Entrepreneurship
Subtopic:
Types of Business Enterprises
Table of Contents

TYPES OF BUSINESS ENTERPRISES
LEGAL FORMS OF BUSINESS OWNERSHIP
Another important decision which an entrepreneur has to make is legal structure of his enterprise. It is important because the choice of ownership form affects the rights, duties and obligations of owners as well as the tax liability. The main forms of ownership may be briefly discussed below;
1. Sole Proprietorship
Sole proprietorship or individual entrepreneurship is a business concern owned and operated by one person. The sole proprietor is a person who carries on business exclusively by and for himself. He alone contributes the capital and skills and is solely responsible for the results of the enterprise.
The salient features of sole proprietorship are as follows;
- Single ownership
- One man’s control ü Undivided risks.
- Unlimited liability
- No separate entity of the business from the owner. ü No government regulations.
Advantages of Sole Proprietorship Business
- Simplicity i.e. it is easy to establish and dissolve the business, no documents are needed and no legal formalities are involved.
- Quick decision making i.e. an entrepreneur need not consult anybody in deciding his business affairs, hence, he can take on spot decisions to exploit opportunities from time to time.
- An entrepreneur is his/ her own boss, he/ she is not controlled by any one as he is the owner.
- High secrecy; he/ she have not to publish his/ her accounts and the business secrets are known to him/ her alone. This reduces on cost and also guards him/ her from competitors.
- In an event of success, he/ she enjoy all the profits alone, since he is alone without co-workers who would share profits.
- Direct motivation; there is a direct relationship between efforts and rewards, since no body shares the profits of the business, the entrepreneur has sufficient incentives to work hard.
- He has full control over his business as there is no outside interference, thus business operations may be carried out well and easily.
- Personal touch; an entrepreneur can maintain personal contacts with his clients/ employees this helps him in growth of the enterprise through good relations with his customers.
- Flexibility; in the absence of government control, there is complete freedom for action, there is no scope for difference in opinions and no problem of coordination.
Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
- In an event of making losses, an entrepreneur suffers the risks alone.
- Limited funds, a proprietor can raise limited financial resources; hence the size of business remains small hence limited scope for growth and expansion.
- Since the proprietor is alone, he is over worked.
- Unlimited liability; the liability of the proprietor is unlimited, i.e. in case of a loss, his private assets can be sold to pay off the business creditors. This discourages expansion of the enterprise.
- Uncertain life, the life of the business depends upon the life of the owner since he works alone, this means that the enterprise may face premature death due to the incapacity or death of the proprietor.
- The proprietor manages the business by her/ himself and does not benefit from input of the other entrepreneurs.
2. Partnership Firms
As a business enterprise expands beyond the capacity of a single person, a group of persons have to join hands together and supply the necessary capital and skills. According to section 4 of the partnership Act, 1932, partnership is the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all. In other words, it is an arrangement between two or more persons to carry on jointly a lawful business and to share the profits arising from there.
Characteristics of Partnership
- Association of two or more persons – maximum of 10 in banking business and 20 in nonbanking business.
- Contractual relationship written or oral agreement among the partners.
- Existence of a lawful business.
- Sharing of profits and losses.
- Mutual agency among partners.
- No separate legal entity of the firm. ü Un limited liability.
Formation of Partnership Firms
These firms can be formed through an agreement between or among persons. The agreement may be oral or in written, but more desirable in written, such a written agreement among partners is known as Partnership Deed. It usually contains the following;
- Nature of the firm.
- Name and address of all the partners. ü Date of the agreement.
- Principle place of the firm’s business.
- Duration of partnership, if any.
- Amount of capital contributed by each partner.
- The proportion in which the profits and losses are to be shared.
- Loans and advances by partners and interest payable on them.
- Duties, powers and obligations of all partners.
- Amount of salary or commission payable to any partner.
- Procedure for dissolution of the firm and settlement of accounts.
- Arrangements in case a partner becomes insolvent.
- Arbitration for settlement of disputes among the partners.
Merits of Partnership Business
- Ease of formation; it is easy to form as no cumbersome, legal formalities are involved.
- Large financial resources, as a number of partners contribute to the capital of the firm, it is easy to collect large financial resources than that of a sole trader.
- Specialization and balanced approach, it enables the pooling of abilities and judgement of several persons, which results into more efficient management of the business, partners with complementary skills may be chosen to avail the benefits of specialization.
- Flexibility of operations; through not as versatile as sole proprietorship, it enjoys sufficient flexibility in its day to day to operations. The nature of business can be changed wherever the partners desire.
- Protection of minority interest; no basic changes in the rights and obligations of partners can be made without the unanimous consent of all the partners.
- Capacity of survival, the capacity for a firm to survive is higher than that of a sole proprietorship, i.e. it can continue after the death of one partner.
- Partners share losses and risks, hence, no great burden being shifted to one person as in sole trade.
- Better human and public relations, due to number of representatives (partners of the firm, it is possible to develop personal touch with employees, customers, government and the general public.
- Business secrecy, it is not compulsory for a partnership firm to publish and file its accounts and reports. Thus important secrets of business remain confidential to the partners and are unknown to the outside world.
Demerits of Partnership
- Unlimited liability; i.e. every partner is jointly and severally liable for the entire debts of the firm.
- Limited resources; the amount of financial resources is limited to the contributions made by the partners due to inadequate access to loans. Therefore it is not suited to undertake business involving huge investment of capital.
- Lack of harmony; the success of partnership business depends upon mutual understanding among partners, any disagreement may paralyze the business hence its death.
- Lack of continuity, a partnership may come to an end with retirement, incapacity, insolvency or death of an active partner.
- Non-transparency of interest, no partner can transfer his shares in the firm to an outsider without the consent of all partners; hence, an individual’s capital is blocked. ü Joint responsibility may lead to delays in making decisions.
- Partners will have to share profits of the business yet some are not equally contributing to its operations.
- Decisions made by one partner are building to all other partners though they may not be agreeable to them.
3. Joint Stock Company
A joint stock company is an in co-operated and voluntary association of individuals to carry out business together under the companies’ Act. They usually have joint capital divided into transferable shares of a fixed value. There are two types of companies, i.e. private and public limited companies. By law, a public ltd company’s membership ranges from seven to no maximum limit, members can transfer their shares freely, they have limited liability, it must also present the above documents (as in private) before it can exist and it can start operating unless it has acquired a certificate of trading. However, with private company, it can commence once it receives a certificate of incorporation.
Advantages of a Company
- Limited liability i.e. shareholders of a company are liable to the extent of the face value of shares held by them.
- Large financial resources; it facilitates the collection of huge financial resources due to a big number of shareholders.
- Continuity; a company enjoys uninterrupted business and life. As a body corporate, it continues to exist even if all members die or descent it.
- Transferability of shares; a member of a public limited company can freely transfer his shares without the consent of other members.
- Professional management, due to its large financial resources, it can avail of the services of expert managers with the required skills which leads to profitability and efficiency.
- Scope of growth and expansion; there is a considerable scope of growth and expansion due to its vast financial and managerial resources and limited liability, this can help it to reap various economics of large scale which improves on efficiency and reduces costs.
- Public confidence, a company can acquire public confidence since its activities are regulated by the government under the company’s act.
- It is a separate legal entity i.e. it is separate from the owners, and hence can be sued on its own. This is advantageous in that in case of a loss made by the business, the owners are not affected.
Disadvantages of a Company
- Difficulty of formation; it is so expensive and difficult to form as a number of documents have to be prepared and presented to the Registrar of companies.
- Excessive government control in form of rules and regulations, submission of periodic reports, which reduces efficiency and flexibility of the business operations.
- Lack of motivation and personal touch as there is a divorce between ownership and management in public companies.
- Delay in decision making; there are many levels in management, which results into the red tape and bureaucracy.
- Conflicting interests; since they are many, there is a possibility of having conflicting interests, for instance, between shareholders and management, this retards growth.
- It is accompanied with corruption, fraud and embezzlement of companies’ funds.
- Lack of secrecy as it is required to disclose and publish a variety of information on its working/ operations.
- Such companies are usually interfered with political situation, for instance, as in electing the top management, it may be influenced by the ruling government for their own benefits that could be contrary to those of the members.
4. Co-Operatives
A cooperative is a group of producers or consumers who voluntarily join together to achieve a common social or economic objective, by pooling their resources and working together. A cooperative society is an association of members who come together and contribute to its capital with an aim of carrying out an activity to realize mutual benefits like profits.
Types of Cooperative Societies
There are majorly four types and they include;
- Consumer co-operative societies; these are owned and operated by a group of final consumers who purchase and distribute goods/ services to themselves at a fair price.
- Producer co-operative societies; these are owned and operated by producers who collect, process, market and transport their produces, they deal in products like coffee, tea, cotton, etc, they normally do this to avoid being exploited by individual buyers.
- Wholesale co-operative societies; these are almost the same as consumer co-operatives, having the same principles, but these normally operate on large scale with huge capital investments.
- Savings and credit co-operatives; these are set up to encourage producers, consumers and other groups to carry out savings and also offer them assistance in form of loans and other facilities to carry out profitable businesses.
- Transport co-operatives; these are formed to provide transport services to the public and members at affordable prices/ fair.
Principles of Co-Operative Societies.
- All members are entitled to a fixed rate of interest on their capital contributed.
- Members get dividends according to their participation, like in consumers’ co-operatives, a member who buys more, gets more dividends.
- Co-operatives are expected to be politically neural with no religious or political bias.
- Members have equal voice because each member has one vote (democratic principle).
- In case one wants to leave the society, he/ she can only sell his shares to another willing person but cannot be refunded.
- Directors are elected by members themselves, but not appointed.
- There is free and voluntary membership, i.e. whoever feels he can abide by the rules and regulations of the society can join.
- Management and decision making is in the hands of the members since they follow a “one man one vote” principle.
Functions of Co-Operative Societies
- They help in the marketing of farmers’ produce at fair prices.
- They provide training facilities to the farmers, like the modern farming methods at low or no cost.
- They provide storage facilities for the farmers’ produce.
- They offer transport facilities for the farmers’ produce to the market centers.
- They carry out research on behalf of farmers and hence extend quality and modern farming techniques to farmers.
- They provide agricultural raw materials and farming tools at low costs.
- They mobilize funds from the members, which can be extended to other members in form of credit facilities/ loans hence, increasing productivity.
- They may also access credit facilities from financial institutions on behalf of their members, which can be used to boost their businesses.
Problems Faced by Co-Operatives in Uganda
- Inadequate capital as members may fail to pay their contributions; this limits the programs of the societies.
- Lack of business experts in management, most societies are run by illiterate members since they lack funds to hire experts, this also hinders the operations of the society.
- Corruption and embezzlement of members’ funds by top managers, this is so common among societies and leads to its collapse.
- Most societies offer little or low interest on capital which is contributed by members, this discourages them and other members from injecting in their money hence, limited growth.
- Most of the areas where such societies operate from are remote, coupled with poor infrastructural development like roads; this makes transportation of their produce expensive and difficult.
- Literacy of the people, most of the people are illiterate and hence, difficult to convince them of the importance of joining such societies, they think it’s a form of taking their funds; this also hinders the growth of such societies.
- Since most of them deal in agricultural produce, they face a problem of price fluctuations in the market, this also leads to fluctuations in profits and incomes of the members.
Factors considered when choosing a Legal Form of Business Ownership.
- Nature of business; i.e. service, trading, manufacturing e.g. manufacturing businesses are more commonly set up by companies since most of them operate on large scale.
- Size and area of operations; e.g. large scale enterprise catering to national and international markets can be organized more successfully as private or public companies.
- Degree of control desired; a person who desires direct control of business prefer sole proprietorship.
- Amount of capital required; e.g. organizations, which require heavy investment, should be organized as joint stock companies.
- Degree of risk and liability, e.g. a single individual may have enough financial resources enough for a medium or large scale enterprise, but due to unlimited personal liability, he may not organize it as a proprietorship business.
- Division of surplus; e.g. a sole trader receives all the profits but bears all the risks alone, so if a person desires or deserves maximum share of profit, proprietorship is preferred.
- Duration of business, temporary ventures can be organized as proprietorship as they are easy to form and dissolve; however, they lack continuity and stability.
- Government control, partnership and proprietorships are subjects to little regulation and control by the government.
- Flexibility of operations, businesses which needs a high degree of administrative flexibility should better be organized as sole proprietorships.
- Tax burden, various forms of ownership are taxed differently under the income tax, proprietorships and partnership share a little or no tax burden as compared to companies.
- Identifying the location of the business, this should also be highly considered because the location should be favourable in terms of easy reach of the market and minimizing operating costs like transport costs from the raw material source and to market centers, Etc.
- Starting business operations; once the above start-up process is accomplished, an entrepreneur is now ready to start business operations.
Assuming it was a trading business, one may commence operations in the following format;
- Mobilizing and setting up required business funds Preparing and cleaning the business premises.
- Procuring the necessary business stocks/ merchandise/ goods to be sold.
- Displaying the stocks/ goods in their shelves properly, ready to open the premises.
- Acquiring bank, accounts and arranging for books to be used in recording business transactions.
BUSINESSES IN UGANDA
A business refers to any economic activity undertaken by an individual with a view to make profits. It involves exchanging goods/ services for money or for goods/ services. Profits in business are realized after selling commodities at higher prices than the cost of producing or providing them.
Types of Businesses
Businesses can be categorized into the following types;
- Agri-businesses; these are businesses that produce agricultural products like crops, animals, poultry farms, etc.
- Manufacturing Businesses; these are businesses that transform raw materials to produce different products or add value to the products. For example, carpentry workshops, car making businesses, those that process agricultural products like food processing, milling factories, etc.
- Trading Businesses; such businesses deal in buying and selling of goods/ merchants, e.g. Kiosks, hawking businesses, etc.
- Service Businesses; These provide services to customers. They use special skills of their owners and workers, e.g. hair salon business, restaurants, health clinics, schools, etc.
Size of Businesses
Businesses vary in size and they can be categorized according to how they measure against some indicators. Such indicators used in determining the size of businesses includes;
- Amount of capital invested in the business.
- The number of paid employees.
- The level of technology used.
- Volume of sales realized over a given period of time. Basing on the factors above, businesses can be divided into the following sizes; micro, small, medium and large, they are further discussed below;
- Micro-Businesses: These are very small and require very little capital/ money to be started. Simple technology used, usually employ their owners and family members, have very low sales, may not need fixed premises to operate from, may not require registration by the authorities for them to operate. They include Kiosks, hawking, road side selling, etc.
- Small Businesses: These have fixed/ permanent premises, they may also employ family labour, require little capital to start, have relatively higher periodical sales than micro, may use simple and basic technology, may not need formal registration to start, majority of them produce for local markets and little for export. They include; shops, bakeries, milling businesses, etc.
- Medium sized Businesses; These are well established businesses, they employ up to 100 people, have well established premises, use advanced technology, produce on relatively large scale, need a lot of capital, they are formally registered as limited liability companies, may produce for both local and foreign markets. They include, big packing businesses, big bakeries, milk processing businesses, mattress manufacturing businesses, etc.
- Large sized Businesses: These are very large, employ over 100 people, have specialized methods of production (like automated methods), need too much capital, normally emanate from medium sized businesses as they grow and expand, have very big and well established premises, produce for both local and foreign markets, etc. They include Mukwano firms, Tea estates like those in Eastern Uganda, Lweza clays limited, Roofings limited, etc.
Importance of Businesses
Businesses play an important role to the owners, families, communities in which they are located, the government and to other businesses. The major importance includes;
- They are a source of income to their owners.
- They provide employment opportunities to people. They produce goods and services needed by people. iv. They bring goods and services nearer to people.
- They provide market for people’s produce.
- They make use of the local resources, which would be idle.
- They contribute to the community social and economic development programs.
- They pay taxes to the government, which can be used to provide social services to the people.
- They use items that would be useless or harmful to the man and environment, like recycling firms.
Business Associations in Uganda
They are formed by businesses which voluntarily come together and agree to work towards achieving a common objective, like an objective of meeting their needs and protecting their interests which cannot be achieved by one business unless they unite.
- Uganda Manufacturers Association (U.M.A).
- Northern Uganda Manufacturers’ Association (N.U.M.A).
- Uganda National Chamber of Commerce and Industry (U.N.C.C.I). Uganda Women Entrepreneurs Association (U.W.E.A).
- Uganda National Farmers’ Association (U.N.F.A).
- Uganda Small Scale Industries Association (U.S.S.I.A).
Objectives of Business Associations
These vary from one association to another, however, the common ones to most business associations includes;
- Securing or accessing local and foreign markets for their members’ produce. ü Sourcing or accessing raw materials for their businesses.
- Accessing and providing training facilities and programs for their members. d. Accessing better production technology for their businesses.
- Accessing financial and technical support from different financial institutions. f. Supporting individual members in times of need.
- Developing and transmitting improved and better production and management systems to members.
- Advocating on behalf of their members to the government for better environment and favourable policies like favourable taxes, economic and political stability, etc.
SERVICES RENDERED BY BUSINESS ASSOCIATIONS
Business associations render services which help their members to achieve their goals and also achieve the objectives for which they were formed. Examples of services rendered includes;
- Providing information on market opportunities and charges.
- Negotiating and securing local foreign markets for the members’ produce.
- Sourcing or accessing raw materials for their businesses.
- Identifying appropriate and better production techniques for their businesses.
- Developing and provision of training programs for member staffs.
- Negotiating and securing financial and technical support from financial institutions and the government.
- Providing moral and material support to members.
- Carrying out advocacy campaigns on behalf of the members with the government for better investment incentives, tax policies, momentary policies, etc.
Benefits from Health Service Businesses
Service businesses also play a role to the owners, families, and community; the benefits are almost similar to those of agri-businesses and manufacturing businesses. However, the following are unique to service businesses;
- They support the operations of other businesses and help to improve productivity, through provision of communication facilities, finance, transport, power, etc.
- The government and communities use some service businesses to promote their development programs like communication businesses, for instance over the radios, televisions, newspapers, etc.
- Service businesses like transport and communication help to open up different parts of the country, and also other businesses can be set up in those areas hence, more opportunities and community development.
- They provide financial assistance to other businesses like giving them loans, safeguarding their deposits, etc, all this is done by financial institutions.
- Through health services, people’s health is improved and this leads to increased productivity and profitability of various businesses.
- Security services promote a conducive and secure working environment for other businesses; this maintains confidence in entrepreneurs and attracts other businesses hence, development.
- Education services instill knowledge and skills; this helps manpower to be equipped with the necessary skills, improved productivity and economics of scale.
Challenges in Health Service Businesses and how to overcome them
Some of the challenges to agri-businesses and manufacturing businesses do also affect service businesses, however, the following are unique to them;
- Since the quality of the service rendered depends on the skills of the entrepreneur and workers, ensuring that workers are motivated and equipped with the necessary skills so as to provide quality service is still a challenge, e.g. how to ensure that a teacher provides what exactly he is supposed to provide.
- Retaining the staff is still a challenge as those who are experienced normally are taken by competing and emerging firms.
- They are associated with high cost of inputs, this is due to the stiff competition, entrepreneurs need to incur higher costs as to provide quality services like high salaries to employees, this leads to reduced profitability.
- Most businesses face bad debts from their clients who fail to meet their obligations, this is a big threat to the profitability of the business.
Ways of Overcoming the Above Challenges.
- Provision of favourable working conditions in order to maintain the workers in business, like good salaries, and allowances, etc.
- Conducting a market survey so as to deal in a business where they have sufficient and affordable technical expertise and ability to face competition.
- Avoiding or minimizing credit facilities in order to reduce bad debts and setting up strict rules for those who fail to pay, like signing contracts of sale of goods which are enforceable by law.
- Ensuring that staff is equipped with all the necessary facilities that would maintain the quality of the services rendered, for instance, providing constant training and workshops to equip them with modern operational skills and techniques, etc.
Some of the indicators used to measure the success of a business include:
- An increase in assets: A successful business will have its production operations increase every after time, (due to increased demand) and this will call for additional assets to handle the increased volume of operations, like buying another production machinery to help increase the production capacity required to meet or cope up with new orders.
- Increased profits: A persistent increase in the level of profits indicates success of a business, may be due to an increase in the volume of operations brought about by increased demand.
- Experience of the business: A successful business will experience a constant expansion in form of market share, production lines (number of products produced), improved quality, increased number of employees and assets, etc.
- Recognition in business community and the general community e. the business reputation in the market and community, other level of respect and recognition an entrepreneur and his/ her business gets from the community, other entrepreneurs’, the government, customers, etc shows how well the business is doing.
- The rate of returns on investment, a successful business will consistently realize an increasing rate/ level of returns on capital that was invested by owners. This is quite different from the overall profits realized.
Factors Leading to the Success of a Business.
- Personal entrepreneurial characteristics of the management and business owners i.e. such people should possess the required PECs if the business is to succeed. This will provide their business with good, effective and effective leadership and management.
- Clear objectives: For a business to be successful, it should have clear and defined objectives and once they are set, an entrepreneur should ensure that he/ she closely follows the guidelines that were set to achieve these objectives.
- Efficient and effective planning: This is an important factor if a business is to succeed sine it enables a business to set its targets, methods of achieving them and resources needed in the process. This therefore enables a business to operate within a known and provided framework hence, saving it from losses, crisis and moving off course.
- Proper location and plant layout: This greatly affects the success of the business. Appropriate location of business in securing the required inputs like raw materials, labour, etc and access markets at lower costs. It also needs to have a proper layout of plant, equipment, machinery, etc to provide efficient utilization of resources, time, labour, energy, materials, etc.
- Availability of market: it is useless to produce goods and services where there are no customers to buy them at a price that will yield profits to the business. So the existence of the market that is people willing to buy the products at profitable prices will lead to high chances of success to the business.
- Conducive government policies: In case policies are conducive, it will lead to business growth and success, e.g. fair taxation, controlled inflation, fair interest/ bank rates, social, economic and political stability, etc.
Benefits of a Successful Business to an Entrepreneur
There are a number of benefits that an entrepreneur enjoys through running or operating successful business, these include:
- Self-reliance and fulfillment: One gets to do things for him/ her, maintain self-confidence and carry out independent decision. He/ she will also be in position to meet or produce some if not all of his/ her needs.
- Increased income and further investment, as profits increase, a part of which can be used for fulfilling his/ her personal needs and then the rest could be used for further investments like putting up another production line or another production line or another business opportunity.
- Recognition in community: A successful entrepreneur and his business are highly respected and recognized in society, because of the goods and services they provide, which in the end attracts more customers to the business.
- Improved standards of living: Due to the increased profits, an entrepreneur enjoys increased income which makes him be in position to meet most of his needs and thus improving on his standard of living.
- Permanent address for an entrepreneur and the workers, i.e. a successful business is always established and permanent which provides confidence and a permanent address for the owner and the workers.
Factors leading to Business Failure
There are very many businesses that are started and fail afterwards, they totally disappear without even noticing their route to disappearance. This is due to a number of factors and they include the followings;
- Inadequate market for the products, i.e. when the business is not having enough people who can buy its products, it will automatically fail, for instance, if there is stiff competition, varying customer tastes, un competitive market prices, etc, all this will lead to a low market share hence failure.
- Poor handling of customers: No business can survive with dissatisfied customers, when customers are handled poorly, e.g. when the entrepreneur and employees are rude, and do not listen to customers’ needs and complaints. This forces them to shift to your competitors and thus failure of the business.
- Poor management of business stocks: when a business, i.e. when a business fails to manage adequate varieties of goods in the shops, customers will end up looking for other competitors who are always equipped with a variety of goods from which they can make their choice, i.e. where there is ready supply of commodities.
- Poor or low quality of products for sale i.e. this is measured in terms of customers’ expectations and competing products, which reduces the number of customers as they move to other businesses which produce better quality products and hence low sales due to high competition which results into failure.
- Unstable business location i.e. when a business was located in a place that is unsuitable, there are various considerations made choosing location like access to raw materials, market, enough land, labour, power and transport. So in case some or all these were not considered, it will affect the profitability of the business due to high costs involved in accessing all those factors, hence leading to business failure.
- Poor management of the business: For instance, if the management is inefficient in utilizing the resources, no proper record keeping, use of wrong costing and pricing methods, etc, all this will lead to increased costs and then losses which in the end leads to business failure.
- Loss of interest of an entrepreneur: Sometimes an entrepreneur may lose interest in the business, may be if it does not suit his/ her personal intentions and characteristics, he/ she ends up losing direction and thus collapse/ failure.
Management Mistakes that cause Business Failures.
It is very important that one gets to know the common management mistakes that lead to business failures. These will enable one to avoid them and save his/ her business from failing due to similar reasons. Some of these management mistakes includes;
- Mistaking cash for profit: Some people tend to mistake cash received from the sale of goods/ services to be profit, so they tend to use it for other purposes that may not be related to business operations, and as it gets finished, the business fails to meet its financial obligations like buying new raw materials, paying employees, etc, thus failure.
- Uncontrolled credit facilities being given to customers: A business requires a constant fund/ cash flow if it is to meet its operations and succeed. But if many people like friends take a lot of goods without immediate payment, the business will soon run out of cash to be used to meet the operating expenses (working capital) and if the entrepreneur does not have more cash to inject in it, it will fail and close.
- Lack of record keeping: Unless there is proper record keeping, it is very difficult to ascertain whether the business is facing financial troubles or not, like if the entrepreneur does not know who owes him and how much is remaining in the business, how much profits are realized in a given period, etc, this will lead to funds flow problems due to failure to detect it before it’s too late and hence, business may fail in the end.
- Poor customer care: If the customers are poorly handled, they will go to other businesses where they are treated better, thus the business runs out of cash leading to collapse and failure.
- Neglect; e. Little attention that is given to the businesses by their owners, this leads to lack of supervision and guidance to business employees, the business ends up losing directions and control, good workers may leave the business and hence quality declines which leads to low sales and eventually failure.
- Incompetence; e. ability of the business owners and employees to manage the business operations efficiently, this may be due to inadequate technical skills and staff required to do the work, hence collapse due to limited market for the poor quality goods produced.
- Theft of business funds, stocks, assets, This may lead to loses in business due to inadequate requirements. Theft may be done by either employees, thieves from outside the business, etc. Hence, low operations and output, leading to low profits and thus collapse and failure
- Interference of the family members in the running of the business, this may lead to misuse of business funds, increased bad debtors, chasing away of useful business employees and partners, etc, this leads to low productivity and output, leading to low sales, low profits and consequently leading to failure.
- Death of the business owner (incapacity of the owner); if the entrepreneur or owner dies or runs mad and there is no one to take over his/ her responsibilities in business, thus may lead to family wrangles and poor management thus leading to business failure.
Indicators of Non-Performing Businesses.
There are very many signs which can show that a business is not doing well. These may include;
- Empty shop shelves i.e. when the business does not have cash to buy fresh stocks to replace old ones.
- Expired or absolute goods i.e. where the business has lost market, may be when its products do not meet customer needs, or due to competition.
- Low profits, i.e. where the operating expenses are high or the prices have declined and the business cannot do anything about it, it cannot re-invest to expand or change line of business. D
- High expenses which reduce the profits of the business, i.e. if the business cannot increase the selling price to offset the increasing expenses.
CONCEPT OF INVENTORY
Inventory refers to good/ stock that are held by a firm for eventual sale Or inventory refers to the stock of goods held in the business at a given period of time
Types of Inventory
Raw materials: these are goods used in the course of production to produce other goods for consumption. They are goods which have been received by the business but not yet committed to the production process.
Work in progress / process (semi – finished goods): these are goods which are still in the production but are not yet completed.
Finished goods: these are goods which have been completed and gone through the production process waiting for sale to customers.
Goods under repair: these are goods that may be damaged during the process of production or distribution and need repair.
Office supplies: these are materials which are used to support the production process for instance stationery, cleaning materials like soap or detergents.
Need for Inventory
It is necessary to hold some inventory both for a manufacturer as well as a trader so that production and sales can continue uninterrupted. The specific benefits of holding inventory may include.
- To avoid loss of sale, by holding inventory, a business firm can avoid sales losses, which may occur because goods are not available when demanded by customers.
- To reduce ordering costs, cost of placing orders e.g typing, mailing etc can be reduced in a firm. A firm places a few large orders instead of several small orders.
- To achieve efficient production run. Holding enough inventory protects against shortage of raw materials that may either delay or halt production due to no availability of materials.
Costs of Holding Inventory
Several costs and risks are involved in maintaining inventory. They may include;
- Material costs. This includes the costs of purchasing the goods, transportation and handling charges less any discount allowed by the supplier of goods.
- Ordering costs. It comprises of cost of placing orders for purchase of raw materials and components. The fewer the orders, the lower the costs.
- Carrying costs. These are composed of expenses for storing the goods e.g insurance, cost of funds tied up in inventory, spoilage costs, decline in price of goods etc.
Inventory Control /Management
Inventory control refers to the system which ensures that the right quantity and quality of the inventory required is supplied at the required time without unnecessary investment in inventory. It includes control of raw materials; semi-finished and finished goods, office supplies and goods under repair.
Reasons for proper management of inventories in business / objectives on inventory management
- To maintain adequate so as to avoid production stoppage, loss of customers and revenue to competitors.
- To avoid excessive investment in inventory ie to avoid tying up a lot of working capital in investment.
- To reduce stock losses while in stores through theft, expiry of products, damages, unauthorized use, pilferage etc.
- To relieve management on excessive supervision of inventory.
- To minimize storage costs in terms of rent.
- To encourage proper accountability for the goods which have been purchased as issued
- To allow flexibility in production scheduling as well as marketing. This is possible through ensuring that inventories are available whenever required for production or for sale
- To ensure efficient use of raw materials
- To ensure timely replacement of raw materials for production of products for sale.
- To meet demand fluctuation and avoid expensive and embarrassing stock out through ensuring that inventories are available whenever required for production or for sale.
Tools for inventory management
- Re-order level. It refers to the minimum level below which the stock should not fall before fresh (new) orders are placed. This technique reminds the entrepreneur to place fresh / new orders because the stock is running out.
- Lead time. This refers to the time it takes from when one places and order for goods and when the ordered goods are received.
- Working capital. This is the amount of money used to buy stock for a given business or to meet daily financial operating needs of the business. Working capital helps the entrepreneur to meet the day to day operations. In case an entrepreneur has a small working capital then he/she has to place small but many repetitive orders.
The Concept of Store management
Store refers to places where stock of raw materials or goods are kept before they are sold or dispatched to business which ordered for them
Stores are important because they help to protect the stock of raw materials or goods from getting spoilt, damages or stolen. It is therefore important that a business manages its stores properly so as to avoid losses through theft, damages, unauthorized use, expiry etc Tools for effective store management
Stock cards. These are cards used for recording stock received and issued in the store. Stock cards normally show amounts of goods available in store, the date when goods have been issued.
Stock requisition and issue form, a stock requisition and issue form refers to a document that shows details of goods being requested for the corresponding need, the issues under this technique, the person in need of goods fills it and gets if authorized by the responsible person / store that against receiving the form issue them.
Physical and stock counting. This refers to the counting of stock physically to find out what is available in store and cross check to what is expected to be there as per the stock cards.
Stock reconciliation. This refers to the process of updating and balancing all the records regarding what is in the store so as to give a true record and then checked to what is physically in the store. This technique helps the entrepreneur to decide whether to order for more goods or not.
Stock taking. This refers to the actual counting of the stock available in the store.
Under this technique, the entrepreneur counts his stock one by one so as to ascertain the actual number.
MANAGEMENT IN SMALL ENTERPRISES
Introduction;
Management can simply defined as the art of getting things done through people and proper utilization of resources of the business so as to achieve its objectives and goals. Management in small enterprises is mainly done by an entrepreneur him/ herself as a top manager and may be a few other employees as lower managers.
The Role of an Entrepreneur in Managing Small Enterprise
- An entrepreneur carries out decision making on various business issues, like initiating and identifying business opportunities, accessing the necessary resources like capital, labour, etc, organizing meetings with other managers, arrangement for expanding or improving the business products, etc.
- He resolves conflicts that may arise with other businesses in the course of competing for the market share, even resolving conflicts among the employees due to misunderstandings. His aim is to make sure that he/ she solves all these differences that could affect the operations of the business.
- He plays an important role in allocation of business resources. Such resources include finance, machinery and equipment, time, etc to different activities of the business. This proper allocation of resources will lead to efficiency.
- An entrepreneur also plays a role of carrying out negotiations with numerous business partners, for instance negotiating for contracts with suppliers of raw materials and machinery. This helps in bargaining for favourable prices charged, also negotiates with prime customers for favourable conditions in the market like prices, etc.
- After getting the necessary information, he/ she convey or disseminate it to the concerned parties like employees, this helps them to be aware of the changing market needs and hence to carry out operations basing on the existing needs. This is done through distributing memos, through phone calls, conducting meetings and workshops, etc.
- He carries out constant monitoring of the business environment, collects information relating to the enterprise, like customer tastes and fashions. Such information could be got through personal touch with customers, over the various forms of media, attending business conferences and seminars, etc.
- An entrepreneur plays a role of leadership, through guiding and directing others with respect, encouraging them to be committed and dedicated to the work, however, he/ she lead by example which encourages employees to perform the assigned activities well and better.
- An entrepreneur acts as a network officer i.e. he/ she coordinates with the outside environment, this is done through regular communication and cooperation. It helps him to assess the competitors’ performance, market changes, the changes in government policies. Such coordination can be achieved through attending conferences, meetings, via the internet, etc.
- He plays a figure head role, for instance, internally, he attends employees’ gatherings like weddings, graduation ceremonies, etc, and externally he receives visitors warmly, signs legal documents, giving speeches in public places, etc. this promote a good image of the enterprise and unity both within and outside the enterprise.
Importance of Management in Small Enterprises
- Management enables an entrepreneur to make maximum use of the business resources, this leads to efficiency due to increased profits and reduced costs.
- Management helps an entrepreneur to recognize the value of a customer in an enterprise, and hence maintaining the quality of products to satisfy the customers, this retains and attracts more customers which increase the firms’ sales and profits.
- Proper management enhances the image of the business which creates a good will for the business and through this; it becomes easier to access funds from outsiders, and obtain credit facilities from suppliers, which leads to expansion of the enterprise.
- It provides a good relationship and open communication with all employees, this promotes team work, dedication and commitment to work hence, increased productivity and efficiency (thus an enterprise achieving its set goals).
- Good management also promotes a stable working atmosphere through its operations that follow the laws and regulations of the government, like prompt tax payment, respect of the environmental laws and those concerning pollution. These stable environments with the state facilities smooth operations of the enterprise.
Functions of Management in Small Enterprises
Apart from the management role, management also carries out special activities that are designed for practical purposes, these are termed as functions, and they include planning, controlling, staffing, communication leading, organizing and budgeting. They can be discussed as below;
- Planning; this involves establishing goals and objectives of the business and identifying ways in which they will be achieved. Planning involves; setting goals and objectives of the business, determining alternative courses of action to achieve the goals and objectives, selecting the best alternative and formulating strategies to translate the chosen alternative action.
- Organizing; this refers to identification of the different activities to be done, grouping them into sections and delegating them to particular individuals to carry them out. In order to carry out efficient organization, an entrepreneur should;
- Identify the tasks that must be performed and group them into sections/ departments like selling and distribution under marketing, buying raw materials under purchasing department, etc.
- Assigning these tasks to individuals and defining their responsibilities and authority e.g. assigning a sales manager to carry out marketing task.
- Delegate this authority to chosen employees, like heads of departments, managers, etc. ü Coordinating these activities to ensure that they are carried out as earlier planned.
- Staffing; This involves the process of recruiting, training, developing and evaluating employees who carry out the identified tasks. It also involves maintaining these employees with proper and favourable incentives like good payments, so as to encourage them remain committed to their work.
- Leading; This involves motivating and guiding employees/ subordinates about the procedure and also lead by example, should also motivate and appreciate work done by the employees, through giving rewards, word of mouth, promotion, etc.
- Controlling; This involves those activities that are undertaken to ensure that activities done conform with the predetermined plans, like looking at the set goals to find out whether they have been 266 achieved as per the plan or not, and in case there is a change from those pre-determined ones, corrective measures should be undertaken to restore them.
- Communication; This is the process of passing or transmitting information, ideas, facts or understandings from one person to another, for instance, an entrepreneur passing ideas to his employees, suppliers, customers etc as to carry out successful operations. It should be noted that communication is a two way form. i.e. it involves an entrepreneur transmitting information to such parties and gets a feedback from them. (Open communication).
- Motivation; This is a process of enticing/ encouraging employees to do their best towards achieving the desired goals of an enterprise. An entrepreneur does this in a desired manner, like favourable working conditions, job security, promotions, etc.
- Budgeting; This is a process of preparing a budget. A budget is a detailed plan that shows the use of funds and other resources over a given period of time. It represents a plan for the future expressed in quantitative/ monetary terms.
Importance of Budgeting
- It provides managers with a way to formalize their planning efforts, since each planned activity is documented and the associated costs to be incurred are determined, hence, proper planning.
- It avails defined/ stated goals and objectives that serve as a bench mark for evaluating the performance of the business during the course of operating.
- It shows/ reveals potential hinderances of problems prior to their occurance i.e. before they occur.
- It co-ordinates various activities in the entire business by integrating the plans and objectives to various departments i.e. management ensures that plans of different sections like production, finance, etc are consistent with the general goals of the business.
- Budgeting helps in daily supervision of cash and receipts and expenditures/ payments made.
- Budgeting facilities banking of the cash surplus or balance that can be used for further business activities like expansion of the business.
- It helps in prompt settlement of business debts like paying business credits on due dates, sheet, etc helps in proper and timely payment of taxes, rent and other related expenses. NB: There are various management tasks that an entrepreneur executes while performing the above functions, these tasks are briefly discussed below.
Management Tasks
A task refers to a specific activity organized and carried out to meet a given purpose or a particular purpose. In small enterprises, management tasks includes production, marketing, personal and financial management as discussed below;
- Production management; This involves planning and controlling production activities, it includes; acquiring inputs (factors of production) and transforming them into output i.e. semi-finished or finished goods.
- Marketing management; This deals with marketing the produced output (from the production management) in order to satisfy the customers as well as making profits. The various aspects involved are;
- Providing/ selling goods/ services that customers need.
- Setting prices for goods that is favourable to customers but profitable to the business.
- Assessing the goods/ services within easy reach of customers. ü Informing and persuading customers to buy the products.
- Personnel management/ Human resource management; This involves managing the people who carry out the business activities, this is important because human resources are the people who acquire the inputs, manages them, into output, markets them and collects the money. This makes it an important part in management since it determines the survival of the business.
- Financial management; This involves routine functions that are performed within the enterprise to ensure efficient use of funds. This may involve the following tasks.
- Supervising daily cash receipts and expenditures.
- Banking of the surplus cash balance.
- Debt settlement i.e. suppliers, funders, etc. ü Proper record keeping, etc.
BUSINESS PLANS
Business Planning
- Planning is the decision making ie deciding what to do, how to do it and when to do it. I.e. determining the future course of action.
- Business planning is an activity that involves the organisation mention and follows up the different business activities right from the beginning of the business.
- A business plan is written document that summaries the operational and financial objectives of a business and contains the detailed plans and budget showing how the objectives are to be realized.
Types of Business plans
- Formal business plan. A formal business plan is a detailed document that usually follows a standard format. They are necessary for securing outside funding for a business.
- Informal business plan. This is a planning tool for the business which is not presented to other people/ organisations. They are merely a planning tool for the business owner.
RATIONALE FOR WRITING A BUSINESS PLAN (OBJECTIVES, AIMS AND PURPOSE)
- To test the feasibility of the business idea. Writing a business plan enables the entrepreneur to establish whether or not an idea for starting a business is feasible other than going out and doing it
- To give the business the best possible chance of success. Business planning encourages the entrepreneur to pay attention to both the broad operational and financial objectives of his new business and the detailed such as budgeting and marketing planning
- To secure funding such as bank loans. Having a business plan gives an entrepreneur a much better chance of getting the money he needs to keep operating or to expand
- To attract investors. A solid business plan enables an entrepreneur to attract investors. Investors normally need a well written document they can take away and study before they make any investment commitment
- To make business planning manageable and effective. A business plan is not only good to starting business but also important for established ones
- To monitor the performance of the business overtime
- In order to calculate and pay the exact amount of tax to the government
- To develop a timetable for implementation of various business activities in a sequenced way
IMPORTANCE OF PREPARING A BUSINESS PLAN
- It helps in adequate preparation for the business; it encourages an entrepreneur to think through his business thoroughly in order to prepare for identified sensitive areas which will need more attention
- It helps an entrepreneur in defining specific goals and objectives which serves as a bench mark to measure the progress of the business in implementing the plan
- It facilitates business monitoring based on the set goals and objectives as a standard of measurement such that any deviation from the set plans can be detected from and corrected in time
- It encourages an entrepreneur to be and remain focused by thinking about the business he/she is in now and business he wants to have in future
- It acts a time table for implementing business activities in a logical manner
- A business plan helps an entrepreneur in accessing financial assistance from the lenders, it is through the business plan that lenders will determine whether to fund
- the project or not and how much it will inject in
- It eases the work of an entrepreneur as his employees will use it to know the business objectives or targets in terms of production, profitability, it will also clearly state their duties and responsibilities plus their related remuneration
- It facilitates easy decision making as it clearly spells out the expected cash inflows and outflows of the designed business
- It shows the feasibility and viability of the business thereby enabling an entrepreneur to determine whether to carry on with the opportunity or try other business alternatives
- Enables the government and local tax authority to determine the tax revenue to be paid by the business and likely effects of the business to the environment
Steps involved in preparing a business plan
- Selecting a business opportunity or type of business to engage in. this involves scanning the environment to generate many business ideas to choose from.
- Conducting market survey for the selected type of business. This involves checking whether the entrepreneur’s chosen business idea can be developed into a profitable business in terms of fulfilling the market needs.
- Collecting all the relevant data concerning the different aspects of business and establish the costs of different items like machinery and equipment, raw materials, transport etc.
- Drafting the business plan to be discussed with experienced people. This business plan enables the entrepreneur to know how the business will be organized, establish the amount of money needed to start and run the business before starting it.
- Discussing the drafted business plan with technical / knowledgeable or experienced people in similar business.
- Making a final business planning after having discussion with knowledgeable people.
- Finalizing the business planning process by preparing an action plan for implementation of the planned activities.
STRUCTURE OF A BUSINESS PLAN ELEMENTS / COMPONENTS OF A BUSINESS PLAN
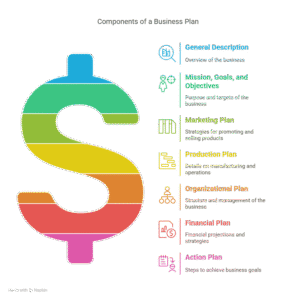
- General description of the business
- Statement of mission, goals and objectives
- The marketing plan
- The production plan
- The Organisational plan/ administrative/ management plan
- The financial plan
- The action plan
General description of the business plan
This involves giving summarized information about the business. Therefore general description of the business, the type of business being planned to be carried on , the needs of the market that is seeks to fulfill giving a summary of how the intended business will be different from other as well as making an analysis of the strength , weakness, opportunities and threats that the business is likely to face.
Statement of mission, goals and objectives
Mission statement, this is a brief statement that indicates the purpose of the business. A mission is a very reason why an organisation exists Uses of mission statement
- It indicates / defines the purpose of the business
- It helps to distinguish an organisations from others
- It helps to keep an organisation focused
- It helps in communicate the direction of the organisation
- It helps to make day – to –day operating decisions
- It helps to motivate employees by indicating their objectives as a team
- It attracts people who support it
- It creates action rather than reaction
- It attracts opportunities and helps an enterprise to maximize them
- It enables an organisation to gain strength and stand chances in the market vision is the result of an entrepreneur’s dream of something that does not exist yet and the ability to paint a compelling picture of that dream for everyone to see vision provides direction as every focus’ his attention on the future.
Goals. A goal is something (target) that one intends to achieve in a given period of time using a given amount of resources
Objectives statement. Objectives are specific targets that must be achieved in a specific period of time. They are
specific (short term) targets that an individual or entrepreneur sets to achieve the established goals Qualities of a business goal
- Should be specific, a good goal should be clear on what should be achieved, when and how to achieve it for example increasing profits by 15% in the next 5 months
- It should be measurable. A good goal should have indicators to prove whether it is being achieved or not and if achieved how much would it take to be achieved
- Should be attainable. A good should be feasible in the area where it is being perused for example setting a bar in a locality where people do not take alcohol
- Should be realistic. A good goal should be achievable given the available resources, entrepreneur’s capacity and legal regulations. It should move in direction of the mission
- It should be time bound. It should have a target time within which it should be achieved for example increasing sales by 20% in 1 year
Marketing plan
This is an analysis of the possible position and opportunities of a business being planned in the present market situation. It is analysis of the marketing objectives, strategies and activities to be followed so as to have improved marketing of the proposed products in order to fight competition.
Factors considered when preparing the marketing plan
- The target market. The entrepreneur establishes who his customers are, where they are located, their needs, their buying patterns ie how they often buy goods and services of the entrepreneur
- Nature of the products or services to be offered. The entrepreneur describes his main products or services and their value to the customers establishes how the products are packed and the features which make his products or services from those of competitors
- Position of the competitors. Here , the entrepreneur establishes the position of firms dealing in similar products like his and those firms dealing in products that may be substituted for his (indirect competitors) in the market he is trying to enter
- Pricing strategies and policies. Under this aspect, the entrepreneur will be required to establish the position of firms dealing in similar products like (direct competitors) and those firms dealing products that may be substituted for his (indirect competitors) in the market he is trying to enter.
- Sales targets. The entrepreneur establishes his total projects sales per given period of time for instance per week, per month etc
- Distribution strategy which is cost effective. This involves selection of the best distribution channels for goods and services in respect of reaching many customers and is cost effective.
- Sales promotion and advertising strategy. This involves selecting the various ways through which entrepreneur will communicate and influence the customers.
- Terms and conditions for selling. Here entrepreneur establishes the terms of sale he is going to adapt for instance selling on credit, cash basis or installment selling.
- Projected marketing expenses e.g advertising and sales promotion expenses
BENEFIT / MERITS OF A MARKETING PLAN TO AN ENTREPRENEUR / BUSINESS
- It helps an entrepreneur to establish his / her target market customers in terms of age, income, occupation, requirement / location
- It enables an entrepreneur to find out the possible of the competitor in order to develop competitive advancement or strategies
- It guides as entrepreneur in deciding on what promotion / strategy to use so as to minimize profits due to increased sales
- It assist an entrepreneur to estimate the projected marketing costs or expenses in business under taking in order to give the appropriate price and eventually determine the likely profits
- Marketing plan enables the entrepreneur to produce relation to the demand / requirements of the customers hence minimizing resource wastage of the business in order to establish the progress of the business or opposition of the business in the market
The production plan
It is an analysis of the projected need for producing (manufacturing) the proposed goods or services (product). It
involves how the entrepreneur is going to carry on production of the proposed goods and services
Factors considered when preparing the production plan
- Business location and its site. Under this aspect, an entrepreneur will have to establish where to locate his business as well as the cost of land (site) and its size. He will have to give reasons as to why he chose this location and estimate the cost of putting up the business buildings
- Production/ manufacturing process. Under this aspect the entrepreneur is expected to show the flow of work and layout, how the machines will be laid down and how they will be used.
- Plant capacities required. This involves establishing the abilities of production machines in relation to meet the demands of the market
- Quantities to be produced or services to be provided and their delivery at different schedules. Quantity to be produced is determined by the target market one is serving ie the number of customers for business
- Production standards and quality objectives to be maintained during production
- Machinery and equipment to be used in production in terms of costs, technical specifications, production capacities, source terms and conditions for payments of machinery and equipment
- Raw material to be used. Here , the entrepreneur establishes the type of raw materials he / she will use to make his / her product(s) while considering various factors like the cost of raw materials, their quality etc.
- Packaging. Under this aspect, the entrepreneur establishes how the products are to be packed, where to buy the packaging materials and their costs, how much will be required per production cycle, how much to stock and how much the packaging materials will be stored properly.
- Labour requirement. Here the entrepreneur establishes the type of workers he/ she will use in production, the skills, how much will be paying them, other incentives and safety of workers during production
- Utilities that will be needed by the business e.g water, power, telephone etc
- Means of transporting raw materials and finished products. Here, the entrepreneur establishes how raw materials will be moved to the production center and how finished products will be delivered to the target market.
- Inventory control plans for stock, work in progress and finished goods(products) e.g inventory control for lead time, re-order level etc
- Disposal of the waste products. Here , entrepreneur establishes the amount of wastes he has, how waste products will be disposed off and at what cost, can the waste converted into other products ie can they be recycled?
The financial plan
It is analysis of the financial requirements of the proposed business. Financial planning for a business deals with estimating the business operations in monetary terms. The financial plan covers the following areas
- Source of funds ie own funds, grants , trade credits, short term loans etc
- Fixed and working capital requirements
- Profitability statement ie gross profit , net profit and breakeven point
- Balance sheet showing the financial position of the business
- Cash flow statement ie projected cash inflow and cash out flow of the business.
Note.
The financial plan focuses on the estimation of the total capital requirements of a business. Businesses require different forms of capital ie fixed capital and working capital. Fixed capital.
This refers to the money held up in permanent fixed assets of a business. Fixed capital consists of property held permanently for continuous use in the production process usually for more than one year e.g land, buildings, machinery, tools and equipment, furniture, motor vehicle Working capital or direct costs.
It refers to the amount of money used to buy stock for a given business or to meet daily financial operating needs of the business e.g raw materials, stock, fuel/transport, direct labour cost, costs of supplier of stationary, spare parts, cash for uncertainties.
Overhead cost.
These are costs of production which don’t vary regardless of the level of output. Examples include selling and distribution overheads like advertising, sales promotion, delivery expenses, wages to sales men, insurance of delivery vans, free gifts and samples
Indirect expenses like rent, insurance, electricity, telephone office expense, operating license
- Administrative over heads. These are indirect cost incurred by the management and supervision example include, general expenses, administrative salaries and allowances
Selling and distribution overheads. These are indirect expenses incurred during the selling and distribution of goods and services. Examples of selling and distribution expenses include, advertising, sales promotion, delivery expenses,wages to salesmen , insurance for delivery vans, free gifts and samples given to potential buyers etc
Organizational plan
This is analysis of the frame work around which the people, machinery/requirement and other physical products of the plan are put together to have a moving or success for organisation
The organizational plan covers the following
- The frame work/ structure around which people are to be put together to have a moving enterprise (organizational structure). This looks at the reporting relationships, tasks and responsibilities of the workers.
- Recruitment and indirect training. This looks at number of workers to be employed their qualifications, experience, skills and age.
- Rewards to employees ie salaries, wages and other fringe benefits to be given to staff for instance allowance like medical, transport, lunch , housing etc
Business implementation plan (Action plan)
An action plan is a management tool that involve laying out a series of sequenced steps that enable an entrepreneur to implement the planned activities of the business in a sequenced way so as to meet itself; target
Importance or uses of an action plan to an entrepreneur
- It helps and guides the entrepreneur to remain focused during implementation of his business activities
- It helps an entrepreneur to identify business obstacles in advance and take appropriate measures to overcome them
- It helps the entrepreneur to allocate the serious sources of information and the resources needed for a business
- It helps an entrepreneur to identify strength, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of his business and those of competitors
- It helps the entrepreneur to obtain information (feedback) on the progress of the business
- It serves as a time to implementing business plan (activities)
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co
We are a supportive platform dedicated to empowering student nurses and midwives through quality educational resources, career guidance, and a vibrant community. Join us to connect, learn, and grow in your healthcare journey
Quick Links
Our Courses
Legal / Policies
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co

