policies that contradict with individual motives and the desire to excel hinder motivation
- A society which doesn’t encourage or facilitate entrepreneurial spirit and the urge to excel can hinder motivation.
- Great risk, developing countries have many risks due to inadequate information and narrow market for goods.
- Psychological factors like high need for affiliation conformity and compliance to rules and regulation, and need for security, all this hinder entrepreneurial drive e.g a politically unstable environment discourage people from investing since one would wish to lose his /her money by investing in a politically unstable environment.
- Non availability of labour and skills, though there is abundant labour supply, there is generally scarcity of skills at all levels.
ways to foster entrepreneurial motivation
- Networking with successful entrepreneurs to acquire their thinking and characteristics.
- Having faith in oneself , success comes to those who use their talents and abilities
- Being result oriented, focus on specific problems and once you have reached a decision take action to solve the problem
- Taking advantage of opportunities to improve your situation whether it is your personal life, work on life in the community
- Having working objectives that are achievable and have the impact
- Identifying successful entrepreneur to be your role model and mentors
- Having a positive mental attitude necessary for achieving success
- Avoiding negative thoughts on ideas
- Involving in positive activities
Risk taking in business
- A risk is a situation where one is required to make a choice between two different alternatives which may result into differing rewards for success or penalties for failure.
- A risk refers to the possibility of suffering harm/loss/danger.
- Every business organisation contains various risk elements when doing the business.
- Business risks implies uncertainty in profits or danger of loss and the events that could pose a risk due to some unforeseen events in future, which causes business to fail
Types of Risks
The different types of risks are classified on the basis of levels and these levels are: low, moderate and high level (risks), they are discussed below
Low Risks. These have high potential of success but are associated with low profits. In such a situation, an entrepreneur starts a business that is common to him and hence bearing few or low risks of failure.
Moderate Risks. These are ones that can be forecasted, calculated and managed by an entrepreneur, in such a situation there are higher chances of managing and controlling i.e ensuring that in case it happens, it does not affect the business. Examples of such risks are: fire, burglary, theft etc.
High Risks. These are risks that have a high chance of occurrence or happening, and in case they occur, one has less or no control over them. Examples of such risks are, smuggling, dodging government taxes, etc. however, such businesses with high risks tend to fetch higher profits in case they succeed.
Various examples of risks that entrepreneurs encounter in business and they include:
- Risk of losing market due to changes in customers’ tastes, demand and fashions leading to limited customers and closure of the business.
- Break down of machinery and consequential loss which comes when one does not service machines or if he over used the machines.
- High staff turnover or loss of key staff members especially if they have unique skills.
- Fire outbreak due to poor electrical wiring or reluctance leaving candles anywhere which can bring about fire outbreak.
- Increased competition due to increased number of similar businesses.
- Loss of money in transit for example when money is being taken to the bank it may be misplaced.
- Many people steal money from where they work like employees and other community members (theft and burglary)
- Failure to comply with legislation, regulation and / or standards
- Bad debts created by customers who may borrow money / goods from business and fail to pay back.
- Danger or loss of goods in transit. Goods may be damaged in the process of loading and off-loading them.
- Corruption and embezzlement of funds by the employees for private use. Business failure due to changes in industrial relations, which may lead to strikes Outbreak of diseases affecting farm animals and crops.
- Risks due to unfavourable government policies like ban on use of polythene papers.
- Poor management decisions hence financial mismanagement, human resource mismanagement and misuse of other resources
Risk Assessment
Is the process of determining whether a particular uncertain circumstance has the potential to threaten your business operation
Or, this involves determining the potential success (that will arise out of the risk not happening) or potential loss (arising out of the risk happening).
Risks can be assessed based on the following factors
- Experience and abilities of management: If the persons involved in managing the business possess the required knowledge, experience and technical abilities, then chance of success are greater and the risk is lower.
- Availability of market: When there is assurance of high and growing market in an area, chances of success are likely to be greater.
- Viability of the idea: Chance of success in the business are greater and the risk is lower if the selected business idea would profitably be done in the selected business area given the available resources.
- Flexibility of the business: If the business can easily be changed in response to changes in consumer’s tastes and preferences without causing negative effects, then the chances of success will be greater and risk is lower.
- Level of consistency of cash flow: This considers the ability of the business to generate enough cash to finance the planned business expenditures. If the business has enough cash (inflow) to finance the planned business expenditures (cash out flow) for success of any business, the cash inflow should always be greater than the cash out flows
- Honesty and reliability of people involved: If the person the business deals with such as suppliers, reliable, then chances are honest and reliable, then chances of success will be higher and the risk is lower.
- Marketing and pricing policies: Given the prevailing competition, chances of success will be greater and the risk lower if the prices charged and marketing strategies used by the entrepreneur are effective and competitive.
Risk Management
Managing of risks refer to the activity that involves controlling risks to ensure that they do not happen and if they happen , they do not lead to severe losses to the entrepreneur’s business. There are mainly two methods that an entrepreneur can employ to manage business risks
Minimizing Risks
In order for an entrepreneur to reduce the chances of business risks happening, he can take preventive measures that will minimize them. Such measures include the following
- Maintaining and up grading production technology and products to minimize the challenge of changes in consumers taste, fashion and demand. This will help to ensure that the products are in line with the customer’s needs
- Locating reliable sources of raw materials and keeping close contact with suppliers to reduce the challenge of shortage of raw materials
- Maintaining adequate security, guarding and strengthening burglar proofs, security lights etc, which will help to control the risks of theft.
- Maintaining good employee relations at work place for example by improving the welfare facilities of workers to minimize poor industrial relations which can result into strikes at work place
- Improving the quality of products and customer care to reduce the risk of business being out competed. i.e the changes in the degree of competition in the market.
- Extensive training of the entrepreneur and staff on new equipment or procedures to reduce the risk of staff and the entrepreneur him / her self being left behind by technological changes
- Employing experienced personnel to reduce the challenge of faulty managerial decisions regarding the use of capital, machines, raw materials, defective inputs.
Ways of maintaining security in the business
- Checking thoroughly all vehicles, motor cycles and persons entering or leaving the business at the entrance.
- Installing security lights and switching on them at night.
- Ensuring that all vehicles, motor cycles, persons and their properties are registered on arrival at the main gate.
- Having in place a well maintained fence and monitoring it at all times.
- Installing security monitoring equipment like CCTV cameras, alarm systems, bomb detectors etc
- Employing well-armed and well trained security workers and giving them clear instructions relating to security.
- Sensitizing workers frequently on appropriate measures aimed at ensuring security.
- Electrifying the wall fence of the business.
- Placing warning notices relating to security at different points within business and outside the premises.
- Restricting permission to enter the business to business customers, workers and other permitted business parties.
- Installing fire extinguishers at the business work place.
- Ensuring that all workers wear business uniforms that have name and number tags on them at all times during working time.
- Having watch dogs to maintain security at the business premises.
- Ensuring close supervision of all workers while carrying out their duties to minimise theft.
- Prosecuting trespassers in the business premises.
- Safely locking all business movable assets like cash, work equipment, computers etc
- Specifying the time beyond which no visitor, unauthorized staff, vehicles and motor cycles should be allowed in business premises.
Ways of ensuring safety /minimising loss of business funds/cash
- Ensuring proper documentation of all cash received and paid out.
- Banking daily cash received from sales and from other sources daily or regularly.
- Keeping the remaining cash at the business premises safely locked up in the money safes and also locking the doors to the cash safe rooms.
- Ensuring that only authorized business workers like the accountants receive cash receipts and recording of all cash received in the cash receipts and other relevant books.
- Ensuring that all cash expenditures are requested for through the heads of department and then approved by an authorized business official.
- Prohibiting any cash drawings from the business but if allowed then restricting the amount and charging interest on the amount withdrawn.
- Ensuring timely collection of debts within one mouth or as soon as they are incurred so as to avoid losing money due to bad debts.
- Buying business items from a nearby reliable and cheap supplier in order to minimize high expenditure due to high transport costs.
- Obtaining the bank statement of the business on a daily basis on working days and ensuring that the accountants reconcile these statements with the cash book of the business.
- Employing certified auditors to check the accounts records for error and fraud
Shifting of Risks
The entrepreneur can also manage business risks by shifting the burden of bearing the risks to other parties such as insurance companies by obtaining suitable insurance cover/ protection against fire, theft, accidents and other insurable risks
Risk Situation
A risk situation occurs when the choice is required between two or more alternative whose potential out comes are not known and must be subjectively evaluated. It involves potential success and potential loss. The greater i.e possible loss or gain the greater the risk involved
Risk takers make decisions in conditions of uncertainty and they balance potential success against potential loss
Choosing a risk alternative depends on:
- How attractive the alternative is
- The extent to which the risk taker is prepared to accept the potential loss
- The relative probabilities of success and failure Procedure for analyzing a risk situation
- Assessing the risk: This is a situation where an entrepreneur is able to establish whether there is a potential risk or not in choosing a particular alternative or cause of action.
- Determining the goals and objectives: The entrepreneur goals and objectives for risk taking must be consistent with the business interest in terms of risk management.
- Surveying on various alternatives available. A survey is carried out to each alternative thought of and details should provide for each alternatives so that costs involved can be assessed in terms of the financial implication of the alternative to taken
- Gathering information and weighing the alternatives: the information gathered is used to assess the various alternatives in terms of future demand, Competitive reactions and the effects of those reactions calculated.
- Minimizing the risk. This is the step that involves realistic assessment of how best to minimize the risks while maximizing the benefits using one or more of the strategies such as using creativity entrepreneur`s ability among others.
- Planning and implementing the best alternatives, once an alternative is selected, a plan is made for the implementation of the alternative this include preparing a timetable, defining clear goals and objectives and feedback plans etc so that changes can be made where possible.
Types of risk takers
- Low Risk Takers. These are needed at a worker level (lower level) so that they can do the routine things and being organizational stability.
- Moderate Risk Takers. These are managers at the middle management level. They are considered as risk takers because they need some freedom to be innovative and make minor modification in procedures and functions.
- High Risk Takers. These are creative and innovative entrepreneurs, willingness to accept change, try various alternatives and develop innovations for products and services in new areas of business.
Term to be used
- Risk avoidance. These are measures that can help to prevent the risk from occurring e.g a driver should not drink and drive
- Risk reduction. This is taking measures to minimize the likely loss or chances of the risk happening
e.g putting in place fire extinguishers, having a stand by generator.
- Risk anticipation. This is forecasting the likely risk that could happen in the business e.g putting in place burglar proofs, employing a security guard, regular servicing of machines etc
- Risk transfer. This is when the burden of taking responsibility of a risk is shifted to another party e.g taking an insurance policy against, fire, accidents, theft etc
Benefits and importance of insurance to a business
- It allows individuals and business to save money that can be used to unexpected emergencies
- An entrepreneur is assured of business continuity as a result of the compensation after the loss has occurred. This assurance of business continuity gives the entrepreneur confidence, stable earning, growth and expansion
- Customers increases their trust in the business as a result of the assurance in his business continuity
- The property of the business people are guarded against all risks like factory against fire. This gives confidence to entrepreneurs to undertake business operations
- They act as trustees and references to their clients who would like to get loans from commercial banks. This is because after a long period of working age of the company and investments can be lent out to earn interests of the insurance policy
- Insurance policy (contract) document is used as security when applying for a bank loan usually prefer security that is insured because they guarantee loan repayment
- It promotes international trade, because entrepreneurs are able to import and export their goods. The entrepreneurs also are able to insure their goods against numerous risks in foreign trade
- Insurance companies pay taxes and therefore raise government revenue used for national development
Sample questions Question 1
- Explain the factors determining risk assessment.
- What are Various examples of risks that entrepreneurs encounter in business
- Suggest the ways through which risks can be reduced.
Question 2
- Define the term risk.
- Distinguish between risk transfer and risk reduction
- Explain different types of business risks.
- Explain the procedures followed when analyzing risk situation.
Business Ethics
- Ethics are a set of moral principles which are recognized in respect of a particular class of human actions or group.
- Business ethics are acceptable measures or ways in which the business should conducts themselves towards their customers, employees, society, government and fellow business.
Or
- They are those virtues that business peoples apply when making business decisions.
Principles of good business ethics
Ethical principles are the values that set the ground rules of all that we do. The ethical principles are
- An entrepreneur should be open and freely share information. He shouldn’t say thing that are false or deliberately mislead others
- Promise keeping. One will not make promises that cannot be kept and will not make promises on behalf of the company unless he has the authority to do so.
- An entrepreneur should create and follow a process and achieve outcomes that a reasonable person would just call. E.g equal treatment of workers, like giving them a fair pay depending on stipulated conditions
- Respect for others. It’s important for one to honour and value the abilities and contributions of others, embracing the responsibility and accountability for our action in the regard
- Compassion, one should maintain an awareness of the needs of others and act to meet those needs whenever possible. They should minimize harm in society
- Integrity, one will always live up to ethical principles, even when confronted by personal, professional and social risks as well as economic pressure, e.g the hiking rate of inflation doesn’t mean reducing worker’s salaries or producing poor quality products
- Cooperation or team work, an entrepreneur should be able to support acts of other business partners and work together to achieve the common goals of the industry e.g. during strike due to high taxes.
- Law abiding. Ethical entrepreneurs abide by laws, rules and regulations relating to their business activities.
- Commitment to excellence. Ethical entrepreneurs pursue excellence in performing their activities, are well informed and prepared, and constantly endeavor to increase their knowledge in all areas of responsibility.
- Reputation and morale. Ethical entrepreneurs seek to protect and build their businesses’ good reputation and the morale of its employees by engaging in no conduct that might undermine respect and by taking whatever actions necessary to correct or prevent inappropriate conduct of others.
- Accountability. Ethical entrepreneurs acknowledge and accept personal accountability for the ethical quality of their decisions and omissions to themselves, their colleagues, their companies, and their communities.
Parties to business ethics
- The clients or customers who deal in the business
- Employees who are employed by the business
- Government of the country or authority in which the business activities take place
- Businesses which competes with the entrepreneur’s business
- The society within which the business operate
- The suppliers of inputs
Business ethics towards customers
- An entrepreneur is supposed to be honest to his/her customers; this will involve charging fair prices for the goods, good quality and affordable quantities etc
- Endeavour to seek and analyze the needs of customers and making sure that goods/services provided conform to those identified needs of customers
- This involves politeness, patience and sincerity when dealing with customers. An entrepreneur should always put his/her self in customer’s shoes, for instance one is not supposed to sell underweight and expired goods to his customers
- An entrepreneur should ensure that the goods or services provided do not have any negative impact on the customers, for instance a professional doctor or nurse should not sell expired drugs to patients or his client since they will affect their lives instead of treating them
- Genuine to customers. An entrepreneur should be kind, cheerful and should always try to control his/her tempers when dealing with clients/ customers, should not use abusive language or shout at customers, he/she should instead try to make them understand what he/she needs in case of any discrepancy
- Provision of the required information to the clients or customers on the use of the products/services. Installation, maintenance and other likely impacts of using the product
- An entrepreneur should try to meet his obligations as agreed on, for instance he/she should fulfill his contractual obligations on agreed time, delivery on time and fulfill his/her part of the deal/bargain
Business ethics towards employees
In order for an entrepreneur to treat the employees in an ethical manner, the following should be highly observed
- Through giving them a fair pay. Payment to employees should be fair i.e. in relation to his value in business and amount of work done. One should also consider the seniority. Experience, responsibility etc of the employee when determining the payment
- Should provide clear and fair terms of employment e.g employees should be given appointment letters stating whether they are employed on permanent, temporary or on a contract business. The salary or wage should be specified as well as duties and responsibilities
- Ensuring job security of an employee. As it is the right of an employee to know the terms of employment, for instance, it can be on a permanent basis, temporary or contractual form of employment which helps on employee to plan accordingly e.g if it is a contract based, one should prepare to look for another job when the term of contract is ending
- Provision of good working conditions. Since employees spend most of their useful time at their work places, the work place should assure a healthy life during and after staying at the business, such conditions may include protective working clothes, helmets, gloves etc good transport, feeding, accommodation, Medical care and other allowances
- There should be constant arrangement for proper training and education of workers, this will improve on their skills in operating their business activities which improve performance
- Listening to employee’s personal problems and complaints, through this, an entrepreneur can help in solving or assisting them where necessary through giving them affordable and relevant support to them
- Politeness i.e. workers should be treated in a polite way in all situations, this also involves those situations where employees go wrong, for instance let a single mistake made by an employee not make an entrepreneur forget the good things made / he has made
- Creating a room for creativity. Employees should be treated as human beings who have the right to think and act i.e. they should be given a chance to exercise activities, this may lead to improved services and productivity to the business
- Respect, the entrepreneur should respect the employees for the contribution they make to the business, for instance the entrepreneur should not publically abuse employees and the norms of the society of the area should be respected when handling employees
- Provision of proper recognition, appreciation and encouragement of special skills to capabilities of workers, this increases their morale and devotions to their work in business
Business ethics towards the society
- Conserving the environment. The business should endeavor to take all the necessary steps needed to conserve the environment e.g trying all the necessary ways of controlling pollution i.e. in air, water and swamps.
- The business should endeavor to protect people’s health and lives during its operations like avoiding emitting poisonous and toxic substances, controlling machinery noise, explosion etc.
- A business should have strict considerations for the norms, for instance during business activities in what is acceptable to the culture or religious beliefs of the society like putting up a disco near a secondary school, selling pork in a Muslim community.
- A business is also expected to get involved and contribute to the needs of the society, like contributing to community health centres, community development like cleaning or road construction.
- A business is also expected to provide employment opportunities to the community members instead of giving them out to foreigners i.e. in case they fit in the existing opportunities in terms of qualification, experience and skills.
Business ethics towards government
- Complying with the laws that govern the business like registration laws, licensing laws, labour laws, occupational hygiene
- Observing and setting the tax obligation as required by law, it is a must for entrepreneur to pay taxes and they should be paid on time and in full
- Businesses should follow the government policies in their operations like selling products that are acceptable by the government, should avoid engaging in illegal commodities like fire arms, expired commodities etc
- The business should meet the production standards in terms of quality, weights etc, dishonesty acts like charging the weighing scales in order to exploit consumers should be avoided
- The business should also comply with occupational hygiene, environmental regulations etc as prescribed by the central and local government
Business ethics towards suppliers
- Paying them promptly
- Offering them a fair price
- Attending to their complaints
- Respecting the terms and conditions of the transactions
Business Ethics towards Competitors
- Ensuring fair trading
- Anti-competitive policies
- Merging where possible
- Giving referrals in favour of competitors
Business Ethnics towards Share Holders
- The business should protect the interests of the shareholders / the entrepreneur for business survival.
- The management of the business should make sure that the capital of the business is safe from misappropriation, should avoid mishandling business property etc
- The management should ensure that the business makes profits and deliver the right dividends to the share holders
- Management should ensure that the business image is amplified so that the entrepreneurs enjoy selfesteem and recognition.
Importance of business ethics to business
- Helps the entrepreneur to be trustful by re-organizing that the customer is the king. This helps to maintain and attract new customers
- Enables business people to meet obligations of their customers and business partners regardless of anything else
- Increases business turn over engaging in fair trading activities like guaranteeing a safer place for your employees, fair pricing for your product guarantee a high business turn over
- Increases business profits when a business that practices business ethics towards its customers, its total sales increases as well as its profits. This facilitates business growth and expansion
- It leads to recognition from the society. Being ethical as a business person builds the image of reliability and establishes reputation with your customers.
- It leads to easy access to human resources through gaining good reputation which enables, it to get human resources to work for it
- It leads to easy access to inputs like raw-materials. By practicing business ethics to society, the business earns a good reputation which enables it to get human resources to work for it.
- It enables the business to win government support. Honest business attract the government supports and sympathy in terms of needs
Unethical practices that are used by entrepreneurs while running their businesses.
- Supplying low quality/inferior goods. Some scrupulous entrepreneurs use unethical practices of supplying low quality goods to consumers. They adulterate the goods; use wrong scales, weights and measures which make consumers buy less than the actual quantities and quality.
- Charging high prices. Another form of exploitation and unethical behavior used by entrepreneurs is through overcharging consumers and selling to them goods at very high prices. Entrepreneurs can create artificial shortage of the good in the market through hoarding so as to charge high prices and earn excessive profits.
- Misleading advertisement. Some firms give false, confusing and misleading information while advertising their goods and the consumers ignorantly base on this false information to buy the goods. For some packaged goods they supply inadequate or wrong information on the packages which misguide the buyers and wrong use of drugs, chemicals and other products harmful to people’s lives.
- Poor remuneration to employees. In a bid to minimize costs and maximize profits, some entrepreneurs behave unethically by paying workers low wages and salaries. The wage paid is usually not matching the workers’ productivity and cannot enable the worker to meet his basic needs. The pay is little, delayed, uncertain and sometimes not paid at all.
- Discriminative employment policy. Some employers are discriminative in their recruitment policies by hiring employees of a certain gender, age, tribe, religion, political affiliation and others. Recruitment is not done on merit and this means people who are qualified for jobs don’t get a chance of competing because the policy of recruiting eliminates them.
- Use of child labour. Labour laws and the constitution discourage the use of children below 18 years in productive employment as they are still minors. But some entrepreneurs behave unethically and employ children and worse still underpay them.
- Payment of low rate of dividend to shareholders Share-holders entrust the management and running of their companies to directors. The directors are supposed to provide information through reports and feedback to the shareholders about the progress of the business at the same time pay a reasonable rate of return. However the directors sometimes use dishonest means to pay low rate of dividends to shareholders and they fail to provide feedback on time.
- Misuse of funds/mismanagement of the company. The shareholders sometimes divert the funds of the company to either personal use or non-priority activities. Sometimes they also give bribes, gifts, donations, payment of kickback money to politicians and the government officers for certain benefits like winning contracts.
- Overexploitation of resources. In order to achieve their goal of profit maximization, some entrepreneurs do over utilize the available resources. Such activities like deforestation, over fishing and others are unethical and deprive society the benefit of using the resources sustainably.
- Disregard of business laws. Some business owners disregard business laws, government policies and misuse the facilities and incentives offered by the government and incentives offered by the government. Failure to comply with public law is unethical, for example dodging and evading taxes.
- Creating inconveniences to local people. Sometimes entrepreneurs create inconveniences to local people due to growing industrial activities without due care to local community. Increased industrial and business activities
Sample questions Question 1
- What is meant by the term business ethics
- Explain the principles of business ethics
- State the ways through which business enterprise are ethical towards i. Customers ii. Entrepreneur and share holders iii. Government iv. Employees v. Society
Question 2
- State the ways in which a business should be ethical towards its competitors
- What is the importance of good business ethics?
Join Our WhatsApp Groups!
Are you a nursing or midwifery student looking for a space to connect, ask questions, share notes, and learn from peers?
Join our WhatsApp discussion groups today!
Join NowWe are a supportive platform dedicated to empowering student nurses and midwives through quality educational resources, career guidance, and a vibrant community. Join us to connect, learn, and grow in your healthcare journey
Quick Links
Our Courses
Legal / Policies
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2026 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved

