Specialized Nursing Care
Subtopic:
Catheterization
Table of Contents
Catheterization
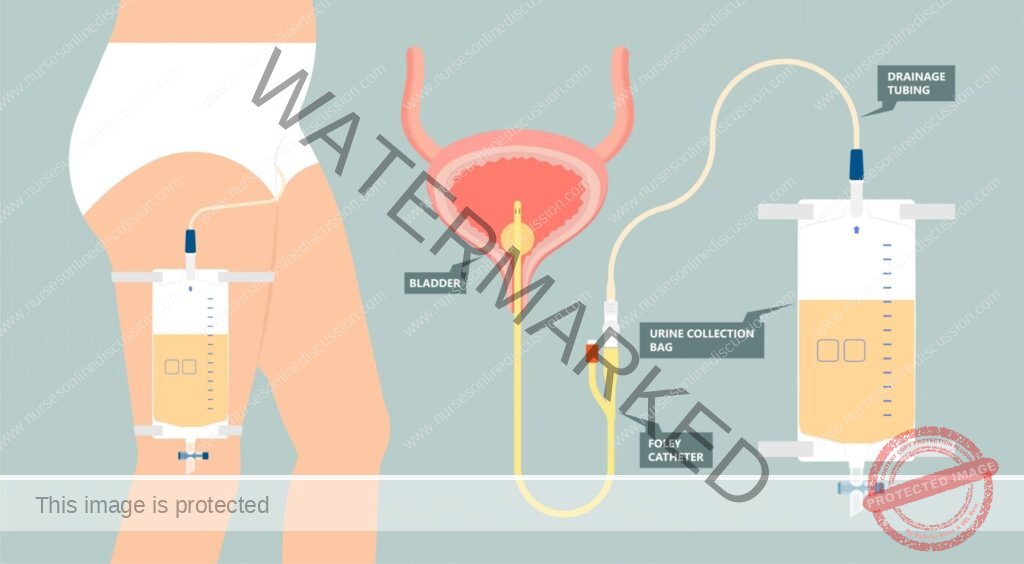
Catheterization is the introduction of a fine plastic or rubber tube (catheter) through the urethra into the urinary bladder in order to remove urine or to keep the urethra open.
Types of Catheters
- Non-retaining or self-retaining (e.g., Foley catheter with inflatable balloon).
- Metallic and non-metallic (e.g., plastic, rubber, silicone).
- Rubber catheters.
- Plastic catheters. Catheter sizes are according to the French (Fr) scale. Sizes include 8 to 10 Fr for children, 14 to 16 Fr for adult females, and 18 to 20 Fr for adult males. Generally, sizes range from 8 to 24 Fr. The smallest effective size should be used to minimize trauma.
Indications for Catheterization
- To obtain a sterile specimen of urine for examination or investigations (e.g., when a clean catch midstream sample is not possible).
- To relieve urinary retention when other nursing measures have failed (e.g., after surgery, due to obstruction, or neurogenic bladder).
- To ensure that the bladder is empty before (pre-operatively), during, and after pelvic or abdominal surgeries to prevent injuries to the bladder.
- To measure the amount of residual urine after voiding (post-void residual). It is done when partial obstruction of the bladder outlet is suspected (e.g., in BPH, VVF patients, patients on bladder training).
- Emptying the bladder before giving a bladder irrigation or installation of medication.
- Splinting the urethra following urethral surgery or trauma.
- In cases of incontinence of urine to prevent bed sores which may occur in diseases of the nervous system, trauma, and other conditions requiring strict intake and output monitoring.
- Monitoring accurate hourly urine output in critically ill patients.
Requirements
Trolley (Top Shelf)
- A sterile catheterization pack containing: Sterile towels (2), Drape (1), Sterile receiver (2), Gauze swabs, Cotton wool swabs.
- Sterile Foley catheter (appropriate size, have a spare)
- Sterile KY Jelly or Lubricant (water-soluble)
- Antiseptic solution (e.g., Povidone-iodine or Chlorhexidine solution) in a gallipot
- A 10 ml syringe (for inflating the balloon)
- Sterile water (or normal saline) for inflating the balloon (amount specified on catheter)
- Specimen bottle(s) with labels (if specimen is required)
- Spigot or clamp
- Drainage bag and tubing (if inserting an indwelling catheter)
- Dressing mackintosh and towel
- Sterile gloves (at least 2 pairs)
- Non-sterile gloves (for initial preparation)
Bedside:
- Hand washing equipment (access to sink, soap, water, towel)
- Screens (for privacy)
- Adequate lighting (e.g., torch or lamp)
- Waste receptacle
- Urine collection container (if not using a drainage bag, e.g., receiver or measuring jug)
- Patient’s chart and Fluid balance chart (if monitoring output)
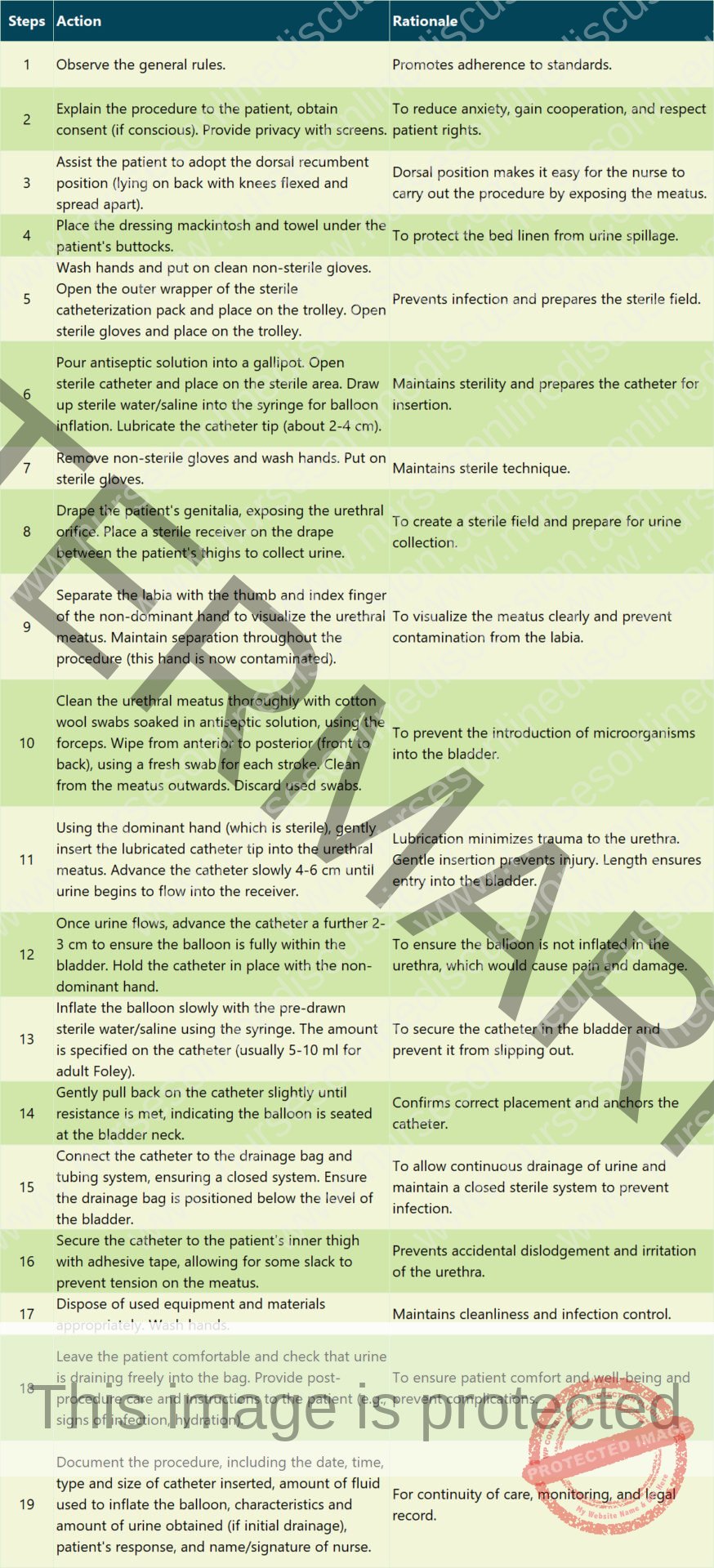
Procedure (Catheterization of a Female Patient)
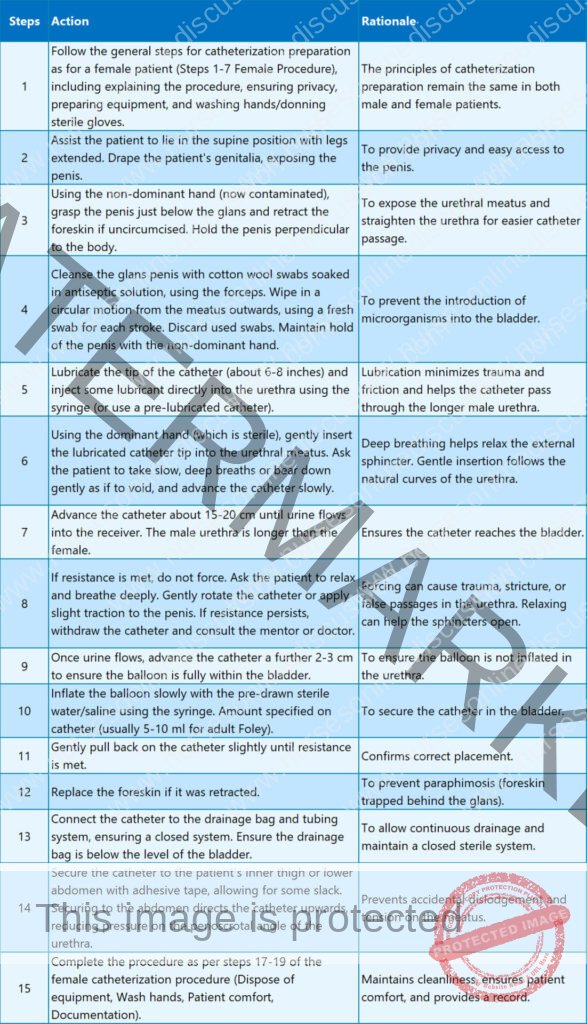
Procedure (Catheterization of a Male Patient)
Points to Remember (Catheterization)
- Catheterization is a sterile procedure; therefore, strict aseptic precautions must always be followed throughout the procedure. Any break in sterile technique should be corrected immediately.
- The procedure should be performed with extreme care to prevent trauma to the delicate urethral and bladder organs.
- Always verify catheter placement before inflating the balloon.
- Never force the catheter against resistance.
- Use adequate lubrication, especially for male patients.
- Choose the correct size catheter to minimize discomfort and trauma.
- Ensure the drainage system is always below the level of the bladder to facilitate gravity drainage and prevent backflow.
- Provide ongoing catheter care (cleaning meatus, checking drainage, ensuring patency) to prevent infection.
- Monitor the patient for signs of complications such as pain, bleeding, inability to pass urine, or signs of infection (fever, cloudy urine, foul odor).
Related Topics
- Wound dressing
- Colostomy Care
- Abdominal Paracentesis(Abdominal Tapping)
- Vulva Toilet/ Swabbing
- Oxygen Administration
- Lumbar Puncture
- Nasogastric tube to feed patients
- Gastrostomy Feeding
- Gastric Lavage
- Catheterization
- Tracheostomy Care
- Caring for patients in traction
- Prepare for application of orthopaedic splints
- Bandaging
- Nursing Process
- Take History of the patient
- Perform a physical examination of the Patient
- Making a Nursing Care Plan
- Admission of a patient
- Drug administration
- Transfer Patients
- Discharge of patients
- Last Office
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co
×

