Specialized Nursing Care
Subtopic:
Oxygen administration
Table of Contents

INHALATION
Inhalation is the breathing of air vapor or volatile medicine into the lungs. Types
Types
Dry inhalation : Oxygen Administration: this is given when the respiratory capacity is diminished as in chest injuries, pneumonia and cardiac failure.
Moist/steam inhalation : It is used in case of inflammation of air passages and the nasal sinuses. These are given to:
- Warm and moisten the air breathed in and relieve irritation e.g. in bronchitis, after tracheotomy and other chest conditions.
- To relieve inflammation and coughing e.g. in colds.
- To relieve congestion and oedema e.g. in sinusitis and acute laryngitis.
- Nebuliser : this produces vapors which is inhaled by the patient for example in asthma to relieve spasms of the bronchial tubes or for the relief of chest pain in angina pectoris. Other indications include Respiratory diseases eg asthma, pneumonia, Airway obstruction, Nasal congestion, Nasal bleeding, Chest injuries and Cardiac failure.
DRY INHALATION (Oxygen administration)
DRY INHALATION (Oxygen administration)
It is given when the respiratory tract is diminished as in chest injuries, cardiac failure and pneumonia.
REQUIREMENTS FOR OXYGEN ADMINISTRATION
Clean tray
- Rubber tubing.
- BLB oxygen mask.
- Flowmeter.
- Nasal catheter.
- Gallipot with gauze pads.
- Humidifier with distilled water
Bedside
- Oxygen source.
- Screen
Procedure (Dry Inhalation)

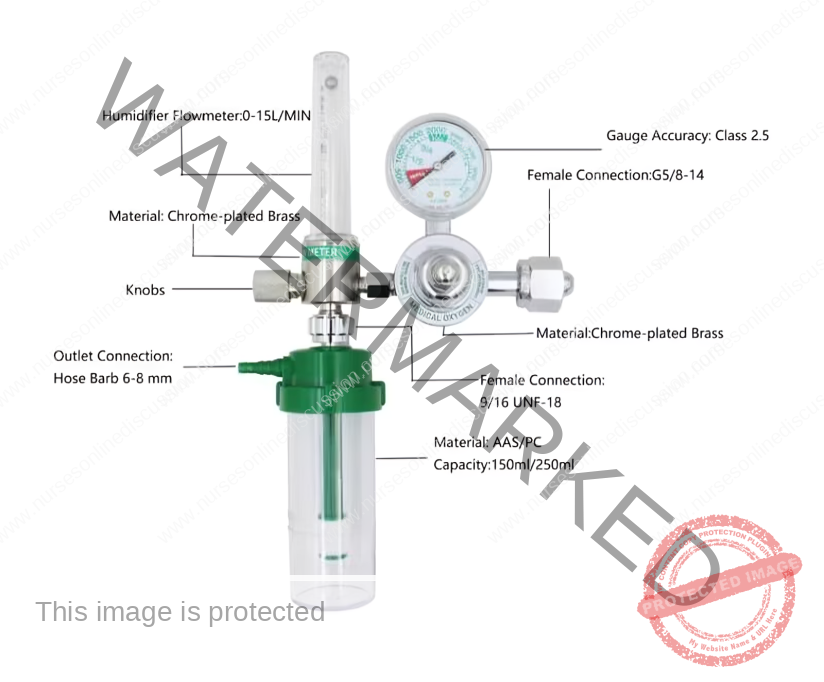
Parts of an oxygen flowmeter
Related Topics
- Wound dressing
- Colostomy Care
- Abdominal Paracentesis(Abdominal Tapping)
- Vulva Toilet/ Swabbing
- Oxygen Administration
- Lumbar Puncture
- Nasogastric tube to feed patients
- Gastrostomy Feeding
- Gastric Lavage
- Catheterization
- Tracheostomy Care
- Caring for patients in traction
- Prepare for application of orthopaedic splints
- Bandaging
- Nursing Process
- Take History of the patient
- Perform a physical examination of the Patient
- Making a Nursing Care Plan
- Admission of a patient
- Drug administration
- Transfer Patients
- Discharge of patients
- Last Office
Get in Touch
(+256) 790 036 252
(+256) 748 324 644
Info@nursesonlinediscussion.com
Kampala ,Uganda
© 2025 Nurses online discussion. All Rights Reserved Design & Developed by Opensigma.co
×

